Accurate Best High Blood Pressure Readers is essential for anyone managing hypertension or at risk for cardiovascular complications. With the rise in home-based health management, more individuals are turning to at-home solutions that empower them to stay informed about their cardiovascular health between doctor visits. As a result, knowing how to choose a good blood pressure monitor has become an essential component of responsible self-care. This guide offers an in-depth look at the types of monitors available, what makes a blood pressure reader effective, and how to ensure reliable results at home. It also provides medically accurate insights into how these devices contribute to early detection and better long-term outcomes for individuals with high blood pressure.
You may also like: Sudden Spikes in Blood Pressure: What Can Cause a Sudden Increase and When to Seek Medical Attention
Understanding the Importance of At-Home Blood Pressure Monitoring
Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of death globally, with hypertension serving as one of the most significant modifiable risk factors. According to the American Heart Association, consistent and accurate blood pressure monitoring is key to preventing and managing hypertension. This is where a high-quality blood pressure reader becomes indispensable. When used correctly, these tools offer a clearer picture of how daily habits, medications, and stress levels influence blood pressure over time. Relying solely on in-clinic readings can be misleading, as white coat syndrome—anxiety-induced spikes in blood pressure—may affect readings and fail to capture true, resting values. A good blood pressure monitor allows patients to track their health in real-time, promoting a proactive approach to disease prevention and management.
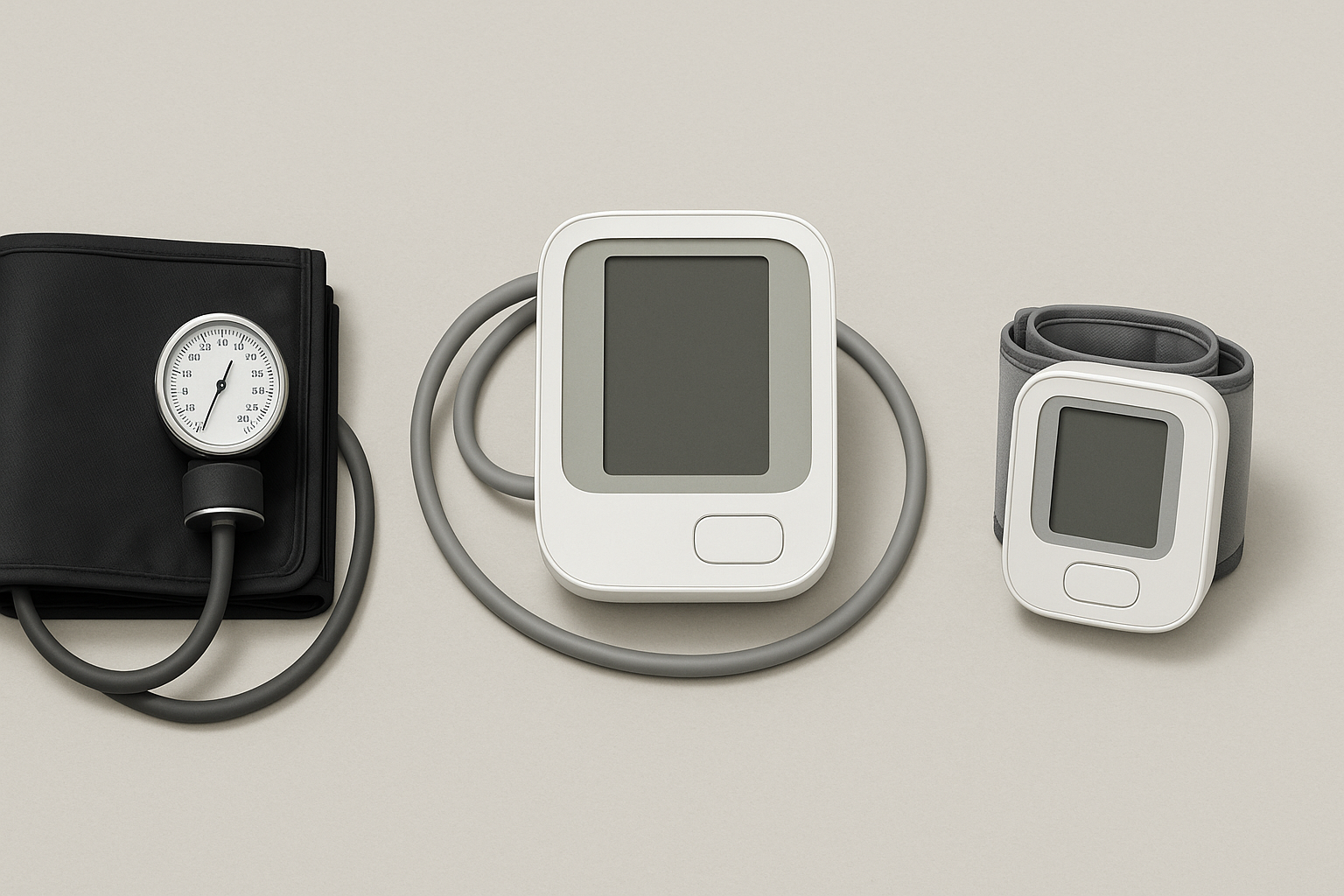

The Different Types of Blood Pressure Monitors and Their Features
Blood pressure monitors come in various forms, but the most common home-use types are upper arm cuff monitors and wrist monitors. While wrist devices are more compact and portable, upper arm monitors are generally considered more accurate due to the consistency in artery location and reduced variability in positioning. Within the category of upper arm monitors, users can choose between manual, semi-automatic, and fully automatic models. Most modern consumers prefer fully automatic models for ease of use, as they inflate and deflate with the press of a button and display digital readings.
Some advanced blood pressure readers also offer additional features such as Bluetooth connectivity, multiple user profiles, irregular heartbeat detection, and smartphone integration. These enhancements make it easier to store long-term data and share results with healthcare providers. However, the presence of these features should not come at the cost of reliability and accuracy. A good blood pressure monitor is one that offers both simplicity and precision, ensuring that users receive consistent, reproducible readings.
Evaluating Accuracy: What Makes a Blood Pressure Reader Reliable
Accuracy is the cornerstone of any medical device, and blood pressure monitors are no exception. An inaccurate device not only defeats the purpose of home monitoring but can also lead to misguided decisions about medication or lifestyle changes. The first step in evaluating accuracy is to ensure that the device is validated by a recognized authority, such as the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) or the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). These certifications indicate that the device has undergone rigorous clinical testing.
Beyond certification, reliability also depends on cuff size and fit. An improperly sized cuff can yield skewed readings. Many high blood pressure readers now come with adjustable cuffs or multiple size options, improving usability across a broader population. Consistent positioning, proper body posture, and adherence to usage guidelines also impact the reliability of readings. Thus, while a good blood pressure monitor must meet technical standards, its effectiveness also hinges on user education and compliance with best practices.
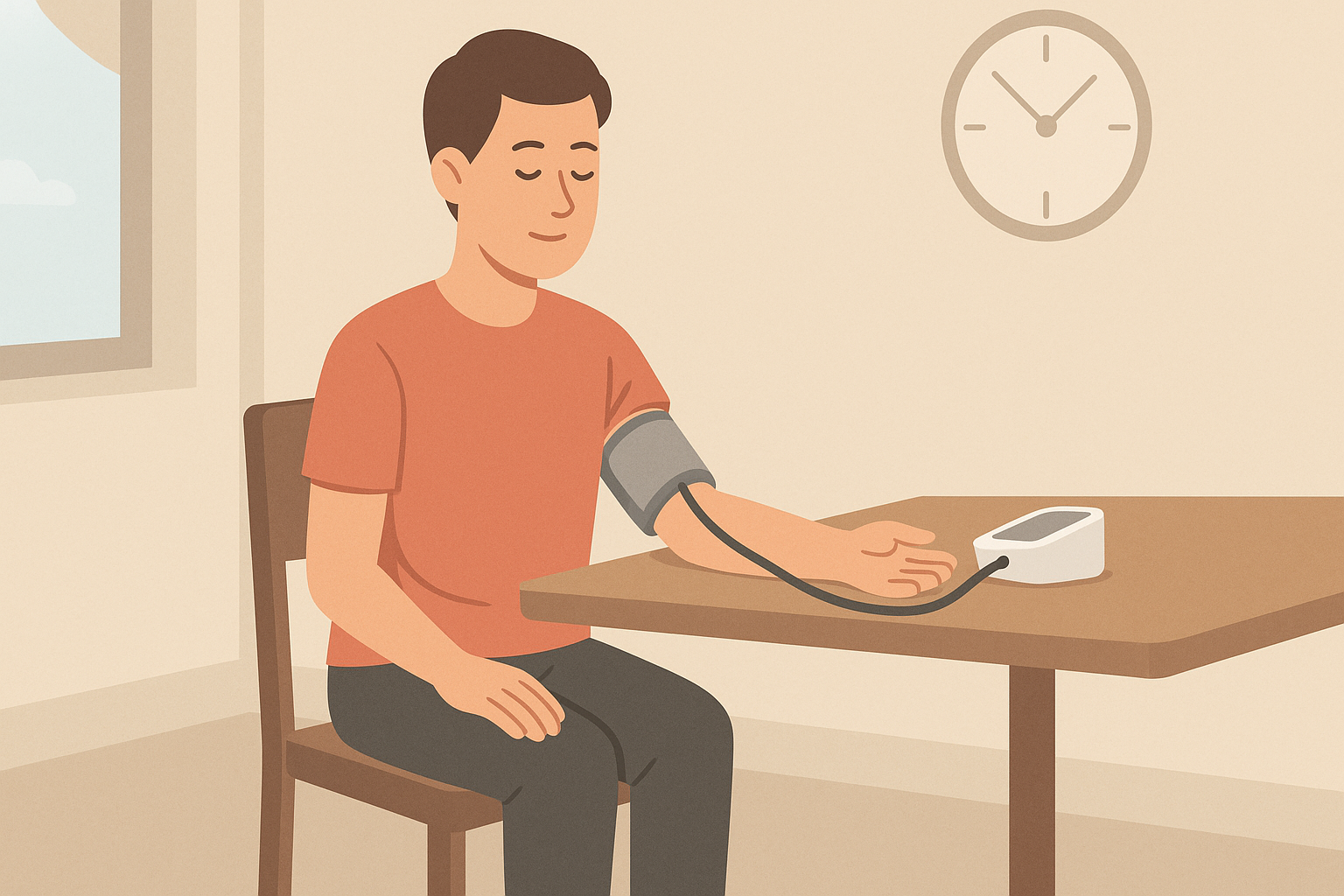

How to Use a Blood Pressure Monitor Correctly for Consistent Results
Using a blood pressure monitor may seem straightforward, but small mistakes in positioning or timing can result in inaccurate measurements. The user should be seated comfortably with feet flat on the floor and back supported. The arm being measured should rest on a flat surface at heart level, with the cuff positioned snugly on bare skin, not over clothing. It is advisable to avoid caffeine, smoking, and exercise for at least 30 minutes before taking a reading, as these factors can temporarily raise blood pressure.
Timing also matters. Consistency in the time of day when measurements are taken can help identify patterns and reveal true baseline values. Many healthcare providers recommend taking readings in the morning and evening over several days to establish an accurate profile. A good blood pressure monitor simplifies this process by allowing easy data storage and retrieval, helping both patients and doctors interpret trends over time. For the most accurate results, multiple readings should be taken a minute apart and averaged.
Key Features to Look for in a Good Blood Pressure Monitor
Choosing the right monitor involves more than just picking a popular brand. A good blood pressure monitor should offer a clear, easy-to-read display, intuitive controls, and high measurement precision. Features such as irregular heartbeat detection and hypertension alerts can be helpful, particularly for individuals at higher risk of complications. Devices with memory storage are essential for tracking readings over time, while Bluetooth-enabled models offer seamless data transfer to smartphones and apps.
Multi-user capabilities are especially beneficial in households where more than one individual needs to monitor blood pressure. Some high blood pressure readers also provide color-coded indicators that quickly show whether a reading falls within a healthy range. Battery life and power options should also be considered, as frequent charging or replacement can become inconvenient. Ultimately, the ideal device strikes a balance between advanced features and user-friendliness, supporting long-term adherence to monitoring routines.

Why Clinical Validation and FDA Approval Matter
When selecting a high blood pressure reader, it is crucial to verify whether the device has undergone clinical validation and received FDA clearance. These certifications serve as assurances that the monitor meets stringent standards for safety and performance. Clinical validation involves comparing the device’s readings with those taken by a professional using a mercury sphygmomanometer—the gold standard for blood pressure measurement. A validated device minimizes the risk of false readings that could lead to inappropriate treatment decisions.
FDA approval further strengthens the credibility of a monitor. While some inexpensive models may lack such credentials, their affordability comes at the cost of accuracy and reliability. In the context of chronic disease management, where decisions often hinge on subtle changes in health metrics, these certifications are non-negotiable. A good blood pressure monitor with both validation and FDA approval offers not only peace of mind but also enhances the physician-patient relationship by ensuring dependable data.
The Role of Blood Pressure Readers in Hypertension Management
Effective hypertension management requires consistent tracking, and a reliable blood pressure reader can be instrumental in this effort. By allowing patients to monitor their readings at home, these devices enable better understanding of how factors like diet, physical activity, stress, and medication influence blood pressure levels. This awareness empowers individuals to make informed lifestyle adjustments and fosters greater accountability.
Moreover, having access to long-term trends can help healthcare providers fine-tune treatment plans. Instead of relying on sporadic office readings, physicians can assess comprehensive data sets that reflect the patient’s everyday environment. A good blood pressure monitor acts as a bridge between routine life and clinical oversight, allowing for earlier interventions and more personalized care. For patients with conditions such as diabetes or kidney disease, where blood pressure control is especially critical, having a high-quality device is invaluable.

Common Pitfalls and Mistakes to Avoid When Using Blood Pressure Monitors
Even the most advanced device can yield poor results if used incorrectly. One of the most common mistakes is taking readings immediately after eating, exercising, or experiencing stress, which can temporarily raise blood pressure. Another frequent error is using a cuff that is too large or too small, leading to inaccurate measurements. Some users may also place the cuff over clothing, which interferes with proper compression and sensor contact.
Relying solely on single readings rather than averaging multiple measurements can skew results. It is equally important to avoid obsessing over daily fluctuations, which are normal to a degree. Instead, users should focus on overall trends and consult healthcare providers if consistent changes are observed. A good blood pressure monitor can only be effective when the user follows established guidelines and resists the urge to self-diagnose or adjust medications without professional input.
When to Calibrate or Replace Your Blood Pressure Monitor
Like any electronic device, blood pressure monitors can degrade over time. Regular calibration ensures the device remains accurate, particularly if it has been in use for several years or has sustained physical impact. Most manufacturers recommend checking calibration every one to two years, although some high blood pressure readers come with auto-calibration features or indicators that notify users when servicing is needed.
If the monitor begins producing inconsistent or implausible readings, it may be time for a replacement. Physical wear and tear on the cuff or display, battery malfunctions, or outdated software can all compromise performance. Investing in a good blood pressure monitor with a reputation for durability and a reliable warranty policy can extend its useful life and provide greater long-term value.

How to Interpret Readings and Understand Blood Pressure Categories
Understanding the numbers displayed by your monitor is essential to using it effectively. Blood pressure readings consist of two values: systolic pressure, which measures the force your heart exerts on artery walls when it beats, and diastolic pressure, which measures the force when the heart rests between beats. According to guidelines set by the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association, normal blood pressure is below 120/80 mmHg. Elevated blood pressure ranges from 120-129 systolic with diastolic below 80, while Stage 1 hypertension begins at 130/80.
Recognizing where your readings fall within these categories can help guide decisions about lifestyle changes or the need for medical intervention. A good blood pressure monitor will often include visual indicators or color-coded scales to help users interpret their numbers. However, it is always advisable to review readings with a healthcare provider, particularly when starting a new medication or experiencing unusual symptoms. Clear understanding of what your blood pressure numbers mean enhances the effectiveness of home monitoring.
The Psychological and Behavioral Benefits of Regular Monitoring
While the primary benefit of a high blood pressure reader is physiological, there are also significant psychological and behavioral advantages. Regular self-monitoring has been shown to improve medication adherence, as individuals are more likely to take prescribed drugs when they see real-time benefits reflected in their readings. It also fosters a sense of control and engagement in one’s own healthcare, reducing anxiety by demystifying the process.
Moreover, family members or caregivers can become more involved, creating a supportive environment that encourages healthy behavior. For older adults or individuals with mobility challenges, having a reliable device at home eliminates the need for frequent clinic visits, which can be stressful and time-consuming. A good blood pressure monitor thus serves not only as a diagnostic tool but also as a motivational aid that supports long-term wellness.
Frequently Asked Questions: Blood Pressure Monitors and At-Home Tracking
1. How often should I replace my blood pressure monitor, even if it seems to be working fine?
While many people continue using the same device for years, a good blood pressure monitor should be evaluated for accuracy at least every two years. Even if the display functions normally, internal sensors may degrade over time, leading to subtle but clinically significant inaccuracies. Using a high blood pressure reader that no longer meets calibration standards could result in missed warning signs or unnecessary medication adjustments. Professional recalibration or comparison with a clinic-grade device can help assess ongoing reliability. Investing in a newer blood pressure reader every five years, particularly if you have chronic hypertension, ensures you benefit from the latest technology and validated accuracy standards.
2. Can a good blood pressure monitor detect irregular heart rhythms or arrhythmias?
Some advanced models can flag irregular heartbeats, but it’s important to understand the scope and limitations of such features. A high blood pressure reader equipped with arrhythmia detection algorithms may alert users to potential concerns, but these are not a substitute for a professional ECG. However, for patients with conditions like atrial fibrillation, a blood pressure reader that detects irregular rhythms may serve as an early alert system to seek timely care. Look for models that specify this functionality and have validation from cardiovascular health organizations. Always follow up with a healthcare provider for a full evaluation if your device frequently flags irregular readings.
3. What are the best times of day to take readings for the most accurate results?
Morning and evening readings tend to provide the most representative averages, particularly if done before taking medications or after daily stressors subside. A good blood pressure monitor should be part of a structured routine that avoids high-variability periods such as right after meals or physical exertion. Consistency is more important than timing alone; for instance, measuring at 7 a.m. daily gives more actionable data than sporadic readings. Using a high blood pressure reader at consistent intervals builds a clear pattern over time. Additionally, recording at the same location and in the same position (seated, relaxed, with proper cuff placement) further enhances data reliability.
4. Are smartphone-connected monitors more accurate or just more convenient?
Smartphone-connected models offer the convenience of automatic logging and data sharing but are not inherently more accurate than traditional devices. The defining factor remains whether the blood pressure reader has been clinically validated and approved by regulatory authorities. However, digital integration can reduce user error by minimizing the need for manual recording, which can lead to missed trends or forgotten readings. A good blood pressure monitor that syncs with your phone may also encourage more consistent use due to visual dashboards and progress tracking. Just ensure that technology doesn’t replace proper technique—even the smartest device must be used correctly to be effective.
5. What role does arm position play in the accuracy of a blood pressure reading?
Improper arm positioning is one of the most common causes of inaccurate readings. A good blood pressure monitor relies on consistent measurement conditions, and placing the arm too low or too high can distort results. Ideally, the cuffed arm should be level with your heart and supported on a flat surface. If your arm is unsupported or hanging at your side, the blood pressure reader may display artificially high or low numbers. Some high blood pressure readers now offer positioning sensors or visual cues to help users correct their posture during measurement, which can significantly enhance long-term accuracy.
6. Can environmental factors, like temperature or humidity, affect readings?
Surprisingly, yes. Extreme cold can cause peripheral blood vessels to constrict, temporarily elevating readings, while high humidity or heat can promote vasodilation, leading to lower readings. A good blood pressure monitor used in such conditions may yield inconsistent results, not due to device failure but environmental variability. To counteract this, try to take readings in a room that is comfortably climate-controlled. If you live in a region with seasonal extremes, consider calibrating your device annually and ensuring your high blood pressure reader is stored away from direct sunlight or damp conditions.
7. Are wrist monitors reliable, or should I always use an upper arm model?
While wrist monitors are often seen as less accurate, that generalization is starting to shift with recent advances in sensor technology. A good blood pressure monitor worn on the wrist can be reliable if it is properly positioned at heart level and used according to instructions. However, due to variability in arterial depth and movement sensitivity, most physicians still recommend upper arm monitors as the standard for daily use. For those with mobility limitations or larger arms, a well-calibrated wrist-based high blood pressure reader may be a better fit than using an ill-sized upper arm cuff. Ultimately, accuracy depends more on proper technique and device validation than on the type of monitor alone.
8. What psychological benefits come from using a home blood pressure monitor regularly?
Frequent at-home monitoring can lead to increased health literacy and emotional resilience. Patients using a good blood pressure monitor often report reduced anxiety during clinic visits, as they feel better informed and less vulnerable to unexpected news. Moreover, having a high blood pressure reader readily available fosters a sense of control and agency, which can be particularly empowering for those managing chronic conditions. This sense of empowerment often leads to more consistent medication adherence and lifestyle improvements. In some cases, caregivers and family members also become more engaged, creating a communal sense of accountability around cardiovascular health.
9. Are there new innovations in the pipeline for blood pressure monitoring technology?
Yes, the field is seeing exciting developments, including wearable monitors embedded in smartwatches, continuous monitoring patches, and cuffless optical sensors that use pulse wave velocity. While not yet a complete replacement for a traditional blood pressure reader, these innovations show promise for high-risk patients who need frequent assessments. A good blood pressure monitor in the near future may be capable of syncing with AI-driven apps that interpret trends and predict episodes of hypertension before they occur. As validation protocols catch up with these technologies, their integration into clinical care is expected to grow. Until then, validated cuff-based monitors remain the gold standard for most users.
10. How can I ensure my readings are truly reflective of my cardiovascular health?
To ensure your readings are meaningful, focus on consistency, context, and communication. A good blood pressure monitor should be used in the same setting, at the same time, and in a calm state to minimize external influences. Keep a log that includes notes on stress, medication timing, and recent physical activity—this will help your physician interpret the numbers in context. A high blood pressure reader is most effective when paired with regular check-ins and clinical feedback, allowing small variations to be evaluated properly. Remember, the goal isn’t perfection in every reading but identifying patterns that inform treatment and support overall heart health.
Final Thoughts on Choosing the Best Blood Pressure Reader for Long-Term Health
In today’s health-conscious world, investing in a high-quality blood pressure reader is a proactive step toward preventing and managing hypertension. With so many options available, selecting a good blood pressure monitor involves balancing accuracy, usability, features, and trustworthiness. Devices that have received clinical validation and FDA approval provide a reliable foundation for monitoring, while features like memory storage, smartphone integration, and multi-user profiles enhance convenience and engagement.
Equally important is the commitment to using the monitor correctly and consistently. Understanding how to interpret readings, avoiding common mistakes, and incorporating results into meaningful health decisions are all essential for maximizing the benefits of home monitoring. A good blood pressure monitor is not merely a gadget—it is a vital partner in your journey toward cardiovascular health, one that fosters awareness, responsibility, and better outcomes. As the landscape of personal health technology continues to evolve, choosing the right device becomes more than a matter of preference; it becomes a cornerstone of empowered, informed living.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out.
Further Reading:
How to Pick a Home Blood Pressure Monitor


