The pursuit of a leaner, healthier body often begins with a single question: what is the best fat burner for belly fat, and is it truly possible to target abdominal weight loss naturally? For many people, excess belly fat is more than a cosmetic concern—it’s a health risk tied to cardiovascular disease, insulin resistance, and chronic inflammation. Yet, navigating the crowded world of fat-burning supplements, detox teas, workout trends, and miracle diets can be overwhelming. With so many promises and conflicting opinions, separating hype from science becomes essential for those who are serious about achieving long-term wellness.
You may also like: Expert-Backed Weight Loss Tips for a Healthier Lifestyle: What You Need to Know for Long-Term Weight Control and Wellness
In this article, we explore the science behind fat-burning, with a special focus on what actually works when it comes to reducing visceral fat—particularly around the abdomen. Drawing from expert-backed strategies and credible medical research, we examine the most effective natural ways to burn fat burning efficiently without relying on gimmicks or unsafe shortcuts. We also take a closer look at lifestyle and dietary choices that can help support sustainable weight loss, while evaluating whether fat burner for belly products live up to their claims.
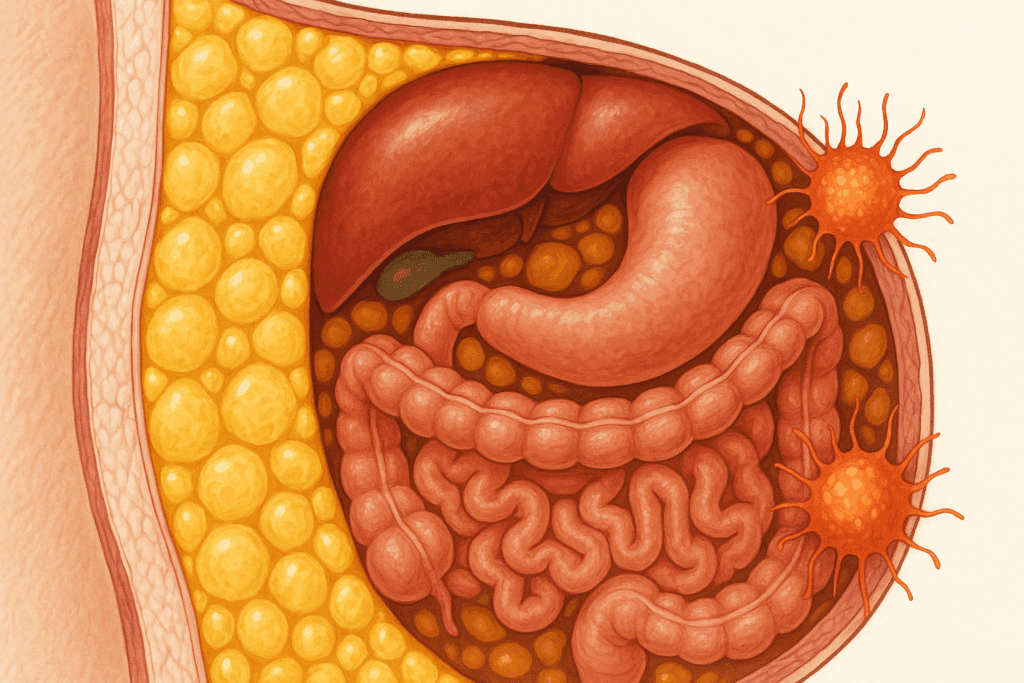
Understanding Belly Fat: More Than Just Aesthetic
Before addressing how to burn belly fat, it’s important to understand what belly fat actually is—and why it’s different from other types of body fat. The fat stored in the abdominal region is categorized into two main types: subcutaneous fat, which lies just under the skin, and visceral fat, which surrounds internal organs such as the liver, intestines, and pancreas. While subcutaneous fat is more visible, it’s the deeper visceral fat that poses greater health risks.
Visceral fat is metabolically active, producing hormones and inflammatory molecules that can interfere with normal metabolic function. This type of fat has been strongly linked to insulin resistance, high blood pressure, and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes and heart disease. Because of its role in disease development, many experts view belly fat not merely as a matter of appearance but as a major indicator of health.
Losing belly fat, therefore, isn’t just about looking slimmer—it’s about improving your long-term health outcomes. However, targeting belly fat specifically is a nuanced challenge. Unlike what some advertisements may claim, there is no magic pill that melts away abdominal fat overnight. Instead, evidence suggests that a combination of consistent physical activity, nutrient-dense dietary patterns, stress management, and adequate sleep plays a central role in how the body burns fat burning most efficiently—especially around the midsection.
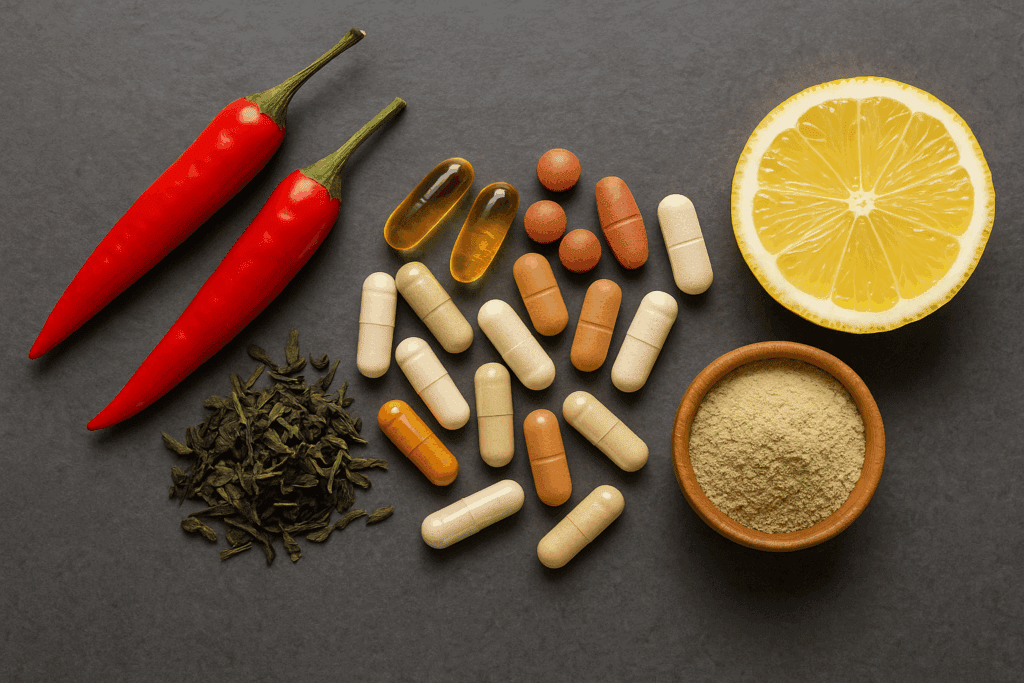

Do Fat Burners for Belly Fat Work?
Fat burners for belly fat have gained popularity as a quick fix, often promoted with flashy marketing that promises rapid transformation. These supplements typically claim to increase thermogenesis, enhance metabolism, or suppress appetite. Common ingredients include caffeine, green tea extract, conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), L-carnitine, and capsaicin. But what does the evidence say?
While some of these ingredients have shown mild metabolic effects in controlled settings, the overall clinical impact of fat burners for belly fat remains inconsistent. Caffeine, for instance, can temporarily increase metabolic rate and fat oxidation, especially during exercise. Green tea extract, rich in catechins like EGCG, has also demonstrated some potential in modestly enhancing fat loss. However, these effects tend to be small and may not lead to significant long-term weight loss without other lifestyle changes.
Moreover, fat-burning supplements are not regulated as strictly as pharmaceutical drugs, which means product quality, purity, and ingredient transparency can vary widely. Some may even contain harmful or banned substances, increasing the risk of cardiovascular events or liver damage. For this reason, most registered dietitians and medical professionals recommend caution when considering over-the-counter fat burner for belly solutions.
Ultimately, while certain supplements may support a broader fat-burning strategy, they are not a substitute for evidence-based health practices. Sustainable weight loss, especially in the abdominal region, requires an integrated approach—one that prioritizes nutritional quality, physical movement, hormonal balance, and mental well-being.
Metabolism and the Science of Fat Burning
Understanding how fat is metabolized is key to optimizing any strategy aimed at reducing belly fat. Fat burning is a complex biochemical process that involves breaking down stored triglycerides into glycerol and free fatty acids, which the body then uses for energy. This process, known as lipolysis, is influenced by hormones such as insulin, cortisol, adrenaline, and leptin.
During periods of low insulin levels—such as fasting, calorie restriction, or aerobic exercise—the body becomes more efficient at breaking down fat stores. On the other hand, chronically high insulin, often due to excessive intake of refined carbohydrates and sugar, inhibits fat breakdown and promotes storage, especially in the abdominal region.
Furthermore, chronic stress can also disrupt fat metabolism by increasing cortisol levels. Cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone, has been associated with an increase in visceral fat accumulation. High levels of cortisol may also trigger cravings for high-fat and high-sugar foods, creating a cycle that promotes weight gain.
To enhance fat burning naturally, experts emphasize the importance of stabilizing blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy insulin response, and engaging in activities that promote hormonal balance. These include regular physical activity, strength training, prioritizing whole foods over processed ones, and getting adequate sleep. These practices collectively support the body’s ability to burn fat burning more efficiently, especially from visceral areas.
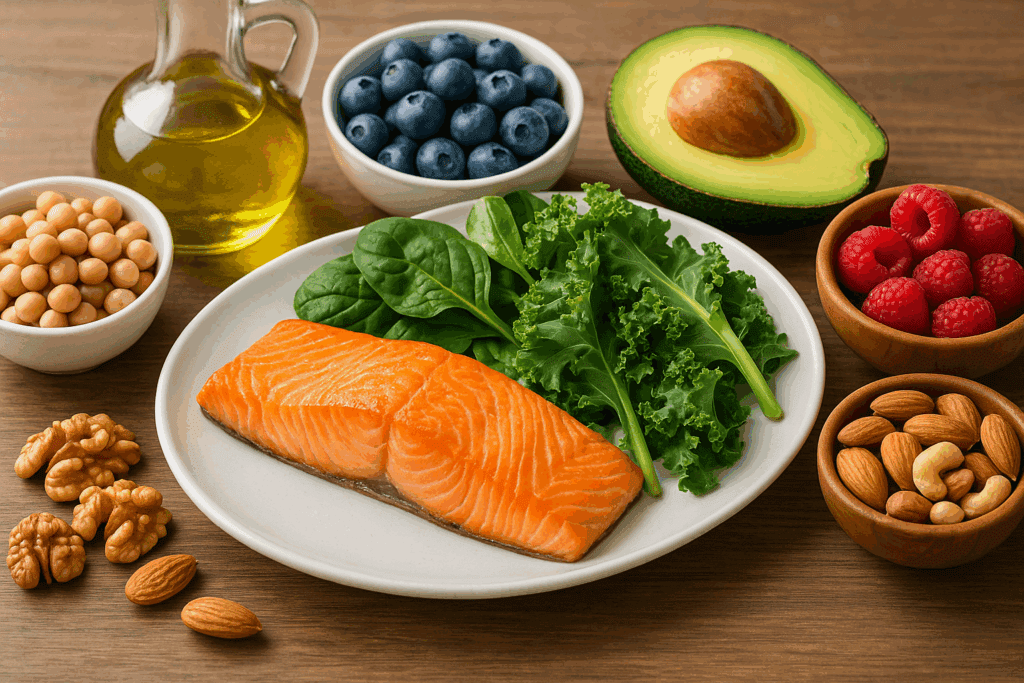

The Role of Diet in Burning Belly Fat Naturally
Diet plays a central role in reducing abdominal fat and supporting long-term fat-burning efficiency. But not all diets are created equal. Research consistently shows that dietary patterns rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats are more effective at reducing visceral fat than low-fat or calorie-restricted diets alone.
High-fiber foods, such as leafy greens, legumes, oats, and berries, improve satiety, stabilize blood sugar, and support digestive health—all of which contribute to better weight management. Soluble fiber, in particular, has been shown to reduce belly fat by slowing digestion and helping control appetite.
Protein is another powerful ally. Adequate protein intake not only helps preserve lean muscle mass during weight loss but also increases thermogenesis—the number of calories the body uses to digest and metabolize food. Including quality protein sources like eggs, fish, poultry, tofu, and Greek yogurt can enhance the body’s natural fat-burning capabilities.
Incorporating healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil may seem counterintuitive, but they play an essential role in hormone regulation and appetite control. Contrary to outdated diet myths, eating healthy fat does not make you fat. Rather, it helps keep you full longer and reduces overeating.
When evaluating dietary approaches, experts often recommend the Mediterranean diet or a modified low-carb plan. These eating patterns emphasize whole foods, minimize added sugars, and prioritize anti-inflammatory ingredients—all factors that contribute to reduced belly fat over time.
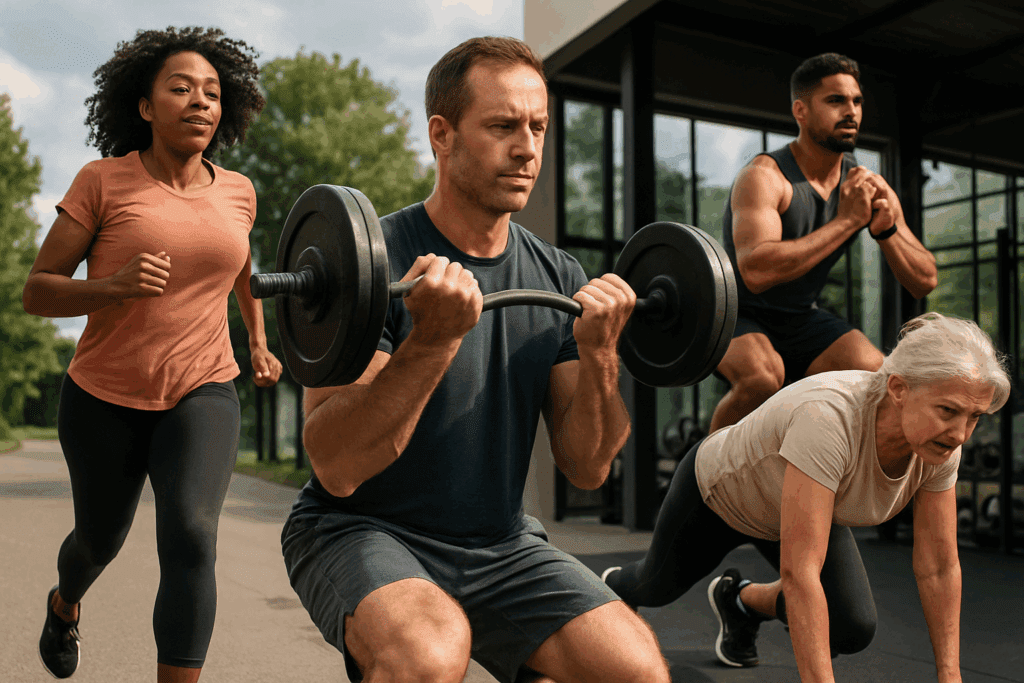

Physical Activity and Its Targeted Role in Belly Fat Reduction
No discussion on belly fat reduction is complete without addressing exercise. While it’s true that spot reduction—targeting fat loss in specific body areas—is largely a myth, regular physical activity remains one of the most effective tools for decreasing overall body fat, including visceral fat.
Cardiovascular exercises like walking, jogging, swimming, and cycling are well-established methods for increasing calorie burn and stimulating fat metabolism. Moderate to vigorous aerobic activity has been shown to significantly decrease abdominal fat, particularly when combined with dietary modifications.
However, strength training should not be overlooked. Building lean muscle mass helps increase resting metabolic rate, meaning the body continues to burn fat even at rest. Resistance training also helps preserve muscle during periods of weight loss, which is critical for preventing metabolic slowdown.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) has garnered particular interest for its time-efficient and potent fat-burning effects. HIIT alternates short bursts of intense exercise with periods of rest or lower-intensity movement. Studies indicate that HIIT may be especially effective in reducing visceral fat and improving insulin sensitivity, even when total exercise time is relatively low.
The key takeaway is that movement matters—whether it’s lifting weights, walking daily, or joining a fitness class. Consistency and variety are crucial. Engaging in a regular exercise routine helps burn fat burning efficiently, supports metabolic health, and enhances the benefits of dietary strategies aimed at reducing belly fat.

Sleep, Stress, and the Hidden Hormonal Links to Fat Storage
Often underestimated, sleep and stress play a critical yet hidden role in belly fat accumulation. Sleep deprivation alters the balance of hunger hormones such as ghrelin and leptin, increasing appetite and reducing feelings of fullness. At the same time, insufficient sleep elevates cortisol levels, further exacerbating fat storage in the abdominal region.
Chronic stress produces similar effects. Prolonged exposure to stress hormones creates a physiological environment where the body is more likely to hold onto fat as a protective mechanism. Even with a healthy diet and exercise routine, unresolved stress can sabotage weight loss efforts.
Mindfulness practices such as meditation, deep breathing, yoga, and regular time outdoors have been shown to lower cortisol levels and improve emotional regulation. Cultivating a consistent sleep schedule—ideally seven to nine hours per night—is equally important.
Experts emphasize the importance of treating sleep and stress management as foundational, not optional, components of a comprehensive fat-burning plan. By improving these areas, the body becomes more hormonally balanced, which in turn supports more efficient and sustainable fat burner for belly outcomes.
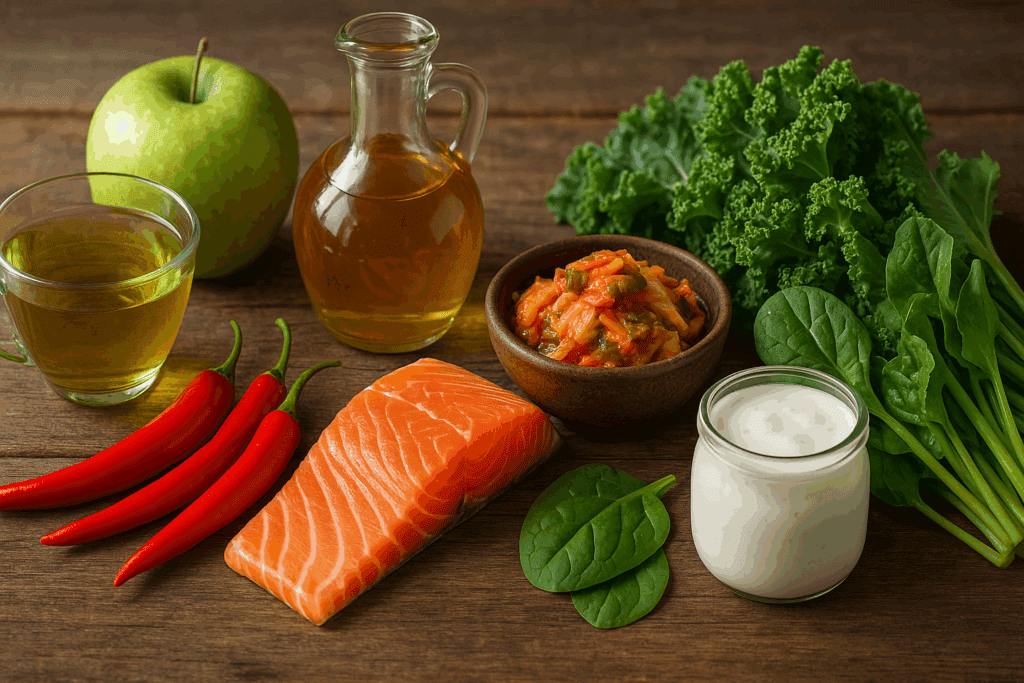

Natural Alternatives to Supplements: Foods That Support Belly Fat Loss
Rather than relying solely on commercial fat burners, many nutritionists recommend turning to whole foods that naturally support fat-burning. Several functional foods have demonstrated the ability to enhance metabolism, regulate insulin, and combat inflammation—factors that contribute to excess belly fat.
Green tea, known for its high concentration of catechins, has mild thermogenic effects and can enhance fat oxidation, especially when combined with exercise. Chili peppers contain capsaicin, which may increase calorie burning and reduce appetite. Apple cider vinegar has been shown to help stabilize blood sugar levels and may modestly aid in fat loss when used in moderation.
Other notable foods include fatty fish like salmon, which provide omega-3 fatty acids with anti-inflammatory benefits, and fermented foods such as kimchi and kefir that support gut health—another emerging factor in weight regulation. A healthy gut microbiome has been associated with lower levels of visceral fat and improved metabolic function.
Choosing nutrient-dense, unprocessed foods not only supports fat burning but also enhances overall health. These natural alternatives work in harmony with the body’s physiological processes rather than disrupting them, making them ideal components of a safe and effective strategy to reduce belly fat.
When to Be Cautious with Commercial Fat-Burning Products
While the allure of quick results is understandable, the decision to use commercial fat-burning products should be approached with caution. Many over-the-counter options contain unregulated or poorly studied ingredients, and their safety profiles are not always well established.
Some products have been associated with adverse effects such as increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, digestive issues, or even liver toxicity. Particularly for individuals with underlying health conditions or those taking medication, the risks may outweigh any potential benefits.
Consulting with a healthcare provider before starting any fat burner for belly supplement is strongly advised. Medical professionals can assess whether the ingredients are safe, potentially effective, and compatible with individual health needs. Moreover, a dietitian or nutritionist can offer personalized alternatives that are rooted in science, not sales tactics.
The most effective path to fat loss remains one that prioritizes long-term lifestyle change over short-term fixes. A slow and steady approach, though less glamorous, is far more likely to produce sustainable results—and to support the body’s health and balance along the way.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ): Natural Fat Burners and Effective Belly Fat Reduction
1. Can stress management significantly improve the results of a fat burner for belly plan?
Yes, managing stress can dramatically improve the success of any fat burner for belly strategy. Chronic stress triggers the overproduction of cortisol, a hormone known to promote fat storage in the abdominal region. When cortisol levels remain high over time, it not only increases cravings for unhealthy foods but also disrupts sleep, digestion, and metabolic function. Integrating stress reduction techniques—such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing, or even regular social connection—can enhance the body’s ability to burn fat burning naturally. These changes support hormonal balance, which makes both diet and exercise-based efforts more effective in targeting stubborn belly fat.
2. How does gut health influence belly fat, and can probiotics enhance natural fat burning?
Emerging research shows a strong link between gut microbiome health and the body’s ability to manage weight, particularly belly fat. An imbalanced gut can lead to systemic inflammation and insulin resistance, both of which encourage fat accumulation in the abdomen. Certain probiotic strains like Lactobacillus gasseri and Bifidobacterium breve have shown promise in supporting a healthy metabolism and improving visceral fat loss. While not a standalone fat burner for belly, probiotics can play a supportive role by enhancing digestion and nutrient absorption, which contributes to more efficient burn fat burning. Including fermented foods or high-quality probiotic supplements in your routine could be a game-changer for those struggling with belly fat.
3. Are there any behavioral or psychological habits that undermine efforts to burn fat from the belly area?
Absolutely, behavioral patterns such as emotional eating, binge-restrict cycles, or even negative body image can unknowingly sabotage fat loss goals. When people view food as a reward or punishment, they are more likely to overeat during times of emotional stress, which contributes to abdominal weight gain. Moreover, poor self-perception can discourage consistent exercise or healthy eating patterns, undermining any fat burner for belly plan in place. Addressing these psychological barriers through cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), journaling, or support groups can reinforce long-term success. In many cases, sustainable burn fat burning results depend as much on mindset as they do on meal plans and workouts.
4. Do specific timing strategies—like intermittent fasting—enhance the effects of fat-burning efforts?
Yes, intermittent fasting (IF) is a growing area of research that shows promising results for targeted fat loss. By restricting eating windows, IF lowers insulin levels and increases human growth hormone, both of which support fat metabolism. Time-restricted eating, such as the 16:8 method, can improve the body’s natural burn fat burning rhythm by encouraging the use of stored energy—especially from visceral fat stores. While IF is not a direct fat burner for belly, it can amplify the effects of clean nutrition and regular movement. As with any regimen, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider before adopting fasting protocols, especially for individuals with blood sugar or hormonal imbalances.
5. Is there a best time of day to exercise for belly fat loss?
While any time of day is beneficial for physical activity, morning workouts may provide a slight edge when it comes to belly fat reduction. Fasted cardio, done shortly after waking, can encourage the body to tap into fat reserves more efficiently since insulin levels are typically lower. This can potentially lead to greater burn fat burning effects over time. That said, consistency matters more than timing. If you’re more likely to stick with a fat burner for belly routine in the evening, that time is the best for you. The key is integrating activity into your day in a way that is sustainable and enjoyable, not forced.
6. Are plant-based diets effective for reducing belly fat and boosting metabolism?
Yes, plant-based diets can be highly effective for reducing belly fat and supporting metabolic health when well-balanced. Diets rich in whole plant foods—such as legumes, leafy greens, fruits, and seeds—are naturally high in fiber and antioxidants, which help reduce inflammation and regulate blood sugar. Fiber, in particular, plays a vital role in decreasing visceral fat by promoting fullness and slowing digestion. Although a plant-based approach is not a fat burner for belly in itself, it encourages a cleaner, more efficient metabolism that supports long-term fat-burning. It’s important to ensure adequate intake of protein and essential nutrients like vitamin B12 and iron to maintain muscle mass and energy levels.
7. How do age and hormonal changes affect fat storage in the abdominal region?
As we age, especially during midlife and beyond, hormonal shifts play a critical role in where the body stores fat. In women, declining estrogen levels during perimenopause and menopause often result in a redistribution of fat toward the midsection. In men, reductions in testosterone can also lead to muscle loss and increased abdominal fat. These changes can make it more difficult to rely on a single fat burner for belly, as the body’s natural fat-burning pathways become less responsive. Strength training, hormone-balancing nutrition, and adequate sleep become increasingly essential for older adults seeking to improve metabolic flexibility and sustain burn fat burning efficiently.
8. Can cold exposure or thermogenesis support natural belly fat reduction?
Cold exposure, such as cold showers or cryotherapy, is an unconventional but scientifically backed method that may support fat burning through a process called non-shivering thermogenesis. This process activates brown adipose tissue (BAT), which burns calories to produce heat. While it won’t replace a healthy diet or exercise, cold exposure can enhance metabolic rate and provide a marginal fat burner for belly benefit over time. Emerging studies also suggest that activating BAT can help regulate blood sugar and reduce insulin resistance, creating a more favorable environment for sustained burn fat burning. For those willing to experiment safely, cold therapy may offer an edge in a comprehensive fat loss routine.
9. How important is hydration in optimizing fat metabolism and reducing belly fat?
Hydration plays an underappreciated yet vital role in the body’s ability to metabolize fat effectively. Water is essential for the process of lipolysis, the breakdown of fat into usable energy. Even mild dehydration can impair physical performance and slow metabolism, undermining the benefits of a fat burner for belly program. Additionally, drinking water before meals may support appetite regulation and reduce caloric intake, indirectly assisting belly fat reduction. Herbal teas like green tea or dandelion root, which have mild diuretic and thermogenic properties, can also contribute to more efficient burn fat burning when used in moderation.
10. What future innovations in science may enhance fat-burning therapies for belly fat?
The future of belly fat reduction lies in precision medicine and personalized nutrition. Advances in genetic testing may soon allow individuals to identify their unique metabolic type and receive tailored recommendations for diet, exercise, and fat burner for belly solutions. Researchers are also exploring the role of mitochondria-boosting compounds and peptide-based therapies that target fat at a cellular level without harmful side effects. In the realm of nutrition, nutrigenomics is uncovering how individual gene variants respond to specific foods or supplements, which could revolutionize how we burn fat burning in targeted areas. As science progresses, we can expect fat loss strategies to become more individualized, effective, and safe—marking a significant leap forward in preventive health and weight management.
Final Thoughts: Sustainable Fat Burning Begins with Science, Not Shortcuts
In the quest for the best fat burner for belly fat, the evidence is clear: no supplement, shake, or shortcut can replace the foundational principles of healthy living. While certain compounds may offer mild metabolic support, true and lasting fat burning—especially in the abdominal region—relies on consistency, evidence-based nutrition, physical activity, sleep, and stress management.
Understanding how to burn fat burning effectively requires a holistic approach. It means moving beyond gimmicks and embracing the slower, more rewarding process of lifestyle transformation. Choosing whole foods over processed ones, getting adequate rest, staying active, and managing stress all work together to support hormonal harmony and metabolic health.
For those seeking to reduce belly fat, the best results come not from chasing the latest trend, but from cultivating daily habits grounded in science and supported by experts. These practices may not promise overnight results, but they offer something far more valuable: sustainable wellness and improved quality of life. And that, ultimately, is the most powerful fat burner for belly you can find.
Further Reading:
What Are Fat Burner Supplements?