Description
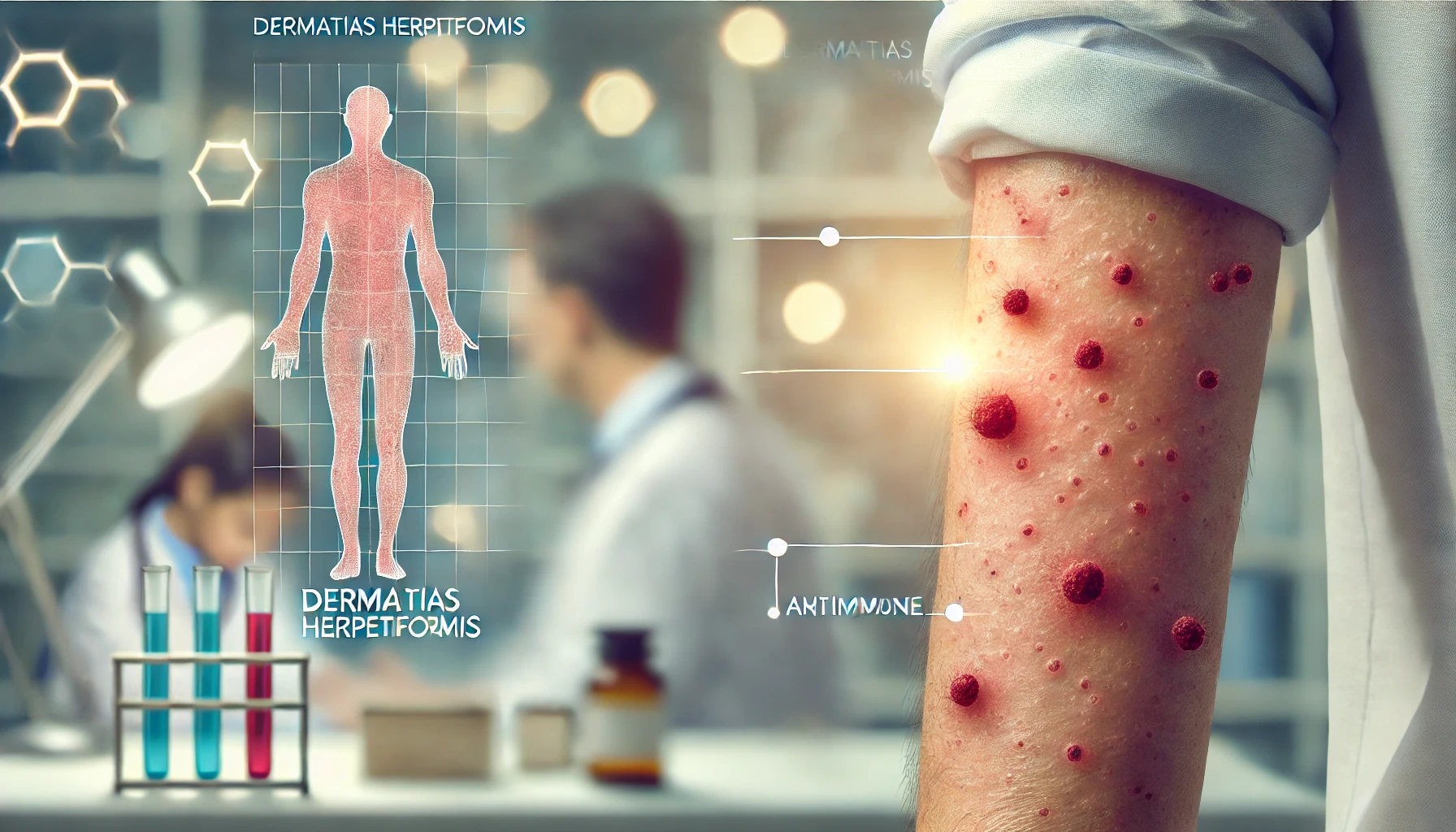
Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH), commonly known as Duhring’s disease, constitutes a chronic inflammatory skin illness that is named for the appearance of very irritating papules and vesicles that frequently develop in clusters or herpetiform patterns. Although they can occur in other parts of the body, these lesions often affect the scalp, buttocks, lower back, elbows, and knees. Highly symmetrical DH lesions may heal with hyper- or hypopigmented markings. Although uncommon, this disorder is closely linked to celiac disease, which is a gluten-sensitive enteropathy. It is commonly known that DH and celiac disorder are related and that they both follow the same immunological mechanism.
However, DH poses particular difficulties for diagnosis and treatment. The chronic nature of DH is characterized by recurring flares of skin lesions in affected individuals. The crippling itching can cause sleep disruptions and a decreased quality of life. Although DH lesions might seem different depending on the individual, they frequently look like a herpes simplex infection, which can sometimes result in a misdiagnosis.
You May Also Like:
Hypogammaglobulinemia: Description, Causes, and Treatment Protocol
Chronic autoimmune urticaria: Description, Causes, and Treatment Protocol
Dermatitis herpetiformis: Description, Causes, and Treatment Protocol is an original (MedNewsPedia) article.
Possible Causes
Having a significant genetic component, dermatitis herpetiformis represents an autoimmune condition. It shares a tight relationship with celiac disease, an autoimmune enteropathy brought on by gluten use. The formation of autoantibodies, particularly IgA antibodies, against the enzyme tissue transglutaminase (tTG), which participates in gluten processing, is a usual immunological mechanism between DH and celiac disease. The following are believed to be the steps in the etiology of DH: –
Gluten exposure: Susceptible people develop anti-tTG IgA antibodies after consuming gluten-containing meals, which stimulates an immunological response.
Genetic predisposition: Given that both celiac disease and DH are linked to particular HLA-DQ8 or HLA-DQ2 gene variations, people with these genes are at an increased risk of acquiring DH.
Cutaneous deposition: The papillary dermis, in particular, is where these antibodies deposit after traveling via the bloodstream.
Itching and blistering: Itching and blistering are caused by inflammation and the development of papules and vesicles.
Inflammation and blister development: Skin IgA antibodies trigger an inflammatory reaction, which results in the recognizable skin lesions observed in DH.

Exacerbating and Mitigating Factors
Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) management involves both aggravating and moderating elements in a substantial way. Specifically, a few typical DH aggravating and reducing factors are covered: –
Following are some of the DH aggravating factors: –
Stress: DH symptoms may get worse under psychological stress. Itching and skin lesions may get worse as a result of stress-related hormone releases that affect the immune system.
Gluten Exposure: Consuming gluten-containing foods is the biggest aggravating factor for DH. Gluten can cause an immunological reaction that results in skin breakouts and itching, even at low levels.
Medications: Some medications may make DH worse or cause flare-ups. These involve nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) and medications that contain iodine. Patients with DH must inform their medical professionals about their illness in order to avoid taking these drugs or acquire appropriate substitutes.
Skin Trauma: Scratching, rubbing, or other physical harm to the skin might make DH lesions worse. To stop further aggravation, patients must refrain from scratching and maintain cold, dry skin.
Hormonal Changes: The progression of DH may be influenced by hormonal changes, such as those that take place during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause. During these circumstances, some people could experience more intense or frequent outbreaks.

The DH mitigating factors consist of the following: –
Stress Management: Participating in stress-reduction exercises, yoga, meditation, or counseling may reduce the negative effects of stress on DH conditions. Stress management can result in fewer flare-ups and milder symptoms.
Gluten-Free Diet: It is best to rigorously follow a gluten-free diet in order to lessen DH symptoms. People with DH can drastically lower their autoimmune response and skin eruption frequency by cutting out gluten-containing items from their diet.
Dapsone and Medications: The main drug recommended for DH, dapsone, can quickly relieve itching and lessen skin lesions. Dapsone may serve as a useful treatment for DH symptoms when used as prescribed by a medical professional.
Skin Care: In places where DH lesions have developed, proper skin care practices, including as gentle washing and moisturizing, can lessen the risk of infection and prevent skin harm.
Topical Treatments: To treat irritation and inflammation in particular skin regions, use topical corticosteroids or dapsone. The discomfort connected with DH may be lessened and relieved by using these therapies.
Avoidance of Trigger Medications: It is possible to prevent potential triggers by being aware of drugs that may worsen DH and informing healthcare providers of this information. When necessary, healthcare professionals can then recommend other medicines.
Regular Follow-Up: Monitoring DH and modifying treatment as necessary depend on routine check-ups with a medical professional. This proactive strategy can assist in identifying aggravating causes and swiftly addressing them.
Dietary Supplements: Dietary supplements, like probiotics or vitamin D, might prove helpful for some people with DH to promote overall health and immunological function. Supplementation, however, needs to be reviewed with a medical professional.
Hormone Management: In collaboration with a healthcare professional, those who experience hormonal changes that exacerbate the symptoms of DH may want to pursue hormone management techniques including birth control.

Standard Treatment Protocol
The main objectives of DH treatment are symptom relief, healing promotion, and outbreak prevention. A stringent gluten-free diet, which tries to lessen the autoimmune reaction and skin lesions, is the foundation of DH care. Standard DH treatment regimens consist of: –
Gluten-free diet: The best treatment for DH is a rigorous, lifelong gluten-free diet. Patients should refrain from eating any goods that contain wheat, barley, or rye. Reading food labels carefully and receiving instructions about healthy eating options are crucial.
Dapsone: The most frequently prescribed cure for DH is the oral drug dapsone. It reduces inflammation and the immunological response. With dapsone medication, patients frequently enjoy short-term itching alleviation and a decrease in skin lesions. Patients must still follow a gluten-free diet because it is not a cure. During dapsone therapy, it is critical to watch for potential adverse effects including liver toxicity and hemolytic anemia.
Topical treatments: To treat irritation and inflammation in particular skin regions, patients may use topical corticosteroids or dapsone. Particularly for isolated lesions, these can be helpful.
Sulfapyridine: When dapsone is either poorly tolerated or not recommended, sulfapyridine is a further oral treatment option for DH. It can help reduce symptoms like dapsone does, but adverse effects must be monitored closely.
Immune modulators: When DH is severe or unresponsive, immune-modulating medications like methotrexate or azathioprine can be considered. The potential side effects of these drugs necessitate careful observation.
Maintenance therapy: In order to prevent symptom recurrence, long-term therapy may include taking a number of drugs and following a gluten-free diet.
Nevertheless, working together with a healthcare practitioner to create a unique treatment plan and keep an eye out for pharmaceutical side effects, is essential for people with DH.

Treatment Options
People with DH may look at adjunct treatments and alternative approaches together with the usual treatment protocol to round out their management strategy. Following are some alternatives for complementary therapies: –
Nutritional Supplements: These consist of the following: –
Probiotics
Probiotic supplements can promote intestinal flora balance and gut health. A healthy gut microbiota may indirectly promote general immune function, despite the paucity of data on their specific significance in DH.
Vitamin D
Immune performance and skin health are influenced by vitamin D. Supplemental vitamin D may be helpful for some people with DH, but dosage needs to be controlled to prevent overdosing.
Fish Oil Supplements
Fish oil supplements contain omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory effects and may help lessen inflammation related to DH. However, there isn’t much information on how they affect DH symptoms.
Enhance your skin’s resilience and reduce flare-ups with Omega-3—Feel the Difference, Shop Now!

Homeopathy: Several individuals research homeopathic treatments for DH, including Rhus toxicodendron and Sulfur. More research is necessary as the effectiveness of homeopathic remedies is still under discussion.
Herbal Remedies: Some herbal medicines, like chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla) and calendula (Calendula officinalis), can possess anti-inflammatory and soothing effects on the skin when applied topically. Their effectiveness in managing DH is not, however, extensively documented.
Aloe Vera Gel: In addition to soothing sensitive skin, aloe vera gel may offer momentary relief from itching. Areas that are affected can receive a topically administered dose.
Acupuncture: Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine, may aid people with DH by minimizing aggravating variables by managing stress and fostering overall wellness.
Stress Management Techniques: By reducing psychological triggers, approaches for stress reduction like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can be able to help control DH symptoms.
However, before adopting adjunct therapies into their treatment strategy, people with DH must speak with a healthcare physician. While in some circumstances these treatments may provide comfort or assistance, they cannot take the place of a diet free of gluten and standard medical care. Healthcare monitoring assures safety and effectiveness in their application because the efficacy of these adjunct treatments can vary greatly among individuals.
Conclusion
Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) is a complex, chronic condition closely linked to celiac disease and characterized by intensely itchy, herpetiform skin lesions. Its successful management requires a combination of strict adherence to a gluten-free diet, medication like dapsone for symptom relief, and addressing exacerbating factors such as stress and hormonal changes. Adjunct therapies, including topical treatments, stress reduction techniques, and nutritional supplements, may provide additional support but should always be used in conjunction with standard medical care and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
By understanding the underlying causes and triggers, individuals with DH can work towards effective control of symptoms and a better quality of life. Ongoing research continues to offer hope for improved treatment strategies and adjunct options to enhance disease management for those affected by this autoimmune condition.

Additional resources for further reference
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0738081X11000861
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.2147/CCID.S69127
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03188.x
Important Note: The information contained in this article is for general informational purposes only, and should not be construed as health or medical advice, nor is it intended to diagnose, prevent, treat, or cure any disease or health condition. Before embarking on any diet, fitness regimen, or program of nutritional supplementation, it is advisable to consult your healthcare professional in order to determine its safety and probable efficacy in terms of your individual state of health.
Regarding Nutritional Supplements Or Other Non-Prescription Health Products: If any nutritional supplements or other non-prescription health products are mentioned in the foregoing article, any claims or statements made about them have not been evaluated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, and such nutritional supplements or other health products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.