Description
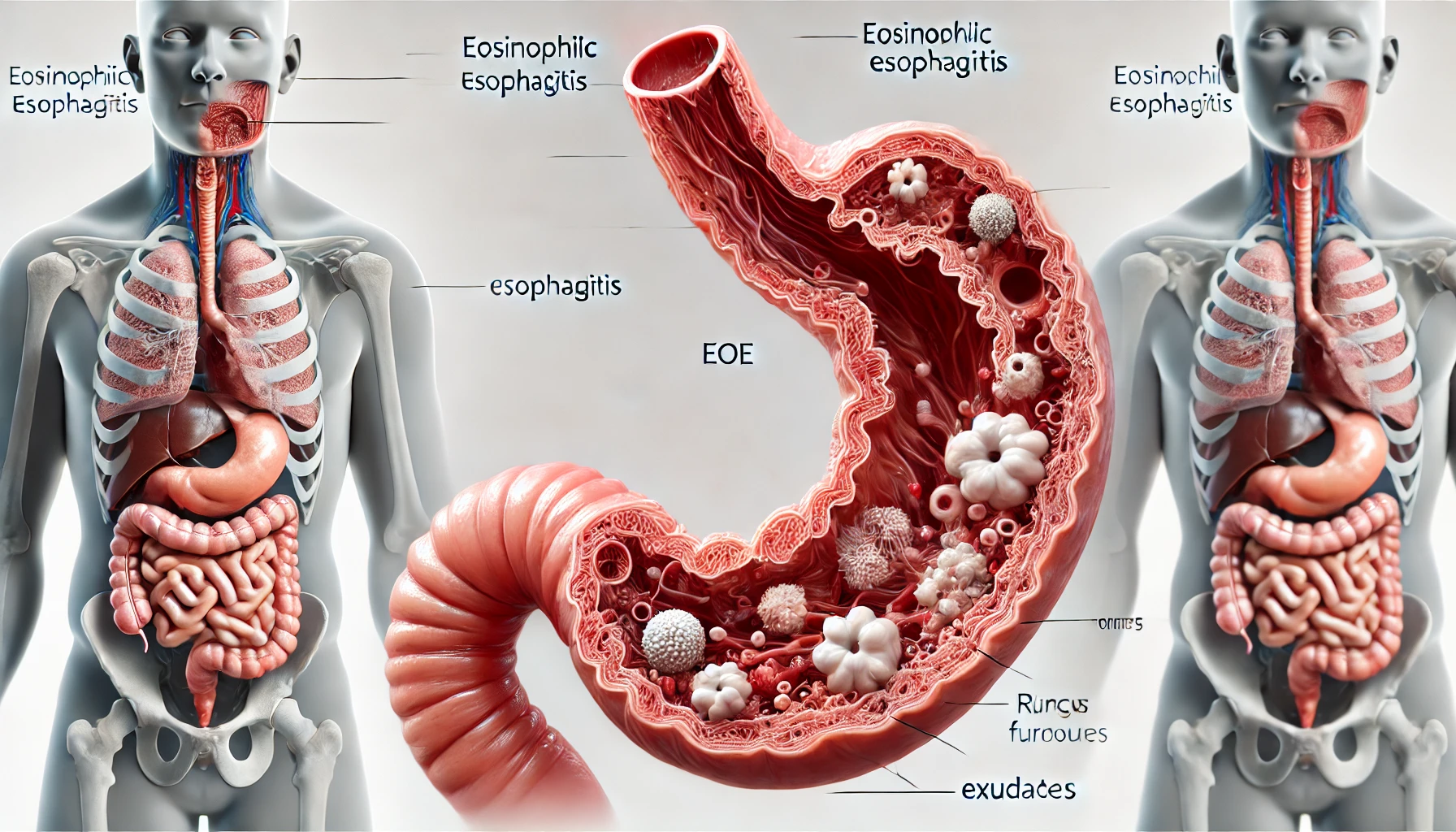
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) represents a complex, long-term inflammatory condition that affects the esophagus. Eosinophil infiltration into the esophagus tissue is one of its defining characteristics. The prevalence of EoE has started progressively rising recently, despite the fact that it was originally thought to be unusual. Eosinophilic esophagitis is largely characterized by esophageal inflammation brought on by an aberrant eosinophil buildup. White blood cells known as eosinophils have a role in the body’s immune response, particularly in the control of allergic reactions and the defense against parasitic diseases.
In the case of EoE, the buildup of eosinophils in the esophagus causes inflammation, which can have a variety of side effects. Although it can affect people of various ages, EoE is typically a childhood illness. The disorder frequently exhibits symptoms that are like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), such as heartburn, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing. Complications include esophageal strictures, food obstruction, and a lower quality of life.
You May Also Like:
Eosinophilic esophagitis: Description, Causes, and Treatment Protocol is an original (MedNewsPedia) article.
Possible Causes
EoE is believed to be a multifactorial illness impacted by an interplay of immunological, genetic, and environmental factors, while its specific causes are still not fully known. A few of the hypothesized causes and drivers for EoE include:
Immune System Dysregulation: The etiology of EoE is primarily characterized by abnormal immunological reactions and esophageal inflammation. Eosinophils are one type of immune cell that contributes to tissue damage and swelling.
Genetic Predisposition: EoE tends to occur in families, which has led studies to hypothesize a genetic component. A condition’s sensitivity to certain gene variants may rise.
Allergies and Atopy: EoE is frequently linked to allergy diseases including atopic dermatitis and asthma. Inflammatory reactions in the esophagus might be triggered by allergens and environment-related factors.
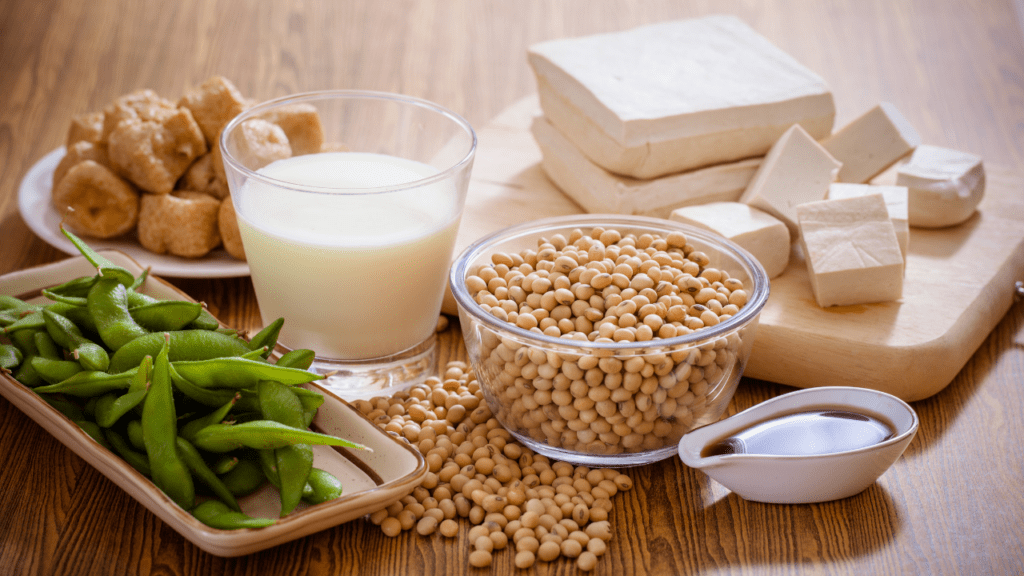
Dietary Allergens: Foods have been recognized as significant EoE triggers, including well-known allergies such as soy, cow’s milk, wheat, and eggs. Elimination diets are frequently used to both diagnose and treat the problem.
Gastroesophageal Reflux: Although EoE is different from GERD, the illness can be made worse by stomach acid reflux into the esophagus. Some people who suffer from EoE might also have GERD.

Exacerbating and Mitigating Factors
A variety of aggravating and moderating variables might contribute to eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), a chronic inflammatory illness of the esophagus. The main aggravating and alleviating factors related to EoE are discussed below:
Exacerbating factors include:
GERD: GERD and EoE are two different conditions, GERD can exacerbate EoE symptoms. The previously inflamed esophageal lining can become more irritated by stomach acid reflux into the esophagus.
Stress: Anxiety and stress are two psychological factors that might make EoE symptoms worse. Chest pain, swallowing difficulties, and esophageal muscular contractions may be caused by these emotional states.
Food Allergens: EoE frequently develops after exposure to allergic foods. In those who are sensitive, common dietary allergies like soy, wheat, cow’s milk, and eggs might increase symptoms.
Environmental Allergens: Environmental allergies in certain people with EoE, such as those to dust mites, pollen, or animal dander, might make their symptoms worse.
Tobacco Smoke: The esophageal disorders EoE and smoking are known to exacerbate. Inflammation can grow and symptoms can become more severe when one is exposed to tobacco smoke, whether actively smoking or passively.
Inadequate Treatment: The symptoms of EoE may worsen if prescribed treatment plans are not followed or if the patient does not receive the necessary medical attention. Inadequate management can cause consequences and persistent inflammation.
Mitigating factors include:
Dietary Modification: With a restrictive diet or the administration of hypoallergenic formulations, specific trigger foods can be identified and eliminated, greatly reducing symptoms. This strategy seeks to lessen eosinophil infiltration and allergen exposure.
Lifestyle Modifications: Changes in lifestyle can help with EoE symptoms. Exacerbation risk can be decreased by elevating the head of your bed while you eliminate late-night meals, sleep, and chewing your food carefully.
Allergen Immunotherapy: Allergen immunotherapy, including allergy injections, may be taken into consideration in specific circumstances. This strategy seeks to lessen people’s general allergic response and desensitize them to particular allergens, which may lessen EoE symptoms.
Medication: Topical corticosteroids and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are two typical prescription drugs used to reduce inflammation and treat the symptoms of EoE. These drugs can be useful in reducing the condition when administered and monitored carefully.
Patient Education and Commitment: Patients must be informed about their disease and available treatments. Patients can lessen symptoms and avoid problems by being encouraged to follow their recommended treatment schedule and follow-up sessions.
Adjunct Therapies: Numerous complementary therapies, including as herbal medicines, dietary supplements, and natural cures, may lessen the symptoms of EoE or boost the efficiency of conventional therapies. With a medical professional, these treatments should be discussed.
Standard Treatment Protocol
EoE is frequently treated with a combination of medication, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle improvements. The recommended treatment regimen may change depending on the needs of each individual patient, the intensity of their symptoms, and other factors. Standard treatment methods frequently incorporate the following components:
Dietary Modification: These include:
Elemental Diet
An elemental diet can be utilized when it is difficult to pinpoint specific food triggers. This entails ingesting a nutritionally full liquid formula that comprises simplified amino acids, which are significantly less likely to elicit an immunological reaction.
Elimination Diet
A key component of controlling EoE is identifying and avoiding particular trigger foods. This could entail removing common food allergies like cow’s milk, wheat, soy, and eggs through allergen-specific elimination dietary regimens.
Hypoallergenic Formulas
There is a reduced chance of inducing EoE symptoms when using specific hypoallergenic formulas to complement or replace some meals.
Medications: These are:
Topical Steroids
To treat eosinophilic esophageal inflammation, oral suspensions of inhaled corticosteroids, like budesonide or fluticasone, are used. These have been demonstrated to lower eosinophil counts and ameliorate symptoms, making them first-line therapies.
Hydrate and support your esophagus with Aloe Vera—Restore Balance, Order Aloe Vera Now on Amazon!

Systemic Corticosteroids
Systemic corticosteroids might be recommended for a brief time in severe situations, although they are normally avoided due to possible side effects.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
PPIs are frequently recommended to decrease the production of stomach acid. Even though they might not address eosinophilic inflammation, they may assist with GERD symptoms that might also worsen EoE.
Leukotriene Modifiers
A potential substitute for corticosteroids is montelukast, a leukotriene receptor inhibitor.
Lifestyle Changes: These involve:
Chewing Food Thoroughly
Consuming food slowly and completely helps improve digestion and lessen esophageal irritability.
Avoiding Late-Night Meals
Eating dinner closer to bedtime may cause reflux and symptoms worsening happen more frequently.
Raising the Bed’s Head
Reflux during the night might be lessened by lifting the top of the bed.
Endoscopic Dilation: Endoscopic dilatation could be required when esophageal strictures or extreme esophageal constrictions have occurred. The esophagus is stretched during this surgery to facilitate swallowing.
Ongoing Monitoring: Healthcare professionals must continue to monitor patients with EoE and modify their treatment approaches as necessary. This might involve routine clinical examinations, symptom evaluations, and endoscopic inspections.
Follow-up Endoscopies: To track disease development and therapy effectiveness, routine endoscopies are advised. These techniques aid in determining the degree of eosinophilic infiltration and potential structural alterations to the esophagus.

Treatment Options
A healthcare physician may recommend several adjunct remedies and treatment choices alongside the conventional therapy schedule. These complementary therapies are intended to increase treatment effectiveness and enhance symptom management. These are as follows:
Prescription Medications: Medicines like 6-mercaptopurine or azathioprine can be considered when traditional therapies are unsuccessful, but only in the most severe and refractory instances.
Over-the-Counter Formulations: These encompass over-the-counter (OTC) antacids and PPIs. PPIs and over-the-counter antacids can temporarily relieve the symptoms of acid reflux and heartburn. Despite not addressing the underlying swelling, they might provide symptomatic relief.
Nutritional Supplements: These involve:
Amino Acid-Based Formulas
Nutritional supplements based on amino acids can offer comprehensive nutrition while removing common food allergies. When dietary elimination becomes necessary, they are frequently utilized.
Probiotics
Supplemental probiotics may improve gut health and may be beneficial for inflammation and immune system health.
Herbal and Natural Remedies: These contain:
Aloe Vera
Supplements or gels containing aloe vera may reduce esophageal irritation and speed up recovery.
Quercetin
This flavonoid, which can be found in some foods and supplements and may help reduce eosinophilic inflammation, contains antioxidant and anti-inflammatory characteristics.

Deglycyrrhizinated Licorice (DGL)
DGL medications contain anti-inflammatory qualities and can calm the esophagus. They are frequently utilized to relieve heartburn.
Slippery Elm
Supplements containing slippery elm may offer the esophageal lining a layer of protection, easing discomfort and symptoms.
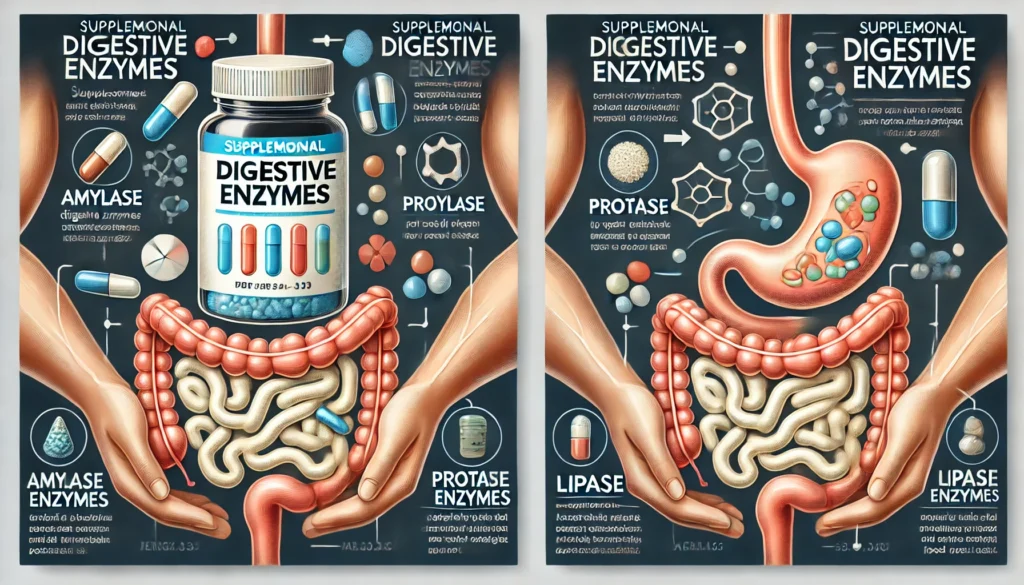
Digestive Enzymes
Supplemental digestive enzymes may help break down food, possibly decreasing the strain on the esophagus throughout digestion.
However, it is crucial to stress that people with EoE should speak with a healthcare professional before adopting any adjunct therapy or making any dietary modifications. Each patient’s requirements, triggers, and level of symptom intensity should be taken into account while creating a treatment plan. The objective is to successfully control EoE, lower inflammation, and enhance the patient’s standard of living while reducing the risk of consequences.
Conclusion
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a multifaceted condition that demands a personalized and comprehensive treatment approach to manage symptoms effectively and enhance patients’ quality of life. By addressing dietary triggers, employing targeted medications such as topical corticosteroids and proton pump inhibitors, and incorporating lifestyle adjustments, individuals with EoE can achieve significant symptom relief and reduce the risk of complications like esophageal strictures. Adjunct therapies, including herbal remedies and nutritional supplements, may further support symptom management when used under medical guidance. As ongoing monitoring and follow-up are vital to adapt treatment strategies to each patient’s unique needs, collaboration with healthcare providers remains essential in achieving long-term control of EoE.
Additional resources for further reference
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459297
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0016508517359528
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41390-020-0770-4
https://aacijournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13223-018-0287-0
Important Note: The information contained in this article is for general informational purposes only, and should not be construed as health or medical advice, nor is it intended to diagnose, prevent, treat, or cure any disease or health condition. Before embarking on any diet, fitness regimen, or program of nutritional supplementation, it is advisable to consult your healthcare professional in order to determine its safety and probable efficacy in terms of your individual state of health.
Regarding Nutritional Supplements Or Other Non-Prescription Health Products: If any nutritional supplements or other non-prescription health products are mentioned in the foregoing article, any claims or statements made about them have not been evaluated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, and such nutritional supplements or other health products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.