Living with eczema, a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and irritated skin, can be a physically and emotionally draining experience. As more individuals search for holistic and evidence-based approaches to managing this condition, growing attention has turned to the gut-skin axis and the role of beneficial microbes in supporting skin health. Among these interventions, the best probiotic for eczema offers promising potential by addressing root causes rather than merely soothing surface symptoms. In this article, we will explore the emerging science behind probiotics and eczema, analyze how specific strains can impact immune response and inflammation, and discuss how incorporating targeted supplements for eczema, including vitamins and beneficial bacteria, may provide comprehensive relief and long-term support.
You may also like: Breakthrough Approaches to Eczema Alternative Healing: What Works and Why It Matters
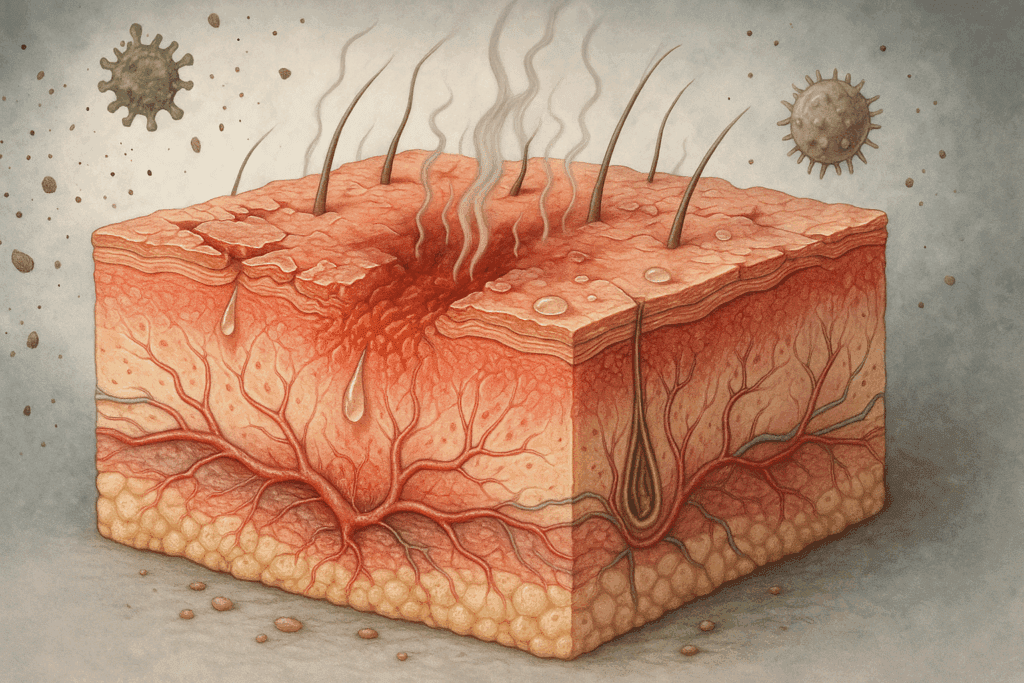
Understanding Eczema and Its Underlying Causes
To appreciate how probiotics may aid in eczema management, it is important to understand the pathophysiology of eczema itself. Eczema, particularly the most common form known as atopic dermatitis, involves a complex interplay of genetic, immunological, and environmental factors. It is marked by skin barrier dysfunction, which allows allergens, irritants, and microbes to penetrate more easily, leading to chronic inflammation and itching. Individuals with eczema often have mutations in the filaggrin gene, which is responsible for producing a protein essential for maintaining the skin’s protective barrier.
This barrier compromise makes the immune system more reactive. Many individuals with eczema experience heightened immune responses to harmless substances, resulting in an overproduction of inflammatory cytokines and an imbalance between Th1 and Th2 helper T cells. This immunological misfiring triggers flare-ups that can vary in severity and frequency. Additionally, microbial imbalance on the skin and in the gut has been implicated in exacerbating eczema, which leads us to the intriguing concept of the gut-skin axis.
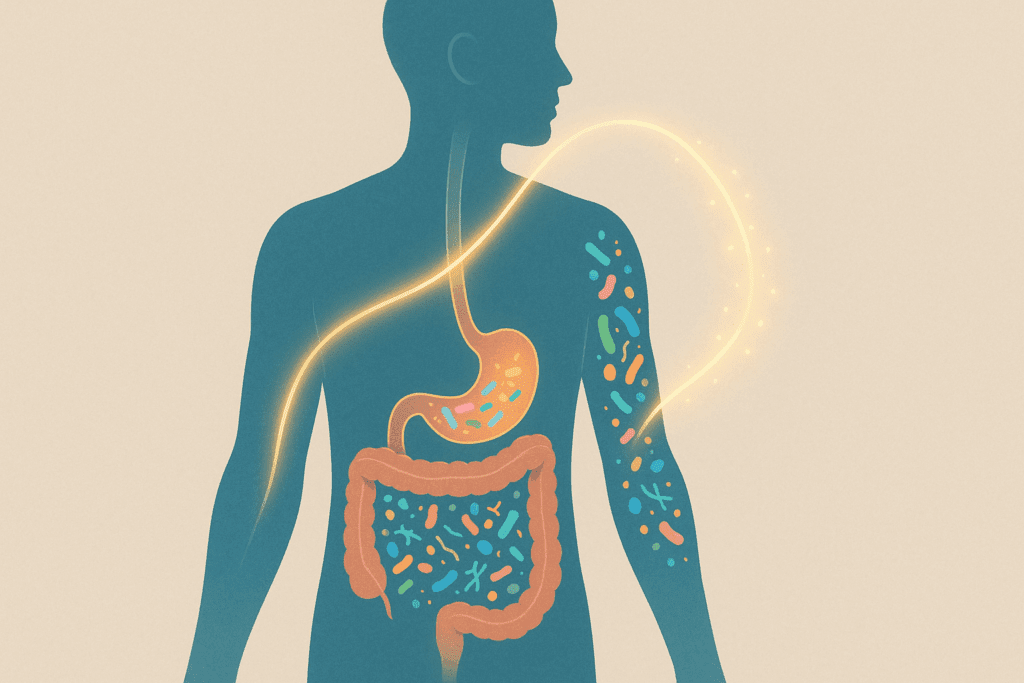
The Gut-Skin Axis and Its Connection to Eczema
The gut-skin axis is a bidirectional communication network between the gastrointestinal system and the skin. The state of our gut microbiota—the trillions of bacteria residing in our intestines—plays a significant role in regulating systemic inflammation and immune response. When this microbiome is disrupted due to factors such as antibiotics, poor diet, stress, or illness, a condition known as dysbiosis can occur. Dysbiosis has been linked to a variety of inflammatory conditions, including eczema.
Scientific studies have demonstrated that individuals with eczema often exhibit imbalances in their gut microbiota, including reduced levels of beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. These bacteria are known to produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, which have anti-inflammatory effects and support the integrity of the intestinal lining. When the gut barrier is compromised, inflammatory molecules can leak into the bloodstream, potentially triggering or worsening skin inflammation.
This connection between gut health and skin conditions has prompted researchers to explore whether restoring microbial balance through probiotics for eczema can lead to improvements in symptoms. Probiotics, live microorganisms that confer health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts, may act as a therapeutic bridge in the gut-skin dialogue.
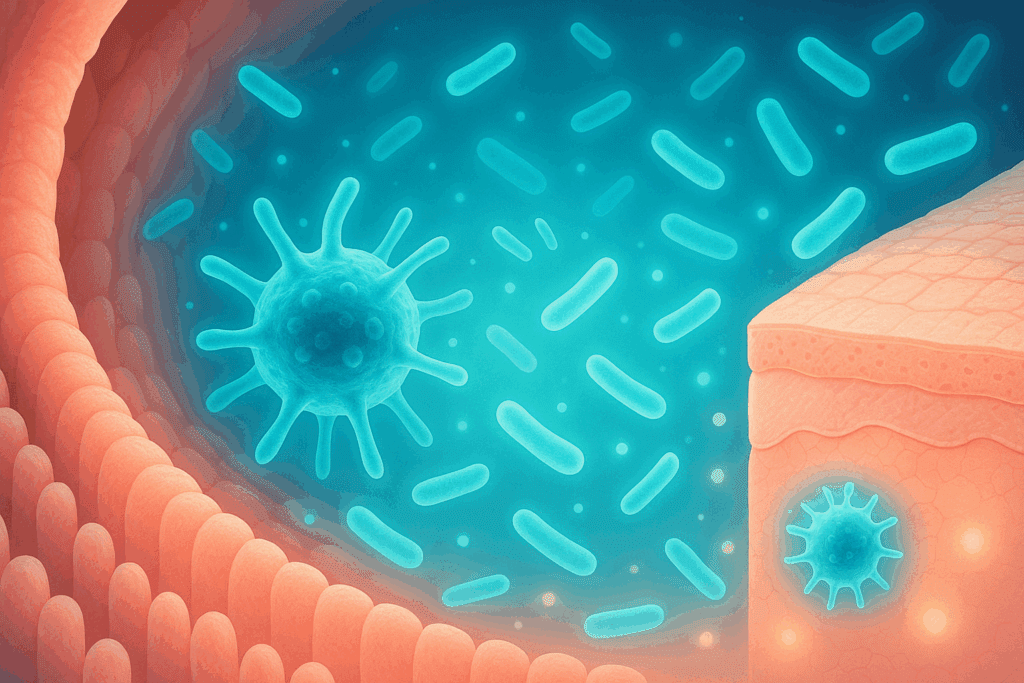
How Probiotics Influence Inflammation and Immunity
Probiotics exert their benefits through several mechanisms, many of which are directly relevant to eczema management. First, they help rebalance the microbiome by crowding out pathogenic bacteria and fostering the growth of beneficial strains. This restoration of microbial diversity is essential for supporting healthy immune function. Secondly, probiotics strengthen the intestinal barrier, reducing the systemic spread of inflammatory molecules that could contribute to eczema flares.
More specifically, certain probiotic strains modulate immune responses by promoting the production of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and suppressing the activity of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-4 and IL-13, which are often elevated in eczema patients. By influencing the Th1/Th2 balance, probiotics help shift the immune system away from the allergy-prone Th2 dominance commonly seen in atopic conditions. These immunomodulatory effects underscore the rationale behind using probiotics for eczema as part of a multifaceted management plan.
Clinical Evidence Supporting the Best Probiotic for Eczema Relief
Numerous clinical trials have investigated the effects of probiotic supplementation on eczema symptoms, particularly in infants and children who are often most affected by the condition. One landmark study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that supplementation with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG significantly reduced the risk of developing eczema in high-risk infants when administered during pregnancy and early infancy. Other trials have demonstrated improvements in itch severity, lesion extent, and quality of life in both pediatric and adult populations following probiotic use.
The best probiotic for eczema is often strain-specific. For example, Lactobacillus plantarum and Bifidobacterium lactis have shown promise in reducing inflammation and supporting skin barrier function. While individual responses may vary, the consensus from meta-analyses suggests that multi-strain formulations may offer superior benefits due to their synergistic effects. It is important to note that probiotic efficacy depends not only on strain selection but also on dosage, formulation, and duration of use.

Choosing the Best Probiotic for Eczema: What to Look For
When selecting a probiotic supplement for eczema relief, there are several criteria to consider. First and foremost, the product should contain clinically studied strains such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, and Lactobacillus reuteri. These strains have been shown to reduce eczema symptoms and support immune regulation. Secondly, a high CFU (colony-forming unit) count is important for ensuring an adequate dose of live bacteria reaches the gut. A daily dosage of at least 10 billion CFUs is generally recommended for therapeutic purposes.
Additionally, the best probiotic for eczema should be shelf-stable and resistant to stomach acid, ensuring the microbes survive the journey to the intestines. Products that include prebiotics—non-digestible fibers that feed beneficial bacteria—may enhance efficacy. Furthermore, third-party testing and clear labeling are essential indicators of product quality and transparency. Consulting a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations is especially important for individuals with underlying health conditions or compromised immunity.

Beyond Probiotics: Vitamins and Supplements for Eczema Relief
While probiotics are a cornerstone in the conversation about gut and skin health, they are most effective when used in conjunction with other supportive nutrients. Among the most promising vitamins for eczema are vitamin D, vitamin E, and vitamin B12. Vitamin D plays a critical role in modulating immune response and has been shown to reduce eczema severity in children and adults with deficiencies. Regular sun exposure or supplementation may be beneficial in maintaining adequate levels.
Vitamin E, a potent antioxidant, helps neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in the skin. This can be particularly helpful in managing inflammation and promoting skin repair. Meanwhile, topical and oral forms of vitamin B12 have demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects and may reduce lesion severity in some patients. Zinc and omega-3 fatty acids, although not classified as vitamins, are also frequently recommended supplements for eczema due to their roles in immune function and skin barrier support.
Integrating these nutrients into a comprehensive regimen alongside the best probiotic for eczema creates a synergistic effect, addressing both internal and external contributors to skin health. However, individuals should avoid self-medicating with high doses of supplements without professional guidance, as imbalances or interactions could exacerbate symptoms.
Dietary Strategies for Supporting Skin Health Through the Gut
Nutrition plays an undeniable role in managing eczema, particularly when aiming to optimize gut microbiota composition and reduce systemic inflammation. An anti-inflammatory diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods can enhance the effects of probiotic supplementation. Emphasizing fiber-rich vegetables, fermented foods like kefir and sauerkraut, and omega-3 sources such as fatty fish helps nurture a diverse and resilient gut microbiome.
Avoiding common dietary triggers, such as refined sugars, trans fats, and allergenic foods like dairy or gluten (if sensitivities are present), may prevent flares. Some individuals benefit from elimination diets under professional supervision to identify food-related triggers. In addition, hydration and adequate protein intake support skin regeneration and barrier function, enhancing the overall efficacy of both dietary and supplement-based interventions.
The Link Between Stress, Eczema, and Probiotic Efficacy
Psychological stress is a well-documented trigger for eczema flare-ups and can undermine even the most diligent treatment regimens. Stress influences gut permeability, microbial diversity, and immune reactivity, further highlighting the need for a gut-centered approach. Probiotics may indirectly mitigate stress-induced flares by stabilizing the gut-brain axis, another key component of the body’s interconnected systems.
Strains such as Lactobacillus helveticus and Bifidobacterium longum have demonstrated anxiolytic properties in clinical studies, potentially improving both mood and skin condition. Incorporating mindfulness practices, regular exercise, and sleep hygiene alongside the best probiotic for eczema may provide a holistic defense against stress-related symptom escalation. Mental and emotional resilience often mirrors physical resilience, emphasizing the value of a comprehensive care model.
Evolving Research on Probiotics and Eczema Management
The landscape of probiotic research continues to evolve rapidly, with new discoveries shedding light on the nuances of strain specificity, timing of administration, and patient response variability. Current investigations are exploring the potential for personalized microbiome mapping to tailor probiotic interventions more effectively. These advancements may pave the way for precision medicine approaches to managing eczema and other inflammatory conditions.
Additionally, researchers are examining synbiotics—combinations of probiotics and prebiotics—and postbiotics, which are bioactive compounds produced by beneficial microbes. These novel agents may offer targeted immune modulation and enhanced skin barrier restoration. While more large-scale, placebo-controlled trials are needed to confirm efficacy, early results are encouraging and suggest a bright future for integrative eczema therapies grounded in microbiome science.
The Importance of Professional Guidance and Individualized Treatment
While the science supporting probiotics for eczema is compelling, it is essential to recognize that not all patients will respond identically. Eczema is a heterogeneous condition influenced by a range of internal and external variables. Genetic predisposition, lifestyle factors, and environmental exposures all contribute to disease expression. Therefore, working with dermatologists, allergists, and nutritionists ensures that interventions are appropriately tailored.
A comprehensive treatment plan should include skin barrier repair strategies, allergen avoidance, stress management, and appropriate use of supplements for eczema. Personalized care not only improves outcomes but also minimizes the risk of adverse effects from unmonitored supplementation. Healthcare providers can also help track progress and adjust protocols based on symptom response and emerging evidence.
The Role of Topical Probiotics in Eczema Therapy
In addition to oral probiotic supplements, topical applications of beneficial bacteria are gaining attention as innovative therapies for eczema. Research has shown that the skin microbiome of eczema patients often exhibits reduced diversity and increased colonization by harmful microbes like Staphylococcus aureus. Topical probiotics aim to rebalance the skin microbiota by introducing beneficial strains directly onto the affected areas.
Preliminary studies suggest that topical formulations containing strains such as Roseomonas mucosa and Lactobacillus johnsonii may reduce inflammation and improve skin hydration. These products work by reinforcing the skin barrier, competing with pathogenic bacteria, and modulating local immune responses. While still in the early stages of development, topical probiotics may serve as a complementary approach to oral supplementation and traditional emollient therapy.
Looking Ahead: Integrating Research into Practical Application
As public interest in natural and integrative health solutions continues to grow, so does the demand for scientifically validated therapies. The exploration of the best probiotic for eczema embodies this intersection of evidence and accessibility. Future research must continue to identify optimal strains, dosing strategies, and delivery systems to ensure maximum benefit. Collaboration between clinicians, researchers, and consumers will be vital in translating laboratory findings into effective, real-world solutions.
For patients, the goal is not merely symptom management but true quality-of-life improvement. By understanding the multifaceted nature of eczema and embracing a personalized, microbiome-centered strategy, individuals can move closer to lasting relief. Integrating probiotics, vitamins for eczema, dietary changes, and stress reduction into daily life forms a comprehensive, sustainable path to healthier skin.
Frequently Asked Questions: Eczema Relief and the Role of Probiotics
Is there a difference between probiotics for eczema prevention and treatment?
Yes, there is a nuanced distinction between using probiotics to prevent eczema and using them as a treatment for active symptoms. Preventive probiotic strategies are often implemented during pregnancy or early infancy, especially for children with a family history of atopic conditions. These protocols typically involve strains like Lactobacillus rhamnosus given prenatally or through breastfeeding to influence immune development and gut colonization. In contrast, probiotics for eczema treatment are selected to reduce inflammation, support gut barrier repair, and restore microbial balance in already symptomatic individuals. The strain composition, dosage, and duration of use may vary significantly between these two purposes, and understanding the timing of intervention can greatly influence outcomes.
What is the best probiotic for eczema in adults versus children?
While there is some overlap, the best probiotic for eczema in adults may differ from the most effective strains used in children. Adults often benefit from more complex formulations containing multiple strains, such as Bifidobacterium lactis, Lactobacillus casei, and Lactobacillus plantarum, which address broader microbiome imbalances developed over time. Children, particularly infants, tend to respond best to simpler, well-researched strains like Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, especially when initiated early. Moreover, dosage considerations differ by age group, as children’s developing systems require more cautious titration. It’s advisable to consult pediatricians or integrative health practitioners when considering probiotics for eczema in children, ensuring both safety and efficacy.
Can combining probiotics with other supplements for eczema enhance results?
Absolutely. Combining probiotics with specific supplements for eczema, such as omega-3 fatty acids, zinc, or vitamin D, can provide a more comprehensive therapeutic approach. Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties that work synergistically with probiotics to calm systemic inflammation. Zinc supports skin barrier integrity and helps regulate immune responses, while vitamin D modulates immune activity and has been shown to improve skin conditions in deficiency states. By layering these interventions, patients may experience faster or more robust improvements in symptom control. However, integration should be guided by a healthcare professional to ensure balance and avoid potential nutrient interactions or over-supplementation.
Do topical probiotics offer the same benefits as oral probiotics for eczema?
Topical and oral probiotics serve different but complementary roles in eczema management. Oral probiotics primarily influence the gut-skin axis by modulating systemic inflammation, enhancing gut barrier function, and promoting immune tolerance. Topical probiotics, on the other hand, aim to directly rebalance the skin microbiome by introducing beneficial bacteria to the skin surface. This can reduce colonization by harmful microbes like Staphylococcus aureus, which is often elevated in eczema patients. While both forms can be effective, their mechanisms and outcomes vary, making them ideal candidates for combination therapy in persistent or widespread eczema cases.
How long should I take probiotics for eczema before expecting results?
The timeline for visible improvements can vary widely depending on the individual, the severity of eczema, and the specific strains used. Most studies suggest that it may take anywhere from four to twelve weeks of consistent daily use to observe meaningful changes in skin condition. That said, some individuals report mild symptom relief within the first few weeks, particularly if their gut microbiota was significantly imbalanced. For chronic or severe cases, long-term supplementation might be necessary to maintain microbial balance and support ongoing skin health. Monitoring progress with a healthcare provider can help fine-tune the regimen and set realistic expectations.
What are the risks or side effects associated with taking probiotics for eczema?
For most healthy individuals, probiotics are considered safe and well-tolerated. However, mild side effects such as bloating, gas, or temporary digestive changes may occur as the body adjusts to the new microbial balance. In rare cases, especially in immunocompromised individuals, there may be a risk of bacterial translocation or infection. It is also possible for the skin to temporarily worsen before improving, as inflammatory processes recalibrate. Choosing high-quality, clinically validated strains and consulting with a medical professional can minimize risks and ensure that probiotics for eczema are introduced in a controlled, supportive manner.
Can diet alone replace the need for probiotics in eczema care?
While a nutrient-rich, anti-inflammatory diet plays a foundational role in managing eczema, it may not fully replace the need for targeted probiotics. Whole foods such as fermented vegetables, yogurt, and kefir contain naturally occurring probiotics, but they may not provide the specific strains or concentrations necessary to influence immune modulation in eczema. Additionally, individuals with food sensitivities or histamine intolerance may react poorly to fermented foods. Supplementing with encapsulated probiotics ensures a more consistent and therapeutic dosage tailored to the individual’s condition. Therefore, while diet is indispensable, it is often best viewed as part of a multifaceted strategy that includes probiotics, supplements for eczema, and lifestyle modifications.
Why are certain strains more effective than others in treating eczema?
The effectiveness of a probiotic strain hinges on its ability to interact with the host’s immune system, survive gastrointestinal transit, and adhere to the gut lining. Strains such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Bifidobacterium longum have demonstrated superior efficacy in reducing eczema symptoms due to their anti-inflammatory and barrier-enhancing properties. These strains can increase regulatory T-cell activity, reduce IgE-mediated allergic responses, and promote microbial diversity. Strain specificity also determines compatibility with individual microbiome profiles, which is why one person may respond well to a formulation that yields no benefit for another. As the science advances, personalized microbiome assessments may help match patients with the best probiotic for eczema based on their unique microbial landscape.
What are the most important vitamins for eczema when used alongside probiotics?
Several vitamins for eczema stand out when used in conjunction with probiotics. Vitamin D supports immune regulation and is often deficient in individuals with chronic inflammatory conditions. Vitamin B12, especially in topical form, has shown promise in reducing itching and inflammation. Vitamin E offers antioxidant protection, helping to counteract oxidative stress in the skin. When combined with probiotics, these vitamins may enhance outcomes by supporting barrier repair and moderating immune responses from multiple angles. Ideally, vitamin intake should be guided by lab assessments to determine individual deficiencies and tailor supplementation appropriately.
How can I tell if I’ve found the best probiotic for eczema for my needs?
Identifying the best probiotic for eczema requires a combination of clinical evidence, symptom tracking, and individual experimentation. Look for products that list specific strains with proven benefits for eczema, such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG or Bifidobacterium bifidum. Consistency in dosing and monitoring changes in symptoms like itchiness, redness, and flare-up frequency can help determine efficacy. Some individuals keep a symptom journal to track progress, which can be shared with their healthcare provider to adjust the protocol. If significant improvements are observed within two to three months, it’s a strong indication that the chosen formulation is well-suited to your needs.
A Holistic Path to Eczema Relief Rooted in Probiotics and Skin Science
In conclusion, the growing body of evidence underscores the proven benefits of choosing the best probiotic for eczema relief. By targeting underlying inflammation, restoring gut balance, and supporting immune modulation, specific probiotic strains offer a natural and scientifically grounded approach to managing this complex skin condition. When combined with essential vitamins for eczema, such as vitamin D and B12, and reinforced by an anti-inflammatory diet and lifestyle, probiotics become a key pillar in a comprehensive eczema care plan.
Rather than relying solely on corticosteroids or emollients that address surface symptoms, this approach delves into the interconnected systems that influence skin health from within. As research continues to illuminate the gut-skin connection, patients and practitioners alike are empowered with more tools to manage eczema effectively. Ultimately, the synergy of high-quality supplements for eczema, thoughtful dietary strategies, and professional guidance creates a robust foundation for long-term healing and skin resilience.
Further Reading:
Alternative and Complementary Treatments
Diet and eczema: a review of dietary supplements for the treatment of atopic dermatitis


