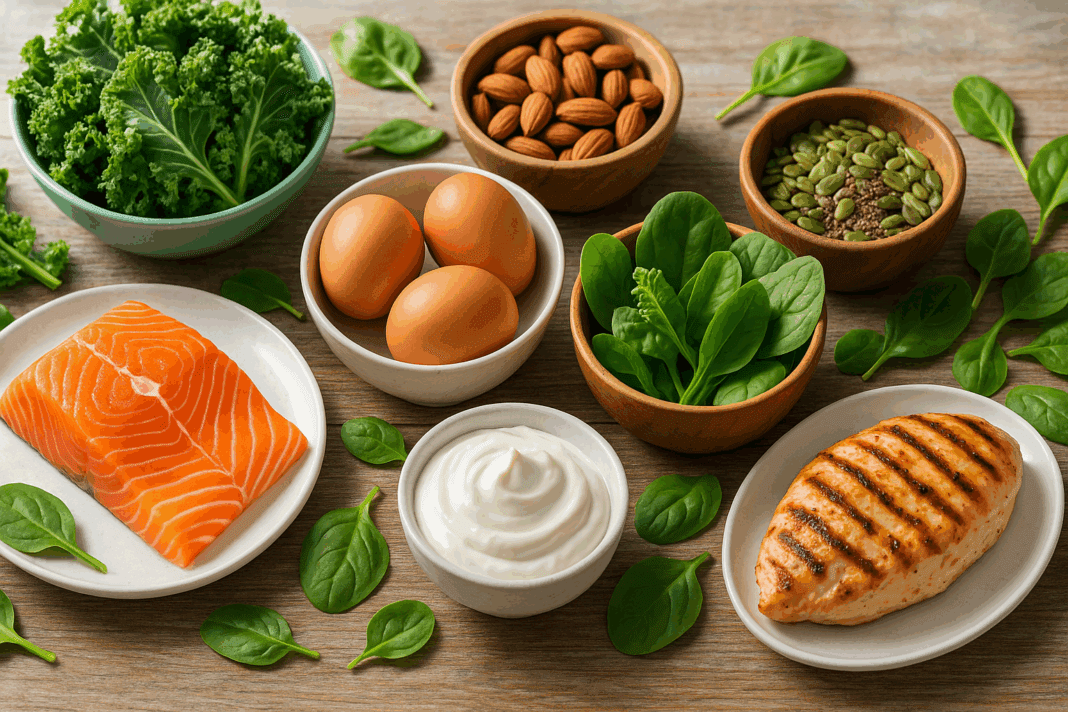
In a world increasingly focused on sustainable health and long-term wellness, the high protein low carb diet has emerged as one of the most trusted and expert-backed approaches for managing energy levels, supporting weight loss, and enhancing metabolic health. More than a trend, this dietary strategy is rooted in physiological principles that favor balanced blood sugar, improved satiety, and lean muscle preservation. While not one-size-fits-all, the strategic reduction of carbohydrate intake in favor of protein-rich alternatives has become a cornerstone for many nutritional frameworks, including the high protein keto diet, the high protein low fat low carb diet, and broader interpretations of the low carb high protein lifestyle.
You may also like: Is the Keto Diet Safe or Dangerous? What Experts Say About the Risks, Benefits, and Basics of the Ketogenic Diet
Understanding the Science Behind a High Protein Low Carbohydrate Diet
The human body’s relationship with macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—is both intricate and adaptable. Carbohydrates are typically the body’s primary energy source, but when limited, the body shifts to metabolize fat for fuel. This metabolic adaptation, known as ketosis, is central to the high protein keto diet. However, when protein intake is increased alongside a reduction in carbohydrates, the body gains several unique advantages. Protein is not only essential for muscle maintenance and repair but also requires more energy to digest, leading to a natural thermogenic effect that boosts metabolic rate.
Moreover, high protein low carb diet foods have been shown to reduce the hormone ghrelin, often dubbed the “hunger hormone,” while enhancing satiety through increased levels of peptide YY and GLP-1. This combination allows individuals to feel full longer, making it easier to adhere to a calorie-controlled eating plan without experiencing the intense cravings that often accompany traditional low-fat diets. The high protein low carbohydrate diet is thus scientifically supported not only for weight management but also for improving metabolic flexibility, insulin sensitivity, and overall energy balance.
Why Experts Endorse Less Carbs and More Protein
Nutritionists and metabolic health researchers continue to highlight the benefits of a less carbs more protein diet due to its versatility and effectiveness. Unlike overly restrictive approaches that eliminate entire food groups, a well-formulated low carb high protein plan emphasizes nutrient-dense choices, encouraging whole foods over processed options. This creates a sustainable eating pattern that minimizes blood sugar spikes and reduces the risk of insulin resistance, a key contributor to metabolic syndrome.
Expert panels from institutions like Harvard Medical School and the American Society for Nutrition point to growing evidence that supports using a high protein low carb diet as a tool for improving lipid profiles, reducing abdominal fat, and managing appetite control. The high protein low fat low carb approach is particularly favored among individuals aiming for weight loss while preserving lean muscle mass—especially important during caloric deficits. Athletes, fitness professionals, and those recovering from metabolic health issues are increasingly incorporating high protein no carb diet strategies during targeted phases of training or recovery.
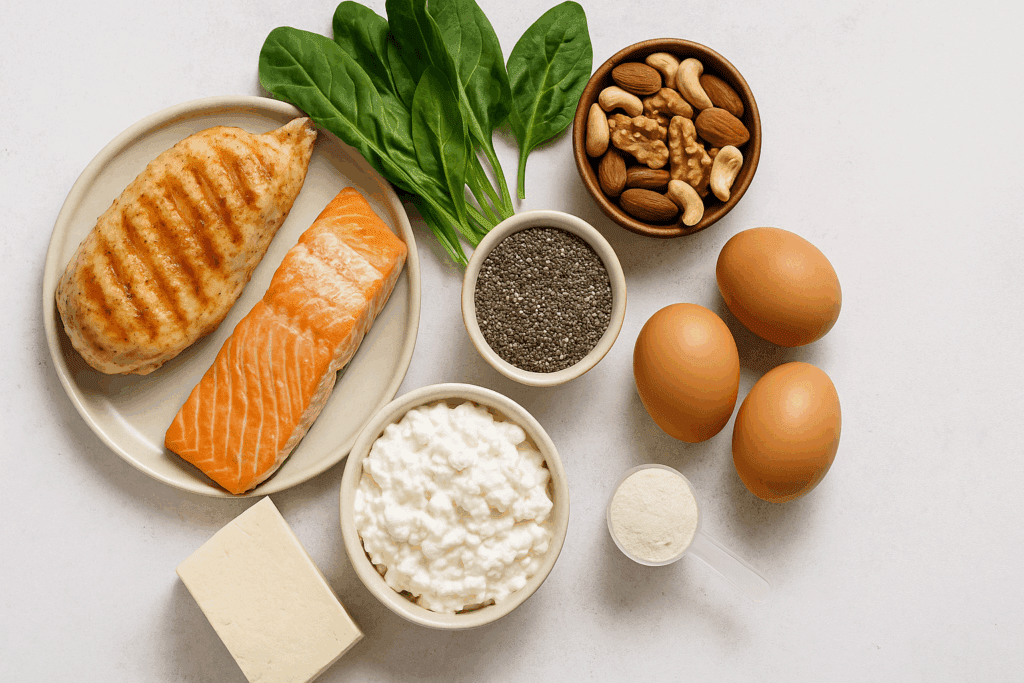

Key High Protein Low Carb Diet Foods to Include
Choosing the right foods within a high protein low carbohydrate diet is essential for maximizing benefits and maintaining nutritional balance. Lean animal proteins such as chicken breast, turkey, eggs, and fatty fish like salmon and mackerel offer high biological value, meaning the protein is efficiently absorbed and utilized by the body. Seafood, in particular, contributes omega-3 fatty acids that are anti-inflammatory and heart-protective, making them staples in both high protein low carb diet foods and general wellness nutrition.
For vegetarians or those seeking variety, plant-based proteins like tofu, tempeh, edamame, and seitan provide excellent low carb protein sources when paired with non-starchy vegetables. Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, and certain protein-enriched dairy options also fit well into a high protein low carbohydrate plan. The goal is to prioritize foods that deliver protein with minimal carbohydrates and added sugars, allowing the body to remain in a fat-burning state while nourishing muscle tissue.
Nuts and seeds—particularly almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts—are nutrient-dense options that offer moderate protein along with healthy fats and fiber. Although they are more calorically dense, their inclusion in a keto high protein or high protein low fat low carb diet can be beneficial when portioned carefully. Protein powders, such as whey, casein, or plant-based blends, are another convenient way to meet daily protein targets without increasing carbohydrate intake.
How a High Protein Low Carb Diet Supports Weight Loss
One of the primary reasons individuals turn to a high protein diet low carb diet is its efficacy in promoting sustainable weight loss. Protein is not only more satiating than carbohydrates or fat, but it also helps preserve lean muscle mass during periods of caloric restriction. This preservation is crucial because muscle mass plays a significant role in maintaining resting metabolic rate. The higher your muscle mass, the more calories your body burns at rest, making fat loss more efficient.
Clinical studies have shown that people following high protein low carb diet foods tend to lose more weight and body fat than those on traditional low-fat diets, even when total calorie intake is similar. This is due, in part, to the hormonal advantages of high protein low carbohydrate plans, including reduced insulin levels and increased glucagon, which promote fat oxidation. Moreover, by reducing carbohydrate intake, the body experiences fewer spikes in blood sugar and insulin—key factors in preventing fat storage and improving energy balance.
Furthermore, a high protein low carb low fat diet may reduce water retention, often mistaken for fat gain, by minimizing the body’s reliance on glycogen, which stores water. This creates a leaner appearance and improves metabolic markers like triglyceride levels and HDL cholesterol. For individuals struggling with stubborn weight or plateauing on traditional diets, the metabolic switch enabled by a high protein keto diet can be a powerful catalyst for change.

Improving Energy and Cognitive Function with Low Carb Protein Foods
Contrary to the belief that carbohydrates are the body’s only efficient fuel, many people on a high protein low carb diet report improved energy levels, mental clarity, and stable mood. This is largely due to the elimination of blood sugar crashes that result from high-glycemic meals. When the body is adapted to burning fat and utilizing ketones—especially in a keto high protein framework—energy becomes more stable and long-lasting.
Protein is essential for neurotransmitter synthesis, including dopamine and serotonin, which regulate mood and cognitive function. By consuming high protein low carb diet foods consistently throughout the day, individuals can support not only muscle health but also brain function. This is particularly valuable in professional and academic settings where mental performance and focus are critical. Stable energy throughout the day also encourages more consistent physical activity, further enhancing the benefits of a low carb high protein lifestyle.
From a biochemical perspective, reducing carbohydrate intake lowers systemic inflammation—a known contributor to brain fog and fatigue. Additionally, incorporating omega-3-rich protein sources like salmon and sardines supports cognitive resilience and mental sharpness. These mechanisms make high protein low carbohydrate diets not only practical for physical transformation but also for sustained mental and emotional well-being.
Metabolic Health Benefits of a High Protein No Carb Diet
The high protein no carb diet, while more extreme in its reduction of carbohydrates, has shown therapeutic benefits for individuals with certain metabolic disorders, including type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. By virtually eliminating carbohydrate intake, this diet facilitates rapid improvements in glycemic control and insulin sensitivity. The liver and pancreas are relieved from the constant demand to manage blood sugar spikes, resulting in improved organ function and reduced inflammation.
For those with insulin resistance, a high protein low carbohydrate diet can help reverse the early stages of metabolic syndrome by restoring proper insulin signaling. This reduces the risk of developing more serious complications such as cardiovascular disease or advanced diabetes. When combined with physical activity, the metabolic improvements are even more pronounced, as muscles become more efficient at utilizing glucose and fat as energy sources.
Experts caution, however, that extreme carbohydrate restriction should be approached under medical supervision, particularly for those on medications that influence blood sugar. While the benefits of a high protein low carb diet are well-established, individual needs vary, and it’s important to tailor dietary approaches based on comprehensive assessments and lab markers. The core principle remains clear: strategic protein intake combined with carbohydrate moderation offers one of the most effective routes to metabolic restoration.

The Role of the High Protein Keto Diet in Body Composition
The high protein keto diet is a nuanced adaptation of the standard ketogenic approach, which emphasizes moderate protein, high fat, and very low carbohydrates. In the high protein variation, protein intake is increased to support muscle mass and prevent lean tissue loss, which can sometimes occur on strict keto plans. This version of the diet is especially popular among bodybuilders, athletes, and those looking to maintain or build muscle while reducing fat.
By prioritizing protein intake while still limiting carbohydrates, the body enters a state of nutritional ketosis, where it becomes highly efficient at using fat and ketones for energy. The increased protein supports anabolic processes, helping the body repair tissue, produce enzymes, and sustain immune health. When paired with resistance training, a high protein keto diet can lead to favorable changes in body composition, including increased muscle definition and reduced visceral fat.
One of the main concerns with standard ketogenic diets is potential protein deficiency, especially for physically active individuals. The high protein keto diet resolves this by ensuring that dietary protein is sufficient to meet both recovery and performance needs. It is also a more palatable and sustainable approach for many, as it allows a wider range of food options compared to ultra-low-protein keto plans. This balance makes the diet more accessible without compromising the core metabolic benefits of ketosis.
Tailoring a High Protein Low Carb Low Fat Diet for Different Lifestyles
While there is no universal blueprint for the perfect diet, the high protein low carb low fat diet offers enough flexibility to accommodate a range of lifestyles, preferences, and health conditions. For those seeking weight loss, this approach emphasizes calorie control without the need for extreme hunger. Meals are satisfying due to their protein content, and the low fat and carbohydrate levels prevent excess caloric intake.
For endurance athletes or individuals with higher energy demands, slightly increasing dietary fats—particularly from whole food sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil—can support hormonal balance and recovery without disrupting the benefits of low carbohydrate intake. On the other hand, sedentary individuals or those with insulin sensitivity issues may benefit more from a strict low carb protein plan with minimal fats to support efficient weight management.
Vegetarians and vegans can also adapt this eating pattern by focusing on legumes, high-protein grains like quinoa, and fortified plant-based products that are low in carbohydrates. Advances in food technology have made it easier to access low carb protein foods that cater to various dietary restrictions, ensuring that the core principles of high protein intake and carbohydrate moderation are achievable for almost everyone. The adaptability of this diet is one of its greatest strengths, helping users adhere to it long-term.
Frequently Asked Questions: High Protein Low Carb Diet Foods Backed by Experts
1. Can a high protein low carb diet help regulate hormones beyond insulin and glucagon?
Yes, a high protein low carbohydrate diet may positively influence a range of hormones beyond insulin and glucagon, particularly those involved in appetite, metabolism, and even reproductive health. For instance, protein-rich meals increase the secretion of satiety hormones like peptide YY and cholecystokinin, while reducing the hunger hormone ghrelin. This hormonal environment supports appetite regulation more effectively than high-carbohydrate meals. In women, especially those with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a high protein low carb diet can assist in normalizing estrogen and testosterone levels. Meanwhile, in men, improved insulin sensitivity from a less carbs more protein diet may indirectly support better testosterone production, enhancing overall metabolic and reproductive function.
2. How can vegetarians follow a high protein low carb diet without relying on processed products?
Vegetarians often face challenges with traditional low carb high protein approaches due to the reliance on meat and fish. However, it is possible to maintain a high protein low carbohydrate diet using whole, plant-based sources. Foods like tempeh, seitan, edamame, hemp seeds, and tofu offer impressive protein content with minimal carbs, especially when prepared without added sugars or breading. Incorporating low carb protein options such as unsweetened protein powders made from peas, rice, or pumpkin seed can also be effective. To maintain a high protein low carb low fat diet, vegetarians can focus on baking, grilling, or steaming these foods with light oils and herbs, rather than relying on highly processed meat substitutes that may contain hidden carbohydrates or unhealthy fats.
3. What are some psychological benefits of following a high protein low carbohydrate lifestyle?
Beyond physical benefits, the mental and emotional effects of a high protein diet low carb diet are gaining increased attention in clinical nutrition circles. Improved mood stability is frequently reported due to the steady blood glucose levels and consistent energy supply that this way of eating supports. Additionally, amino acids derived from high protein low carb diet foods serve as precursors to neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, which play crucial roles in managing stress, motivation, and sleep quality. People also experience reduced food-related anxiety and decision fatigue because meals tend to be more structured and predictable in a high protein keto diet or similar plan. These psychological advantages contribute to improved adherence and a stronger sense of personal control over eating behaviors.
4. Is there a risk of nutrient deficiencies on a high protein no carb diet, and how can they be prevented?
While a high protein no carb diet can be effective for short-term goals or therapeutic uses, it does come with certain risks if not carefully managed. Eliminating nearly all carbohydrates may reduce intake of essential micronutrients typically found in fruits, whole grains, and legumes, such as vitamin C, potassium, and certain B-complex vitamins. To prevent deficiencies, individuals should prioritize high protein low carb diet foods that are naturally nutrient-dense—like leafy greens, sea vegetables, and organ meats. Supplementing with electrolytes and a high-quality multivitamin is often recommended, especially for those following stricter versions like a keto high protein plan. It’s also wise to regularly monitor nutrient status through blood tests if adopting a long-term high protein low carbohydrate approach.
5. How does a high protein low carb diet impact athletic performance and recovery?
A high protein low carbohydrate diet can be tailored to enhance specific athletic goals, but its effect on performance depends on the type and intensity of the activity. For strength-based sports, the increased protein intake supports muscle repair, protein synthesis, and reduced exercise-induced muscle breakdown. Athletes who adopt a high protein low fat low carb regimen may experience faster recovery and reduced inflammation post-training. Endurance athletes, however, may need to adjust carb intake around training windows to maintain glycogen levels. Many now follow a cyclical keto high protein method, which alternates periods of low carbohydrate intake with strategic carb refeeding, allowing for both metabolic efficiency and performance sustainability.
6. What role does meal timing play in maximizing the benefits of a high protein low carb diet?
Meal timing, or nutrient timing, can amplify the benefits of a high protein low carbohydrate diet, especially in terms of muscle building, fat loss, and energy management. Consuming low carb protein meals early in the day helps support satiety and balanced blood sugar levels, setting a stable tone for the rest of the day. Post-exercise meals that include high protein low carb diet foods help initiate muscle repair while keeping fat storage at bay. Some individuals also practice time-restricted eating, aligning a high protein diet low carb diet with intermittent fasting for enhanced metabolic flexibility. Ultimately, aligning protein intake with times of highest demand—such as after physical exertion or during periods of stress—ensures optimal physiological response.
7. Are there long-term studies supporting the safety of a high protein low carb low fat diet?
Longitudinal studies on high protein low carb diet foods and their long-term impact are expanding, particularly in relation to cardiovascular health, weight maintenance, and metabolic disease prevention. Emerging data from clinical trials and observational research suggests that high protein low carbohydrate diets are not only safe but beneficial for most people when based on whole, minimally processed foods. Some older concerns about kidney strain have been debunked in healthy individuals, although those with pre-existing renal conditions should proceed with medical supervision. The long-term safety of a high protein low fat low carb approach appears favorable when attention is given to micronutrient balance and overall food quality. Researchers continue to monitor potential impacts on gut microbiota, encouraging inclusion of fibrous vegetables and fermented foods even in low carbohydrate contexts.
8. How does social and cultural context influence adherence to a low carb high protein lifestyle?
The social and cultural dimensions of following a high protein low carb diet are often overlooked but highly influential. In cultures where rice, bread, or pasta are central to social meals, individuals may feel isolated or restricted. However, adapting traditional recipes using high protein low carb diet foods—such as cauliflower rice, almond flour flatbreads, or legume-based pasta—can help bridge this gap. Social support and communal eating behaviors also affect dietary adherence; people are more likely to maintain a high protein low carbohydrate lifestyle when family members or peers share similar health goals. Cultural flexibility, combined with strategic meal planning, helps individuals harmonize personal health choices with broader community norms.
9. Can a high protein keto diet improve sleep quality and circadian health?
While diet is not the only determinant of sleep quality, a high protein keto diet may offer surprising benefits for circadian alignment and deeper sleep. Protein-rich meals support the production of tryptophan, an amino acid necessary for melatonin and serotonin synthesis. Additionally, the stable blood sugar levels induced by high protein low carb diet foods reduce the likelihood of nocturnal hypoglycemia, which can disrupt sleep. Some studies suggest that individuals who reduce carbohydrate intake in favor of a high protein low fat low carb diet experience more time in restorative sleep stages. Aligning dinner with circadian biology—eating a high protein, low carb meal at least two hours before bedtime—can further improve sleep efficiency and hormonal rhythms.
10. What are the most promising innovations in high protein low carb foods and dietary planning?
The food industry is rapidly innovating to support the high protein low carb diet movement with smarter, cleaner, and more customizable options. Advances in precision fermentation and plant-based protein isolates are making low carb protein products more accessible to a broader population. New high protein low carb diet foods include functional snacks with added adaptogens, low-glycemic protein bars, and fermented protein-rich condiments that enhance gut health. Digital tools and AI-driven nutrition platforms are also helping people optimize high protein low carbohydrate diets based on individual biomarkers and goals. As the demand grows for sustainable, convenient, and science-backed options, the next frontier lies in fully personalized meal plans that combine medical data with lifestyle preferences—pushing the boundaries of what a high protein low carbohydrate diet can achieve.
Final Thoughts on Building a High Protein Low Carbohydrate Lifestyle for Lifelong Health
At its core, the high protein low carb lifestyle is about more than just food choices—it represents a shift toward mindful eating, metabolic empowerment, and long-term health stewardship. By emphasizing high protein low carb diet foods, individuals can achieve better control over their appetite, blood sugar, and energy levels, all while reducing their risk for chronic disease. When applied with the guidance of nutrition professionals and tailored to individual needs, the benefits of a high protein low carbohydrate approach are both immediate and lasting.
From managing weight and improving mental focus to reversing signs of metabolic dysfunction, the evidence in favor of low carb high protein diets continues to grow. The inclusion of high protein no carb diet days, periodic keto high protein phases, or long-term high protein low fat low carb meal plans can provide a flexible yet powerful framework for health optimization. The key is consistency, customization, and commitment to real, whole-food nutrition.
As more research supports the role of high protein low carbohydrate diets in disease prevention and wellness promotion, integrating this knowledge into daily life becomes not just a dietary choice, but a proactive approach to better living. Whether you’re starting your journey or refining an established routine, embracing the science-backed wisdom of high protein low carb nutrition is a smart, sustainable way to fuel your body, focus your mind, and fortify your future.
Further Reading:
High Protein Low Carb Foods: Benefits and Meal Examples
Foods to eat that are high in protein and low in carbs
25 High-Protein, Low Carb-Foods To Keep You Fueled


