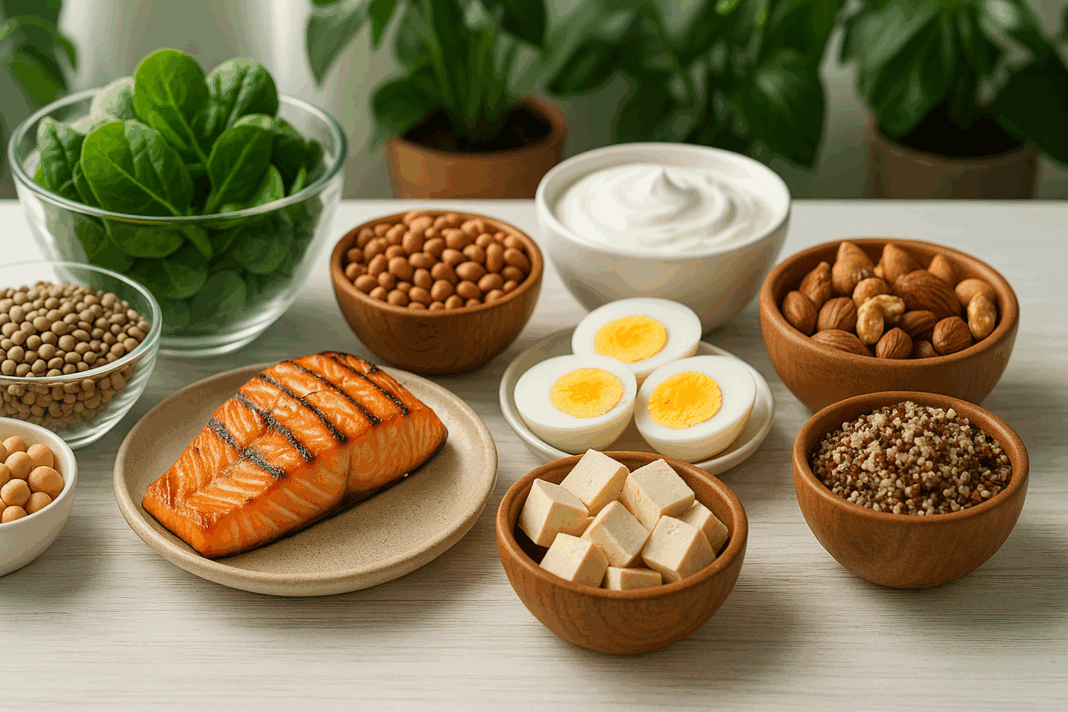
Protein is a fundamental macronutrient essential for nearly every biological process in the human body. From building and repairing tissues to supporting immune function and synthesizing hormones and enzymes, protein plays a multifaceted role in maintaining health and promoting longevity. As awareness grows about the importance of balanced nutrition, an increasing number of individuals are seeking expert guidance on integrating adequate protein into their everyday meals. This article explores science-backed strategies and practical tips on ways to include protein in daily diet routines while highlighting their benefits for sustained energy, muscle maintenance, and healthy aging.
You may also like: 4 Ways to Have a Healthy Diet: Expert Tips Backed by Science for Better Nutrition and Long-Term Wellness
Understanding Protein’s Role in Health and Longevity
Protein is composed of amino acids, which serve as the body’s building blocks. Nine of these amino acids are considered essential, meaning they must be obtained through dietary sources because the body cannot produce them on its own. High-quality protein sources contain all essential amino acids in the right proportions, making them especially important in supporting physiological functions. As people age, their protein needs often increase due to declining muscle mass and changes in metabolic efficiency. This makes the inclusion of protein-rich foods not just beneficial, but crucial for promoting longevity and preventing conditions like sarcopenia, which is the age-related loss of muscle mass and strength.
Energy levels also benefit significantly from steady protein intake. Unlike simple carbohydrates that cause spikes and crashes in blood sugar, protein provides a more stable source of energy by slowing the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream. In this way, it acts as a metabolic buffer, sustaining focus and stamina throughout the day. When seeking to optimize physical performance or simply maintain vitality through daily activities, consistently including high-quality protein becomes a strategic nutritional choice.
The Science Behind Daily Protein Distribution
Many individuals consume the bulk of their daily protein during dinner, leaving breakfast and lunch relatively protein-deficient. However, emerging research suggests that evenly distributing protein intake across all meals may be more beneficial for muscle protein synthesis, especially in older adults. This means aiming for a consistent intake of 20 to 30 grams of protein per meal can enhance the body’s ability to utilize amino acids for tissue repair and muscle maintenance.
This even distribution also supports metabolic efficiency and appetite regulation. Protein-rich meals are more satiating, helping to curb excessive snacking and manage overall calorie intake. For individuals focused on weight management or reducing the risk of chronic conditions such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, or cardiovascular disease, incorporating protein strategically throughout the day can yield significant advantages. Thus, understanding both the quality and timing of protein intake is central to long-term dietary success.
Breakfast: A Prime Opportunity to Elevate Protein Intake
Many breakfast options are heavily skewed toward carbohydrates, such as cereals, toast, and pastries, which tend to be lower in protein and high in added sugars. Shifting the breakfast paradigm toward protein-rich choices is one of the most effective tips on ways to include protein in daily diet habits. Opting for Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, eggs, or plant-based protein smoothies in the morning helps establish a foundation of sustained energy and improved satiety throughout the day.
An often-overlooked strategy involves adding protein boosters to existing meals. For example, sprinkling chia seeds, hemp hearts, or a spoonful of nut butter into a bowl of oatmeal can increase the protein content significantly without sacrificing flavor or convenience. Similarly, pairing whole-grain toast with scrambled eggs or tofu scramble enhances the nutritional density of a traditionally carb-heavy meal. These simple adjustments reflect two tips of including protein in your daily diet that can be implemented with minimal disruption to routine.
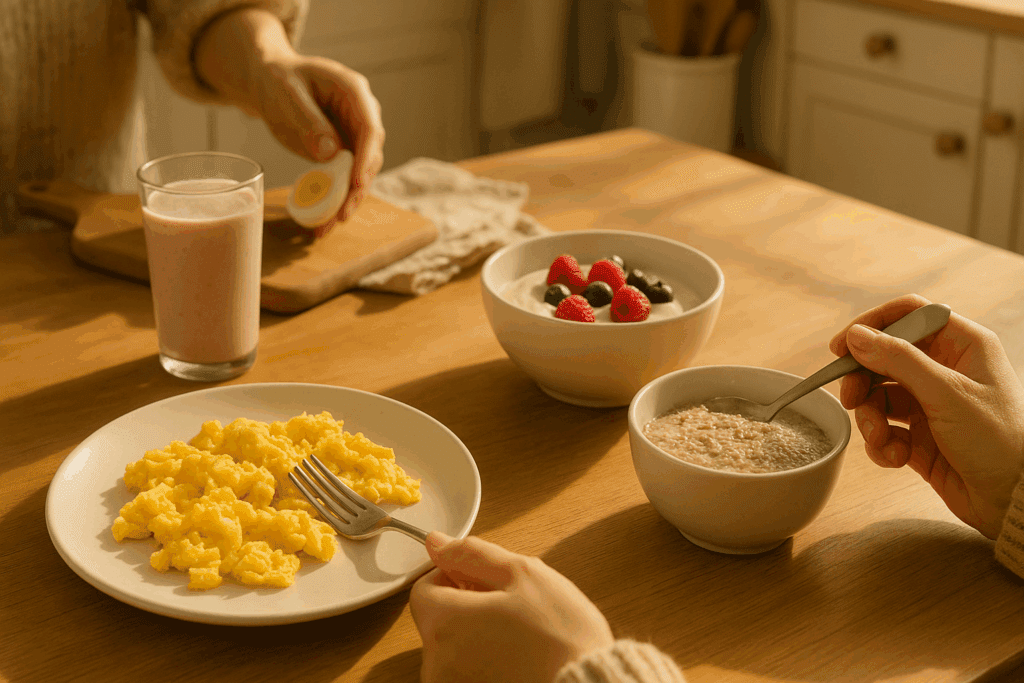

Lunch Strategies for Maximizing Protein Content
Lunch is an ideal moment to reinforce your daily protein goals. Instead of relying solely on traditional sandwiches or pasta dishes that may be heavy on refined grains, consider centering the meal around a high-protein component. Grilled chicken, turkey breast, tempeh, or legumes can serve as the cornerstone of a balanced midday meal. When combined with fiber-rich vegetables and healthy fats, these proteins promote a feeling of fullness and help stabilize blood sugar levels.
Leftovers from dinner can also be repurposed into protein-packed lunch bowls, offering both convenience and nutritional value. For example, quinoa or lentil salads topped with hard-boiled eggs, salmon, or marinated tofu create a flavorful, satisfying dish that supports long-term health goals. These meal designs not only reflect thoughtful planning but also embody expert-endorsed tips on ways to include protein in daily diet patterns that support energy, muscle preservation, and longevity.
Snacking with Purpose: Protein Between Meals
While snacks are often thought of as indulgences or cravings, they can also serve as valuable opportunities to support your protein needs. Choosing snacks that contain at least 7 to 10 grams of protein helps bridge the nutritional gap between meals while preventing energy dips and promoting muscle maintenance. Portable, protein-rich options include roasted chickpeas, string cheese, boiled eggs, edamame, and protein bars made with clean, recognizable ingredients.
Smoothies also represent a highly customizable snacking solution. When fortified with protein powder, nut butters, or silken tofu, smoothies can deliver a significant dose of nutrients in a convenient and digestible form. These options work particularly well for individuals with busy schedules who struggle to find time for sit-down meals. Integrating such high-quality snacks into your routine aligns with practical, evidence-based advice and reflects two tips of including protein in your daily diet that are easy to apply regardless of lifestyle.
Dinner: Reinforcing Nutrient Density and Variety
Dinner often serves as the main meal of the day, providing a chance to incorporate a wide range of nutrients and ensure that daily protein needs are met. While animal-based proteins such as lean beef, poultry, and seafood are commonly featured, incorporating plant-based sources like lentils, black beans, and seitan can diversify the amino acid profile and support cardiovascular health. A balanced dinner plate ideally includes a high-protein element alongside complex carbohydrates and colorful vegetables to maximize both flavor and nutritional balance.
It’s important to vary protein sources regularly to avoid nutritional monotony and to obtain a broader spectrum of nutrients. For instance, rotating between seafood, legumes, eggs, and fermented soy products not only prevents meal fatigue but also introduces new textures and tastes that enhance meal satisfaction. These nuanced adjustments are integral to the broader framework of tips on ways to include protein in daily diet structures tailored for optimal well-being.
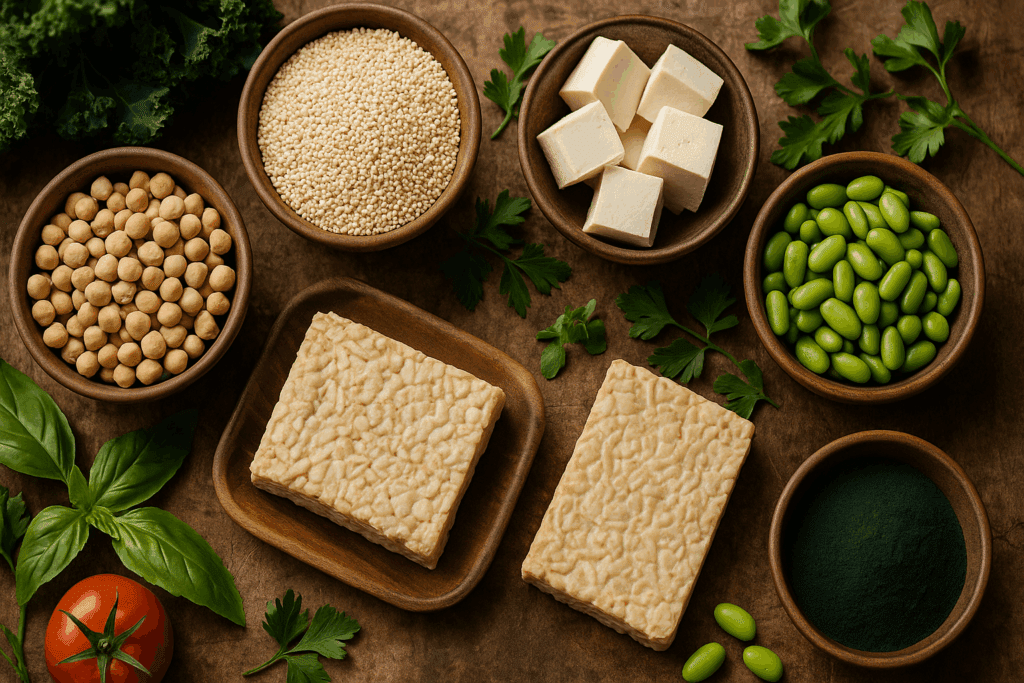

Plant-Based Protein Integration for All Diets
The growing popularity of plant-forward eating patterns has sparked interest in alternative protein sources that meet nutritional demands without relying on animal products. For vegetarians and vegans—or even those simply aiming to reduce meat consumption—options such as tofu, tempeh, legumes, quinoa, buckwheat, and spirulina offer robust protein profiles. These foods not only support muscle synthesis but also provide phytonutrients, fiber, and antioxidants that contribute to long-term health.
Combining complementary plant proteins—such as rice and beans or hummus and whole-grain pita—ensures a complete amino acid profile. This practice, known as protein complementation, is especially important for those relying solely on plant foods. Educating oneself on these strategies supports a well-rounded approach to nutrition and reinforces actionable tips on ways to include protein in daily diet regimens that align with ethical and environmental values.
Overcoming Common Barriers to Adequate Protein Intake
Despite the known benefits of protein, many individuals struggle to meet their daily requirements due to busy schedules, dietary restrictions, or lack of knowledge. Meal prepping and planning ahead can eliminate guesswork and ensure protein availability throughout the week. Preparing protein-rich staples such as hard-boiled eggs, grilled tofu, cooked lentils, or quinoa in advance can significantly streamline daily choices.
Budget constraints may also pose a challenge. However, affordable protein sources like canned beans, frozen edamame, eggs, and peanut butter make it possible to meet nutritional needs without excessive spending. Educational outreach from registered dietitians, online cooking tutorials, and community programs can empower individuals to implement two tips of including protein in your daily diet, even under limiting circumstances. Accessibility and adaptability remain key themes in achieving nutritional consistency.
The Role of Protein in Specialized Diets and Lifestyles
Different lifestyles and health conditions may require personalized approaches to protein consumption. For instance, athletes and individuals engaging in resistance training have higher protein needs to support muscle recovery and hypertrophy. In such cases, timing becomes critical, with protein ideally consumed within an hour post-workout to maximize muscle protein synthesis. Whey protein, due to its rapid absorption, is frequently recommended in these scenarios.
Conversely, individuals with kidney disease or other metabolic concerns may need to monitor protein intake more closely to prevent excess strain on renal function. In these cases, the emphasis shifts from quantity to quality, with dietitians often recommending low-sodium, minimally processed protein sources. Customizing tips on ways to include protein in daily diet routines requires an understanding of individual biochemistry, lifestyle demands, and medical background—underscoring the importance of professional guidance in crafting effective, safe dietary plans.
Culinary Creativity: Making Protein Enjoyable and Sustainable
Enjoying your meals is an essential part of sustaining any dietary pattern. Culinary innovation plays a key role in transforming protein-rich foods into delicious, memorable dishes. Experimenting with international cuisines—such as Indian dal, Japanese miso soup with tofu, or Mediterranean lentil salads—adds variety and excitement while delivering substantial protein content.
Marinades, spice blends, and texture pairings can also elevate plant-based proteins, making them more appealing to even the most discerning palates. Cooking methods such as grilling, roasting, and stir-frying add flavor without compromising nutritional integrity. By embracing these culinary tools, individuals can more effortlessly implement two tips of including protein in your daily diet: prioritizing flavor and making meals something to look forward to.
Rethinking Protein: A Sustainable and Holistic Approach
While individual protein needs vary, the principles of balanced, consistent intake remain universally beneficial. This involves looking beyond single meals and assessing the overall dietary pattern. Keeping a food journal or using nutrition tracking apps can help identify protein gaps and successes over time. Such tools not only increase awareness but also promote accountability and long-term habit formation.
Additionally, understanding the environmental impact of different protein sources can guide sustainable choices. Prioritizing plant-based proteins, reducing food waste, and sourcing local ingredients align personal health goals with planetary well-being. These integrated perspectives further enrich the discussion around tips on ways to include protein in daily diet frameworks that are both nutritionally effective and ethically informed.

Frequently Asked Questions: Protein Intake for Energy, Muscle Support, and Longevity
What are some creative tips on ways to include protein in daily diet habits for people who dislike traditional sources like meat or eggs?
For individuals who are not fond of conventional protein sources like meat or eggs, exploring alternative options can open up an entirely new world of nutrition. Fermented plant-based proteins such as tempeh or miso not only offer high-quality protein but also support gut health due to their probiotic content. Incorporating spirulina into smoothies or soups provides a protein boost alongside essential micronutrients like iron and B vitamins. Savory muffins made with chickpea flour or lentil-based pasta are also excellent ways to diversify your meals while maintaining protein intake. These options represent lesser-known yet effective tips on ways to include protein in daily diet choices that cater to unique preferences and culinary creativity.
How can social dynamics impact one’s ability to follow high-protein eating habits?
Social environments, including family mealtimes, cultural traditions, and peer influence, can subtly shape or obstruct an individual’s dietary decisions. Someone trying to prioritize protein might find themselves at odds with a household where carb-heavy dishes dominate or when dining out with friends who favor low-protein fare. This is where planning and assertive communication come into play. Suggesting potluck-style gatherings or bringing high-protein dishes to social events can help normalize these dietary choices. Empowering others with your own nutritional knowledge, such as sharing two tips of including protein in your daily diet that have worked for you, can shift group behaviors in a positive direction.
Are there seasonal strategies for increasing protein intake?
Absolutely. Seasonal produce and food trends offer a strategic advantage for incorporating more protein into meals. In summer, cold quinoa salads mixed with grilled tofu or legumes offer both hydration and nutrition, while autumn might invite hearty lentil stews or chickpea chili. Winter is ideal for egg bakes and high-protein soups, and spring provides an opportunity to integrate fresh peas, asparagus, and young spinach into protein-rich omelets or wraps. Utilizing local, in-season ingredients is not only cost-effective but can make the tips on ways to include protein in daily diet patterns more engaging and flavorful. It also encourages a connection to sustainable eating practices, which supports long-term consistency.
How can emotional or stress eating be navigated while maintaining a high-protein focus?
Emotional eating often leads to the consumption of comfort foods that are typically high in refined carbohydrates and low in protein. However, developing an awareness of emotional triggers and pairing it with mindful eating techniques can make a significant difference. Instead of reaching for chips or sweets, preparing snacks like turkey jerky, Greek yogurt parfaits, or roasted edamame ahead of time offers a more balanced emotional and physiological response. Additionally, integrating two tips of including protein in your daily diet during high-stress periods—such as starting with a protein-heavy breakfast or pre-planning dinners—can stabilize blood sugar and reduce cravings. This approach also supports serotonin production and mood regulation, making it an emotionally intelligent dietary choice.
What are some emerging innovations in the protein food industry?
The protein industry has undergone remarkable transformation with innovations that cater to sustainability and convenience. Lab-grown meat, insect-based protein powders, and algae-derived products are gaining traction as future-forward options that minimize ecological impact. Companies are also developing high-protein baked goods, snacks, and beverages that seamlessly integrate into modern lifestyles. Personalized nutrition platforms now offer AI-driven meal planning that includes precise tips on ways to include protein in daily diet practices based on individual biomarkers. These innovations not only expand the range of protein sources but also make it easier to meet dietary goals in an environmentally responsible way.
Can meal timing and circadian rhythm influence how well protein is utilized by the body?
Yes, recent research highlights the role of circadian biology in nutrient metabolism, including protein utilization. The body’s ability to synthesize muscle protein and regulate appetite hormones is more efficient earlier in the day, making it advantageous to front-load protein intake during breakfast and lunch. This approach counters the common habit of protein-skewed dinners and supports more balanced energy levels. Implementing two tips of including protein in your daily diet—such as consuming a protein-rich morning smoothie and a substantial midday protein entrée—can enhance your metabolic rhythm and muscle preservation. Aligning protein intake with natural body cycles adds a biochronological dimension to dietary strategy.
What long-term health conditions may benefit from consistent protein intake?
Consistent protein consumption supports far more than just muscle health. Emerging studies indicate a strong correlation between protein adequacy and reduced risk for osteoporosis, metabolic syndrome, and cognitive decline. Protein’s role in producing neurotransmitters and supporting immune response means that chronic conditions like depression, diabetes, and autoimmune diseases may improve with better protein regulation. Including a variety of sources—from dairy to legumes—broadens nutrient availability. Applying tips on ways to include protein in daily diet regimens can thus be part of a holistic preventive health strategy, especially when combined with other lifestyle interventions like physical activity and stress management.
How can people with small appetites or medical conditions still meet protein goals?
Meeting protein needs can be particularly challenging for those undergoing chemotherapy, recovering from illness, or managing digestive disorders. In such cases, focusing on nutrient density rather than volume becomes essential. High-protein broths, concentrated shakes, or soft-textured foods like scrambled eggs and cottage cheese can be easier to consume and digest. Nutritional supplementation may also be considered under medical supervision. Even integrating just two tips of including protein in your daily diet—such as adding protein powder to soups or prioritizing soft, protein-dense snacks—can make a measurable difference in recovery and daily strength.
Are there psychological benefits linked to higher protein diets?
Protein intake doesn’t just influence physical health—it also has notable effects on mental well-being. Amino acids like tryptophan and tyrosine are precursors to serotonin and dopamine, two key neurotransmitters involved in mood regulation. People following higher-protein diets often report reduced brain fog, improved emotional stability, and better concentration. By applying consistent tips on ways to include protein in daily diet patterns—such as diversifying sources and ensuring balance across meals—individuals may also experience reduced anxiety and depressive symptoms. These benefits highlight the mind-body connection fostered through thoughtful nutrition.
What role do cultural food traditions play in high-protein dietary planning?
Cultural heritage significantly shapes food choices, and many traditional cuisines offer inherently protein-rich options. For instance, Indian dals, Mediterranean chickpea dishes, and Japanese miso-based meals are rich in both protein and other vital nutrients. Rather than abandoning cultural staples, modern diets can adapt them using current knowledge, such as tips on ways to include protein in daily diet routines more deliberately. This fusion of tradition and science creates a sustainable, enjoyable eating experience that honors both heritage and health. Introducing just two tips of including protein in your daily diet, customized to your cultural preferences, fosters long-term adherence and satisfaction.

Conclusion: Building a Protein-Rich Lifestyle for Energy, Strength, and Healthy Aging
Incorporating more protein into your everyday meals is not just a fleeting trend—it is a strategic move supported by nutrition science and clinical evidence. From stabilizing energy and enhancing satiety to supporting muscle maintenance and healthy aging, protein serves as a cornerstone of long-term wellness. The key lies in making mindful, consistent choices that align with individual needs, preferences, and goals.
By exploring diverse sources, adjusting meal timing, and embracing culinary creativity, anyone can successfully apply expert-recommended tips on ways to include protein in daily diet routines. Whether it involves starting the day with a protein-packed breakfast or carrying high-protein snacks on the go, these adjustments are both practical and powerful. Even modest changes—such as implementing just two tips of including protein in your daily diet—can yield lasting benefits over time.
Ultimately, a protein-enriched diet is more than a nutritional upgrade—it is an investment in your energy, vitality, and longevity. With the right strategies, knowledge, and a touch of curiosity, building a balanced, protein-forward lifestyle becomes not only achievable but deeply rewarding.
Further Reading:
10 Science-Backed Reasons to Eat More Protein


