A key aspect of the hypoallergenic diet is its focus on identifying and eliminating potential food allergens or sensitivities. By eliminating common triggers such as gluten, dairy, soy, and certain grains, individuals can gain insights into how their bodies respond to specific foods. We’ll unveil several upsides to practicing a hypoallergenic diet.
Food allergies and food intolerance are a concern for countless Americans. According to one estimate, around 32 million Americans have some sort of food allergy. This includes 5.6 million children. For people seeking a healthy and allergen-free diet, as well as people who need assistance figuring out the source of their allergic reactions, the hypoallergenic diet could be the answer.
This article will cover the hypoallergenic diet. This includes an explanation of the diet, the diet’s phases and usage, and the benefits of this diet. This article will also discuss some of the most common food allergies and inform on how you can support your own hypoallergenic diet.
You May Also Like:
THE PROS AND CONS OF PROTEIN SUPPLEMENTS
HOW LONG DOES IT TAKE FOR COLLAGEN SUPPLEMENTS TO WORK? HERE ARE THE FACTS.
What’s the Buzz About The Hypoallergenic Diet? Unraveling the Benefits is an original (MedNewsPedia) article.
What is the hypoallergenic diet?
The hypoallergenic diet, sometimes referred to as an elimination diet, entails consuming only foods that are unlikely to trigger allergies. People choose this diet for a variety of reasons. Parents often use this kind of diet for very young children as they try to avoid foods that could trigger a child’s developing immune system. Additionally, as tests to determine food allergies and food intolerance can sometimes be unreliable, hypoallergenic diets can help to identify the precise cause of your food allergies. This makes a hypoallergenic diet good for those who aren’t sure if they have food allergies.
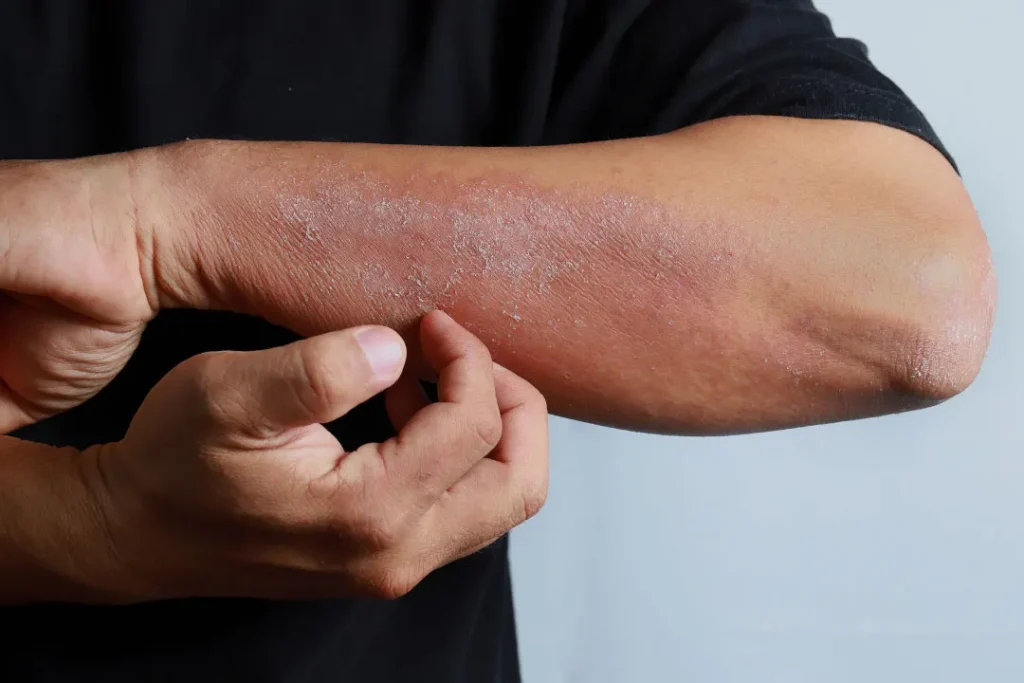
Lastly, some people may opt for a hypoallergenic diet for health reasons. For instance, one study found that a hypoallergenic diet could serve as a temporary treatment for adolescents and adults suffering from atopic dermatitis (more commonly known as eczema).
How does the hypoallergenic diet work?
While everyone has a different diet journey, hypoallergenic and elimination diets are often divided into two phases.
The first phase is elimination, during which you don’t eat any allergenic foods (tree nuts, dairy, wheat, seafood, etc.). This lasts for approximately 6 weeks.
The second phase is reintroduction. In this phase, you work with your dietitian to reintroduce allergens into your diet one at a time. This can help you determine which allergen or allergens are causing your health issues. You can then stop eating any food that causes your symptoms to reappear.
During this process, people can eat a variety of foods that are considered to be hypoallergenic. Examples include rice, apples, beans, and most vegetables. Certain grains, such as millet and quinoa, can also be hypoallergenic. Additionally, some packaged foods are designed to be hypoallergenic, as they’re made without common allergens like wheat, nuts, and dairy.
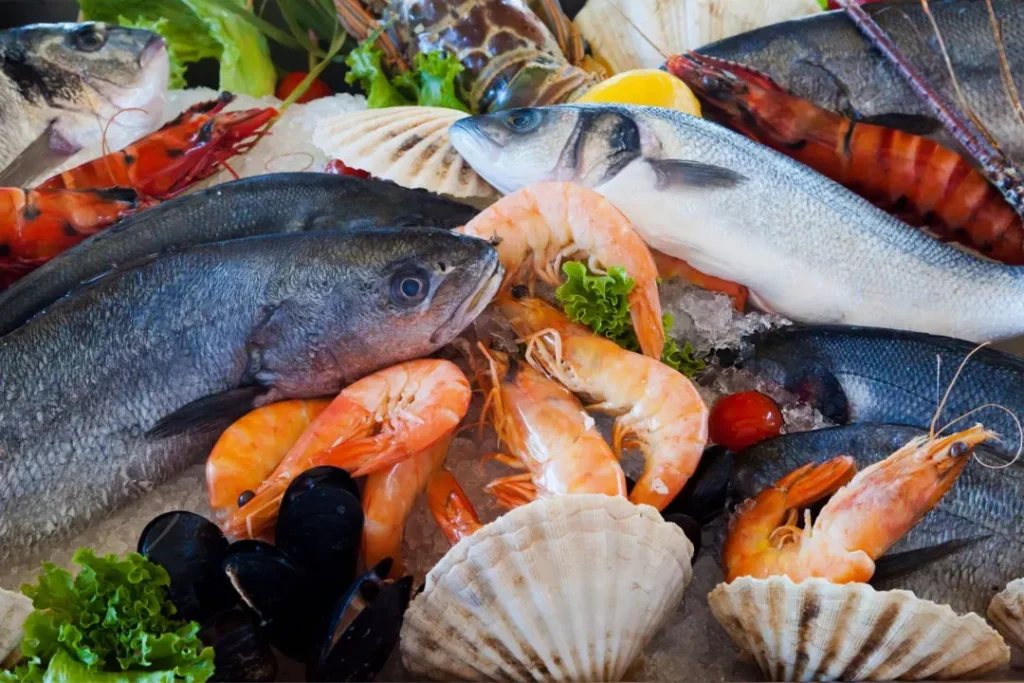

The hypoallergenic diet and food allergies
Food allergies can be caused by a number of culprits. Tree nuts are one of the best-known food allergies. Nut allergies are commonly linked to anaphylaxis, which can be fatal. Tree nut allergies usually last a lifetime, with less than 10% of those affected later outgrowing it.
Another prevalent food allergy for both children and adults is cow milk. When a person with a milk allergy is exposed to milk, the protein in milk binds to antibodies in the person’s immune system. This triggers reactions that can range from mild to very severe.
Fish is another common source of food allergies; around 1% of the U.S. population has a fish allergy. Compared to many other allergies, this allergy doesn’t always appear in childhood; around 40% of people with fish allergies have their first allergic reaction as an adult.
Finally, we should note that this summation of food allergies is by no means complete. Anyone concerned about food allergies, whether mentioned in this article or not, should consult their doctor or dietitian.

Supplements to a hypoallergenic diet
One way to support your hypoallergenic diet is through supplements. Despite the benefits offered by the hypoallergenic diet, you may be missing key vitamins and nutrients. For this, one strong option is Nuzest-USA’s Good Green Vitality.
The founder of Nuzest-USA, Trevor Bolland, was inspired to start the company by his daughter’s battle with Multiple Sclerosis; to this day, a portion of the company’s global sales go toward funding MS research. According to Bolland, Nuzest-USA’s commitment to clean and allergen-free products is at the core of the company’s mission, stating that Nuzest-USA makes “products that are suitable for everyone, which means plant-based to start with.”
Good Green Vitality is a plant-based nutritional superblend designed to fill in the holes in your diet. Some of the ingredients in Good Green Vitality include pea protein, spirulina (which serves as an antioxidant and may reduce cancer tumors), wheatgrass leaf (which can fight infections and gastrointestinal diseases), and red marine algae (which has anticancer and antiviral properties). Together, this blend offers numerous vitamins and minerals, ranging from Vitamin A to Vitamin E to iodine. For these reasons, Nuzest-USA’s Good Green Vitality is an excellent choice to fill any gaps in your hypoallergenic diet.
You can buy Nuzest-USA’s Good Green Vitality online for a reasonable price.

Final verdict
A hypoallergenic diet can have several benefits. This includes identifying the source of allergies, enabling a healthier diet, or even helping treat eczema. For people who are concerned that their hypoallergenic diet could be missing key nutrients and vitamins, supplements could help fill those gaps. With the help of supplements and proper nutrition, a hypoallergenic diet can optimize your health. Regardless of how you proceed, make sure to work closely with a medical professional during your hypoallergenic or elimination diet. This will not only make sure you’re still getting what you need from your diet but also that you get any necessary treatment for medical conditions like celiac disease and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Whether you’re concerned about potential allergies or just want to eat healthier, a hypoallergenic diet is worth considering.
Further references
Food and Drug Administration – Food Allergies: What You Need to Know
Livestrong – List of Hypoallergenic Foods
Ask Dr. Sears – Most and Least Allergenic Foods
EatingWell – Elimination Diet Meal Plan
Important Note: The information contained in this article is for general informational purposes only, and should not be construed as health or medical advice, nor is it intended to diagnose, prevent, treat, or cure any disease or health condition. Before embarking on any diet, fitness regimen, or program of nutritional supplementation, it is advisable to consult your healthcare professional in order to determine its safety and probable efficacy in terms of your individual state of health.
Regarding Nutritional Supplements Or Other Non-Prescription Health Products: If any nutritional supplements or other non-prescription health products are mentioned in the foregoing article, any claims or statements made about them have not been evaluated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, and such nutritional supplements or other health products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.


