Introduction
Monkeypox, now officially referred to as mpox, has been a subject of growing concern due to its sporadic outbreaks and potential health risks. While it is not as widely known or deadly as diseases like smallpox, mpox has nonetheless prompted public health agencies to monitor its transmission and assess its potential threats to human populations. With the resurgence of cases in recent years, many people wonder: can you die from monkeypox? Understanding the risks, symptoms, and prevention methods is crucial for protecting yourself and your community. This article delves into the severity of mpox, its mortality rate, symptoms, transmission pathways, and the best prevention strategies to curb its spread.
You May Also Like: New Virus Discovered: What Experts Are Saying About Its Global Health Impact
What Is Monkeypox?
Monkeypox is a viral zoonotic disease caused by the monkeypox virus, a member of the Orthopoxvirus genus, which also includes smallpox. The disease was first identified in 1958 in laboratory monkeys, hence its name, though the primary reservoirs are believed to be rodents and other small mammals in Central and West Africa. The first human case was documented in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and since then, the virus has caused intermittent outbreaks, primarily in African nations, but with occasional spread to other regions.
Although mpox shares similarities with smallpox, including skin lesions and flu-like symptoms, it is generally considered less severe. However, some strains of the virus can lead to serious complications, particularly in immunocompromised individuals, children, and pregnant women. The disease has recently gained international attention due to outbreaks in non-endemic countries, raising concerns about its global impact.
Can You Die from Monkeypox?
While the majority of mpox cases resolve without severe complications, the disease can be fatal, particularly in vulnerable populations. The monkeypox fatality rate varies based on the strain and the patient’s overall health. The Central African (Congo Basin) strain has a higher mortality rate, estimated at around ten percent, whereas the West African strain is considered less severe, with a fatality rate of approximately one to three percent.
Death from monkeypox usually results from complications such as secondary bacterial infections, sepsis, encephalitis, or severe dehydration due to extensive skin lesions. Individuals with weakened immune systems, including those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or organ transplants, face a greater risk of developing severe illness. Children under the age of eight and pregnant individuals are also more susceptible to severe outcomes. Despite these risks, most healthy adults recover within a few weeks without lasting effects.
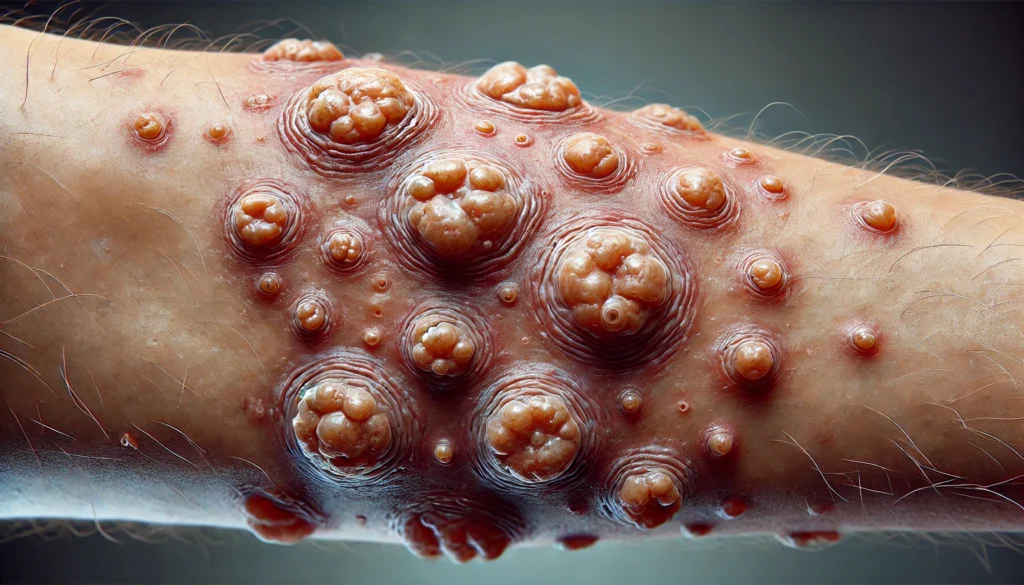
Symptoms of Monkeypox
Mpox presents in two distinct phases: the prodromal phase and the rash phase. Symptoms typically appear within five to twenty-one days following exposure to the virus.
In the early stage of infection, patients often experience flu-like symptoms, including fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes. The presence of swollen lymph nodes helps differentiate mpox from other poxviruses, including smallpox. These symptoms indicate that the immune system is responding to the viral infection.
A few days after the onset of fever, a distinctive rash develops, progressing through several stages. It begins with flat, discolored skin lesions known as macules, which then evolve into raised bumps called papules. These lesions fill with fluid, forming vesicles, which later develop into pus-filled sores known as pustules. Eventually, the lesions dry and form scabs, which then fall off. The rash typically begins on the face and spreads to other parts of the body, including the palms, soles, and genital areas. In severe cases, lesions may be widespread, coalescing into large areas of damaged skin, which increases the risk of secondary infections.
Mpox at Birth: Risks to Newborns
Mpox poses significant risks to newborns if transmitted from a pregnant individual to the fetus. This can occur through vertical transmission via the placenta or during delivery. Studies indicate that mpox infection in pregnancy may lead to complications such as stillbirth, miscarriage, or severe neonatal infection. Newborns exposed to the virus at birth may exhibit congenital skin lesions, respiratory distress, or systemic infection. Due to the potential for severe outcomes, healthcare providers must take precautions to prevent maternal-to-child transmission, including isolation measures and antiviral treatments when necessary.
Does Monkeypox Go Away on Its Own?
Most cases of mpox resolve on their own within two to four weeks. Treatment is primarily supportive, focusing on relieving symptoms, preventing secondary infections, and ensuring adequate hydration. However, individuals with severe cases or those at higher risk of complications may require medical intervention.
Antiviral medications such as tecovirimat (TPOXX) have shown promise in treating severe mpox cases, particularly in immunocompromised patients. Additionally, the smallpox vaccine (JYNNEOS or ACAM2000) has been found to provide cross-protection against mpox and may be administered post-exposure to reduce symptom severity.
Monkeypox Death Rate: Analyzing Mortality Trends
The monkeypox death rate varies by region, healthcare access, and patient demographics. Historically, the Central African strain has had a mortality rate of up to ten percent, while the West African strain, responsible for the 2022 global outbreak, has a lower fatality rate of around one to three percent.
Factors influencing mortality rates include healthcare access, viral strain, comorbidities, and age or immune status. Prompt medical care improves outcomes, and the Congo Basin strain is known to be more virulent. Chronic illnesses increase the risk of severe disease, and infants, elderly individuals, and immunocompromised patients face higher mortality risks.
Prevention Strategies: How to Protect Yourself from Mpox
Preventing mpox involves multiple strategies, including vaccination, personal hygiene, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals or animals. Vaccination with the JYNNEOS vaccine is recommended for high-risk individuals. Regular handwashing with soap and water is essential, as is avoiding close contact with infected persons or animals. Healthcare workers should use protective gear when handling suspected cases to reduce the risk of exposure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Monkeypox
1. What are the long-term effects of monkeypox on survivors?
Survivors of monkeypox may experience long-term effects that vary depending on the severity of their illness. While most individuals recover fully, some may develop scarring due to the pustular rash, particularly if lesions were widespread or secondarily infected. Additionally, lingering fatigue and post-viral syndrome have been reported in some cases, making recovery a prolonged process for certain individuals. Neurological complications such as encephalitis can also leave lasting cognitive impairments, though these are rare. Ongoing studies are examining whether mpox has any long-term impacts on immune function, particularly in those with pre-existing conditions.
2. Can monkeypox be transmitted through sexual contact?
While monkeypox is not classified as a sexually transmitted infection, it can be spread through close, prolonged skin-to-skin contact, which includes intimate and sexual encounters. Recent outbreaks have shown a higher prevalence of transmission within sexual networks, particularly among men who have sex with men. The virus can spread through bodily fluids, lesions, and contaminated surfaces, making it possible for intimate interactions to contribute to its transmission. Proper protective measures, including avoiding contact with symptomatic individuals and practicing good hygiene, are essential in reducing the risk. Researchers are further investigating the role of genital secretions in viral spread to determine the exact risk levels associated with sexual activity.
3. How does monkeypox impact pregnant individuals and their babies?
Mpox at birth poses significant risks, as the virus can be transmitted from an infected mother to the fetus through the placenta or during delivery. This can lead to congenital mpox, which has been associated with preterm birth, stillbirth, and severe neonatal complications. Newborns who contract the virus may experience respiratory distress, skin lesions, and systemic infections that require intensive medical care. Due to the potential for severe outcomes, pregnant individuals suspected of having mpox should be closely monitored by healthcare providers. In some cases, antiviral treatments or immune globulin therapy may be recommended to mitigate complications.
4. Does monkeypox go away without medical treatment?
In most cases, monkeypox resolves on its own within two to four weeks without requiring specific antiviral treatment. Supportive care, including pain management, fluid intake, and prevention of secondary infections, plays a crucial role in recovery. However, individuals with weakened immune systems, severe skin involvement, or respiratory complications may require hospitalization and targeted interventions. Antiviral medications such as tecovirimat (TPOXX) are available for high-risk patients, helping to reduce symptom severity and duration. Public health experts continue to monitor whether early antiviral intervention could benefit broader populations during outbreaks.
5. What is the monkey pox death rate, and how does it vary by region?
The monkeypox death rate differs based on viral strain, healthcare access, and individual health factors. Historically, the Central African (Congo Basin) strain has exhibited a mortality rate of up to ten percent, while the West African strain, responsible for the recent global outbreaks, has a lower fatality rate of around one to three percent. Countries with robust healthcare systems and early intervention strategies tend to have lower mortality rates, as supportive care and antiviral treatments improve survival outcomes. The risk of death is highest in children, pregnant individuals, and those with compromised immune systems. Ongoing surveillance helps refine mortality estimates and develop targeted response strategies for different regions.
6. Can monkeypox mutate into a more dangerous strain?
Like other viruses, monkeypox has the potential to mutate over time, but it remains genetically stable compared to rapidly evolving viruses such as influenza or SARS-CoV-2. Scientists have been closely monitoring genetic variations in recent outbreaks to determine whether mutations influence transmission rates or severity. While no significant mutations have drastically increased virulence thus far, the potential for adaptation remains a concern in high-transmission settings. Continued research and genomic sequencing are essential in identifying emerging variants and assessing their impact on public health. Preventative measures, including vaccination and outbreak containment, remain key in reducing the likelihood of viral evolution.
7. How does monkeypox affect the global healthcare system?
The emergence of monkeypox outside its endemic regions has placed additional strain on healthcare systems already managing existing infectious diseases. Hospitals and clinics have had to implement isolation protocols, increase diagnostic testing, and provide antiviral treatments for affected individuals. The financial burden of outbreak response, contact tracing, and vaccine distribution has further highlighted the need for global health preparedness. Additionally, misinformation and stigma associated with mpox have created challenges in public health communication and prevention efforts. Strengthening international collaboration and investment in infectious disease infrastructure is essential for mitigating future outbreaks.
8. Are there long-term immunity benefits after recovering from monkeypox?
Individuals who recover from monkeypox typically develop long-term immunity, reducing the likelihood of reinfection. Studies suggest that this immunity can last for several years, similar to smallpox, which belongs to the same viral family. However, the exact duration of immunity is still under investigation, and factors such as immune suppression or subsequent exposure could influence protection levels. The role of prior smallpox vaccination in boosting immunity against mpox has also been studied, with evidence suggesting some cross-protection. Public health guidelines continue to evolve as researchers gather more data on post-infection immunity and vaccine effectiveness.
9. How does monkeypox compare to other poxviruses in terms of severity and spread?
Monkeypox is often compared to smallpox due to their similarities, but it is generally less severe in terms of symptoms and mortality. Unlike smallpox, which was eradicated through global vaccination efforts, mpox continues to circulate in animal reservoirs, leading to sporadic outbreaks. The transmission dynamics also differ, as monkeypox spreads primarily through close contact, whereas smallpox had a higher rate of airborne transmission. The availability of vaccines and antivirals provides an advantage in controlling mpox outbreaks, but the disease remains a public health concern due to its unpredictable emergence in new regions. Ongoing comparisons with other Orthopoxviruses help researchers refine containment strategies and treatment approaches.
10. What are the biggest challenges in controlling monkeypox outbreaks?
Controlling monkeypox outbreaks presents several challenges, including delayed diagnosis, limited vaccine availability, and public misinformation. Since the disease shares symptoms with other illnesses, misdiagnosis can contribute to unchecked community spread. Vaccine distribution has been uneven, with some regions facing shortages that hinder prevention efforts. Additionally, stigma and misconceptions surrounding mpox have led to reduced reporting and healthcare access among certain populations. Public health authorities emphasize the importance of rapid response strategies, increased education, and enhanced surveillance to overcome these barriers. Addressing these challenges requires a coordinated global effort to ensure timely containment and prevention.

Conclusion
While mpox is generally not fatal for most healthy individuals, it poses significant risks to vulnerable populations. The monkeypox fatality rate depends on various factors, including the viral strain and patient health status. Understanding the symptoms, modes of transmission, and effective prevention methods is essential in mitigating its spread. Ongoing research, improved healthcare interventions, and widespread vaccination efforts remain crucial in controlling the disease. Staying informed and adopting preventive measures can help reduce the impact of mpox outbreaks globally.
monkeypox outbreak response, viral zoonotic diseases, orthopoxvirus infections, smallpox vs monkeypox, monkeypox transmission methods, emerging infectious diseases, viral rash illnesses, global health security, zoonotic disease prevention, monkeypox vaccine efficacy, public health containment strategies, antiviral treatments for viral infections, monkeypox risk factors, epidemiology of monkeypox, viral disease mortality rates, mpox symptoms and treatment, monkeypox and immunocompromised patients, healthcare preparedness for outbreaks, monkeypox in non-endemic regions, impact of monkeypox on global health
Further Reading:
Monkeypox Virus Infection in Humans across 16 Countries — April–June 2022
Mpox (monkeypox): a comprehensive updated of current epidemic evidence
Monkeypox: A Comprehensive Review of Transmission, Pathogenesis, and Manifestation