Description
A harmful immune reaction to gluten, a protein present in barley, wheat, and rye, is the main characteristic of celiac disease, a chronic autoimmune condition. The small intestine’s lining becomes inflamed and damaged as a result of this immune response, which affects how well nutrients are absorbed. While following a gluten-free diet is the mainstay of traditional treatment, new research has revealed a growing interest in alternative treatments that could help with symptom relief, inflammation reduction, and general well-being.
The symptoms of celiac disease are varied, ranging from non-digestive symptoms like lethargy, anemia, and skin rashes to digestive problems like diarrhea, bloating, and stomach pain. Individuals having HLA-DQ2 or HLA-DQ8 genetic variation who are genetically prone to the disease are affected. The immune system attacks the small intestine’s lining in response to consuming gluten, which causes recognizable malabsorption and villous atrophy.
You May Also Like:
Chronic autoimmune urticaria: Description, Causes, and Treatment Protocol
IgA nephropathy / Berger’s disease: Description, Causes, and Treatment Protocol
Celiac disease: Description, Causes, and Treatment Protocol is an original (MedNewsPedia) article.
Possible Causes
The following environmental and genetic variables work together to influence celiac disease, a type of autoimmune disease that affects the small intestine: –
Environmental Trigger: The main environmental trigger is the protein found in barley, wheat, and rye called gluten. Gluten eating causes gut lining damage in those who are genetically predisposed to it.
Genetic Predisposition: A crucial part is played by genetic susceptibility. The risk of acquiring celiac disease is increased by HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8 genetic variations. These genes are essential for the immune system’s ability to recognize gluten peptides.
Early Life Factors: It is being examined when gluten should be introduced to infants. The development of immunological tolerance and the risk of disease may be impacted by the introduction of gluten either too soon or too late.
Breastfeeding: The benefits of breastfeeding are up for discussion. Although it might be protective due to immune components in breast milk, more research is needed to determine exactly how it affects the risk of celiac disease.
Gut Microbiome: The makeup of the gut flora may play a role. Microbiome imbalances may interfere with immune control and perhaps trigger or worsen celiac disease.
Viral Infections: Investigations into probable triggers include certain viral infections, specifically those that occur early in life. The immune system’s reaction to gluten may be impacted by infections.
Epigenetic Changes: Gene expression can be affected by epigenetic changes without changing DNA sequences. These alterations may have an impact on the onset of celiac disease due to environmental influences.
Stress and Trauma: Trauma or psychological stress may influence how a disease develops or worsen its symptoms. Genetic predisposition may interact with stress’s impact on the body’s immune system.
Autoimmune Connections: The autoimmune diseases thyroid issues and type 1 diabetes frequently coexist with celiac disease. It is possible that they are related genetically and immunologically.

Exacerbating and Mitigating Factors
The following factors, which can either increase or reduce the symptoms and course of celiac disease, can have an impact on it: –
The exacerbating factors include: –
Gluten Consumption: Consuming gluten-containing foods constitutes the main cause of celiac disease symptoms. Gluten can trigger an immunological response and harm the gut lining even in modest doses. Unrestricted use of gluten is a significant aggravating factor.
Hidden Gluten: Processed meals, seasonings, sauces, and certain non-food items like pharmaceuticals and cosmetics can contain gluten. Gluten can aggravate symptoms and impede the healing process if it is accidentally consumed.
Cross-Contamination: Whenever gluten-free foods or surfaces get into contact with foods or materials containing gluten, cross-contamination occurs. This can occur when preparing or cooking food, and it presents a risk to those who have celiac disease because even minute amounts of gluten may cause an adverse reaction.
Medications: As binders or fillers, gluten may be present in some pharmaceuticals and dietary supplements. While using prescription or over-the-counter medications, individuals with celiac disease must use caution and speak with a doctor to make sure they are gluten-free.
Undiagnosed Conditions: The symptoms of celiac disease can be made worse by underlying problems like type 1 diabetes, thyroid issues, and other autoimmune disorders.
Stress: The intensity of symptoms of celiac disease might be influenced by stress and psychological variables. Stress may aggravate gut inflammation and impair gut health, potentially worsening symptoms.

The mitigating factors include: –
Strict Maintenance of Gluten-Free Diet: The best strategy to lessen celiac disease symptoms is to rigorously follow a gluten-free diet. Eliminating cross-contamination hazards and gluten-containing foods greatly decreases inflammation and promotes intestinal healing.
Nutritional Support: The management of celiac disease depends on proper diet. Malabsorption-related deficits can be addressed with a nutritious, well-balanced diet. Supplementing with nutrients, as advised by medical experts, can help promote general health.
Consultation with Medical Professionals: It is crucial to schedule routine follow-up visits to gastroenterologists, and other medical professionals. These experts can keep an eye on the disease’s progression, correct issues, and modify treatment regimens as necessary.
Label Reading and Education: Understanding the potential origins of hidden gluten and becoming knowledgeable about ingredients that contain gluten may help reduce unintentional gluten intake.
Supportive Lifestyle: A healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, enough sleep, and managing stress can improve general well-being. Practices that reduce stress, like mindfulness and meditation, might decrease symptoms.
Patient Advocacy: At social and dining occasions, it is crucial to speak up for oneself. To help prevent unintentional gluten exposure, let relatives, acquaintances, and restaurant employees know what one needs to eat.
Seeking Expert Advice: People should speak with medical specialists before making any adjustments to their treatment programs when exploring adjunct therapy or natural cures. These treatments should not be used in place of a gluten-free diet.

Standard Treatment Protocol
The primary focus of the typical celiac disease treatment plan is the full eradication of gluten-containing items from the diet. The normal treatment method typically consists of the following components: –
Gluten-Free Diet: Complete compliance with a diet free from gluten constitutes the basis of celiac disease treatment. This entails eliminating all sources of rye, barley, and wheat along with any products made from those grains. Bread, cereals, pasta, baked products, and even processed foods and sauces can all contain gluten.
Dietary Education: The identification of foods that contain gluten and effective label reading is taught to patients. Dietitians or nutritionists frequently aid people in making dietary adjustments and in creating nutrient-dense, well-balanced meals.
Observation and Follow-Up: It is critical to schedule routine follow-up visits with medical specialists like gastroenterologists and nutritionists to assess development and resolve any issues. To evaluate the efficacy of a diet free of gluten, blood tests are frequently conducted to evaluate nutritional status and antibodies associated with celiac disease.
Nutrient Supplementation: Individuals experiencing celiac disease may need supplements to correct vitamin deficiencies because malabsorption is a result of intestinal lining damage. Supplements with calcium, iron, folic acid, vitamin D, and vitamin B12 are typical. On the basis of patient requirements and the results of tests, these supplements are prescribed.
Lifestyle Modifications: A healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, enough sleep, and reducing stress can improve general well-being and aid the body’s recovery procedures.
Treatment Options
Although avoiding gluten is still the best way to treat celiac disease, several complementary therapies, such as herbal supplements and homeopathic medicines, have also been studied for their capacity to reduce symptoms and speed up the recovery process. Following are a few other therapies: –
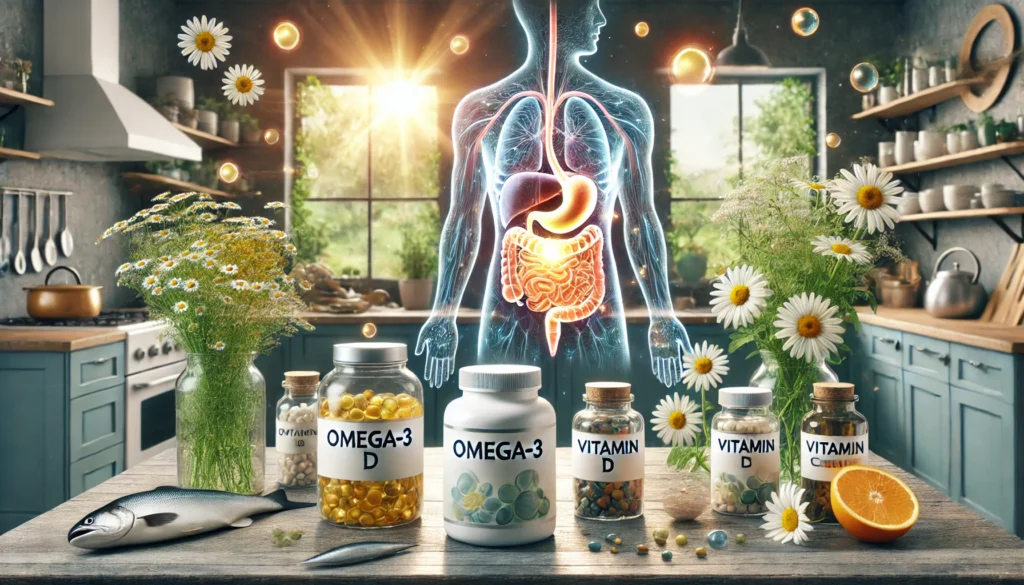
Nutritional Supplements: These consist of the following: –
Curcumin
An ingredient in turmeric called curcumin has both antioxidant and anti-inflammatory qualities. It may help relieve symptoms related to celiac disease and has demonstrated the potential in minimizing intestinal inflammation.

Probiotics
Live, helpful bacteria are known as probiotics, and they can help the gut stay healthy. According to some research, particular probiotic strains, including those from the Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus species, may help regulate the gut microbiota and lessen intestinal inflammation.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Fish oil has anti-inflammatory properties due to the omega-3 fatty acids it contains. Supplemental fish oil, according to some research, may help celiac disease sufferers lessen intestinal inflammation. Walnuts, flaxseeds, and fatty fish are some foods that are good omega-3 fatty acids sources.
Herbal Remedies: These include the following: –
Marshmallow Root
Mucilage, which is present in marshmallow root and which soothes and reduces irritation of the intestinal lining, is a substance. For people with celiac disease, it might provide relief from gastrointestinal pain.
Aloe Vera
Anti-inflammatory substances are found in aloe vera. It has been investigated as a potential treatment for easing gastrointestinal problems brought on by celiac disease.
Chamomile
The relaxing properties of chamomile are well recognized, and it may also ease intestinal problems. It might aid in reducing digestive system discomfort and inflammation.
However, before adopting these supplemental therapies into a treatment plan, it’s crucial to exercise caution and seek the advice of medical professionals. Instead of replacing a gluten-free diet, these treatments ought to supplement it. Furthermore, each person’s response to these therapies may differ, making it crucial to closely monitor each patient and maintain constant communication with their healthcare specialists.
Conclusion
Celiac disease is a complex autoimmune disorder requiring a lifelong commitment to a gluten-free diet as its primary treatment. Proper management involves addressing exacerbating factors such as hidden gluten, stress, and cross-contamination while implementing mitigating strategies like dietary education, regular medical follow-ups, and nutritional supplementation to counteract malabsorption-related deficiencies.
Complementary therapies, including probiotics, omega-3 fatty acids, and herbal remedies, may offer additional relief, but they should only be used as supplements to a strict gluten-free diet. Collaborating with healthcare professionals is essential to tailor treatment plans, monitor progress, and avoid potential triggers.
Through comprehensive management strategies, individuals with celiac disease can achieve improved intestinal healing, reduced symptoms, and an enhanced quality of life. As ongoing research continues to uncover potential adjunct therapies, there is growing hope for even more effective solutions to support long-term health and well-being for those affected by this condition.

Additional resources for further reference
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5437500
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/20587384211008709
https://www.jacionline.org/article/S0091-6749(15)00230-4/fulltext
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14240-celiac-disease
Important Note: The information contained in this article is for general informational purposes only, and should not be construed as health or medical advice, nor is it intended to diagnose, prevent, treat, or cure any disease or health condition. Before embarking on any diet, fitness regimen, or program of nutritional supplementation, it is advisable to consult your healthcare professional in order to determine its safety and probable efficacy in terms of your individual state of health.
Regarding Nutritional Supplements Or Other Non-Prescription Health Products: If any nutritional supplements or other non-prescription health products are mentioned in the foregoing article, any claims or statements made about them have not been evaluated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, and such nutritional supplements or other health products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.