Introduction: Why Yogurt and Keto Are Sparking So Much Debate
Among keto followers and nutrition experts alike, yogurt remains one of the most hotly debated foods. While traditionally considered a staple of healthy eating, yogurt now finds itself under the microscope of the low-carb community. The core question many keto dieters ask is: Is yogurt keto friendly? Can it truly be incorporated into a ketogenic lifestyle without disrupting ketosis or derailing metabolic goals? This article explores what the research says, what nutrition professionals recommend, and how yogurt in keto diet plans might offer surprising benefits when chosen wisely.
You may also like: Is the Keto Diet Safe or Dangerous? What Experts Say About the Risks, Benefits, and Basics of the Ketogenic Diet
What Is the Ketogenic Diet and Why Carbs Matter
To understand whether yogurt belongs in keto, it’s essential to revisit what the ketogenic diet entails. At its core, keto is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate diet designed to shift the body into ketosis—a state in which fat becomes the primary fuel source instead of glucose. Achieving and maintaining ketosis generally requires keeping carbohydrate intake below 20–50 grams per day, depending on the individual. Because most dairy products, including yogurt, contain lactose—a naturally occurring milk sugar—many worry that even plain yogurt might contain too many carbs.
However, it’s not a one-size-fits-all scenario. Not all yogurts are created equal, and the type, portion, and carbohydrate content play a major role in determining whether yogurt on ketogenic diet plans is helpful or harmful to ketosis.

Yogurt’s Nutrition Profile: Not All Yogurt Is Created Equal
When evaluating yogurt in keto eating plans, examining its nutritional content is the first step. Plain whole milk yogurt typically contains around 4–5 grams of carbs per 100 grams, whereas flavored or low-fat versions can exceed 15 grams per serving. This significant variation underscores why label reading is crucial.
Greek yogurt, particularly full-fat, is one of the most popular options among keto enthusiasts. Its thick texture comes from straining, which removes whey and lowers its carb content. Icelandic yogurt (skyr), though slightly higher in protein, also provides a low-carb alternative when unsweetened. These varieties offer rich, creamy textures while keeping net carbs low, making them ideal for those looking to enjoy yogurt in keto diet protocols without sacrificing taste or texture.
Whole milk versions are preferable because they align better with the high-fat structure of a ketogenic diet, helping to provide satiety and encourage fat metabolism.
Yogurt and Gut Health: The Probiotic Advantage
One of the most compelling reasons to include yogurt on ketogenic diet plans is its probiotic content. Fermented foods like yogurt contain live cultures that support gut microbial diversity. This is especially important in ketogenic diets, which may reduce intake of fibrous prebiotic foods that typically support microbiota.
Experts emphasize that supporting a healthy gut microbiome contributes not only to digestion but also to immune function, inflammation regulation, and even mood stability. Additionally, the fermentation process used in yogurt production helps break down lactose, reducing its carb content and improving tolerability in those who are lactose-sensitive.
Including yogurt in keto plans can act as a natural source of probiotics, potentially reducing the need for supplemental gut-supporting pills.

Selecting the Best Yogurt for a Ketogenic Lifestyle
Choosing the right yogurt is essential if you’re hoping to keep your body in ketosis. First and foremost, avoid sweetened or flavored yogurts. These typically contain cane sugar, syrups, or fruit purée—ingredients that can easily cause carb intake to spike beyond keto-friendly levels.
Instead, seek out unsweetened, full-fat varieties with limited ingredients. The ideal product will list only milk and bacterial cultures. Greek yogurt often stands out in this category, typically providing 3–5 grams of carbohydrates per 150g serving. Pay close attention to serving sizes as well. Even a low-carb yogurt can become problematic if consumed in large amounts.
Keto-specific yogurts are now entering the market with formulas designed to be low in carbohydrates and high in fat. Some even contain medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) to enhance fat-burning. While these products can be helpful, it’s important to read labels carefully, as not all are free from gums, starches, or artificial sweeteners that could trigger inflammation or disrupt digestion.
Scientific Evidence on Dairy and Low-Carb Diets
Scientific studies offer strong support for including yogurt in well-structured low-carb diets. Research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition showed that full-fat dairy is associated with favorable body composition and does not increase cardiovascular disease risk. Furthermore, a 2021 study in the Nutrients journal demonstrated that fermented dairy products, such as yogurt, were associated with better insulin sensitivity and improved metabolic markers.
These findings suggest that not only is yogurt in keto potentially acceptable—it may actually support some of the diet’s core goals, such as blood sugar control and appetite regulation. With its combination of fat, protein, and beneficial bacteria, yogurt helps provide satiety and curb cravings that often emerge during the early phases of a ketogenic transition.
Experts point out that when dairy is tolerated well, its inclusion can contribute meaningfully to the nutrient density of a ketogenic eating plan.
Debunking Myths About Yogurt and Keto Compatibility
Despite scientific support, myths about yogurt’s unsuitability for keto persist. One common misconception is that all dairy is high in sugar. In reality, fermentation reduces the lactose content, making yogurt more carb-friendly than milk. Another widespread belief is that any yogurt, regardless of variety, will immediately disrupt ketosis. But in practice, ketosis is not a fragile state easily disrupted by small amounts of naturally occurring sugars—particularly if consumed alongside fat and protein.
Another area of confusion involves net carbs versus total carbs. Many keto dieters track net carbs, subtracting dietary fiber and sometimes sugar alcohols from total carbs. In yogurt, fiber is minimal, but the fermentation process converts a portion of lactose into lactic acid, effectively lowering its glycemic impact. This nuance is often overlooked by those relying solely on carbohydrate labels without understanding the fermentation chemistry behind the product.
Furthermore, individual metabolic responses differ. Some individuals can maintain ketosis while consuming small amounts of yogurt daily, while others may need stricter limits. The key is not avoidance but personalized experimentation.
Expert Guidance: How Nutritionists Recommend Eating Yogurt on Keto
Nutritionists and registered dietitians increasingly support the inclusion of yogurt in keto meal planning—provided it aligns with overall macronutrient goals and comes from high-quality sources. According to functional nutrition experts, yogurt’s rich supply of calcium, B vitamins, and probiotics offers more than just gut health benefits. These nutrients can help correct micronutrient deficiencies often seen in long-term keto dieters.
Practitioners in integrative medicine also recommend yogurt for those with digestive imbalances or immune dysfunction, given its immunomodulatory effects. These clinicians view yogurt as both food and medicine, able to restore microbial equilibrium while contributing to satiety and metabolic regulation.
Psychologically, including yogurt helps increase the sustainability of a ketogenic diet. Rigid food restrictions can create a sense of deprivation, potentially leading to binge eating or non-compliance. Including familiar, comforting foods like yogurt can create a sense of normalcy, making the diet feel less restrictive and more adaptable over time.
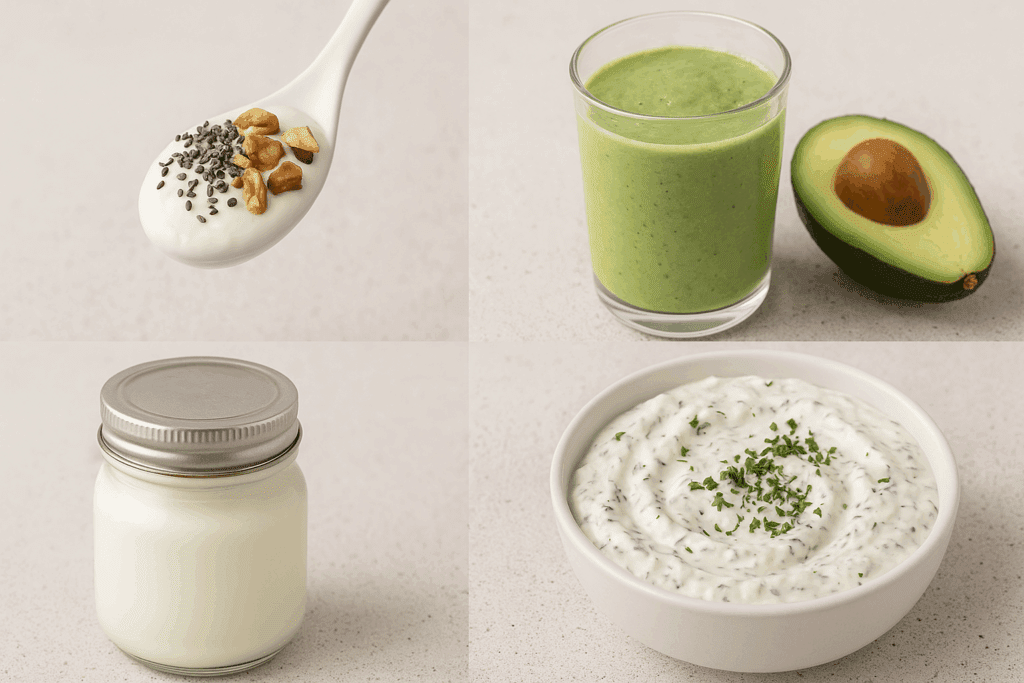

Practical Tips for Including Yogurt in Your Keto Plan
If you’re ready to experiment with yogurt in keto diet routines, a few practical strategies can optimize your results. Start by choosing plain, full-fat varieties, and limit your serving to about 100–150 grams. Enhance the yogurt’s keto profile by mixing in toppings like chia seeds, hemp hearts, or a spoonful of nut butter. These add healthy fats and fiber without elevating your carb intake.
For a more indulgent experience, blend yogurt into a smoothie with avocado, unsweetened cocoa powder, and coconut milk. This transforms it into a creamy, low-carb dessert or post-workout recovery shake. Some also enjoy making homemade yogurt using high-fat cream or full-fat milk, which gives greater control over fermentation time and carbohydrate content.
It’s also a good idea to track your response. Some individuals use ketone meters or continuous glucose monitors to observe how their bodies respond to different foods. If yogurt doesn’t affect your blood glucose or ketone levels negatively, it’s likely a good fit for your personal version of keto.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ): Yogurt and the Ketogenic Diet
1. Can eating yogurt regularly support long-term success on a ketogenic diet? Yes, yogurt can play a supportive role in long-term keto success when incorporated thoughtfully. While some view it as a “gray area” food, the right type of yogurt in keto diet plans offers nutrient density and variety—both of which are crucial for diet sustainability. Full-fat yogurt with live cultures provides a satisfying option for those who miss creamy, comforting textures without triggering carb overload. It also delivers essential nutrients like calcium and B vitamins that are sometimes underrepresented in very low-carb regimens. When balanced with non-starchy vegetables and healthy fats, yogurt in keto helps reduce dietary monotony, making it easier to adhere to the plan over time.
2. How does yogurt affect blood ketone levels in keto dieters? The effect of yogurt on ketone levels varies depending on the individual and the specific product consumed. Generally, small portions of plain, high-fat yogurt on ketogenic diet plans do not significantly impair ketosis, especially when consumed alongside fats or proteins. Because fermentation reduces lactose, the glycemic load of many yogurts is lower than expected. However, personalized testing—using a blood ketone monitor—can provide the most accurate feedback. Monitoring how different types of yogurt in keto affect ketone production is key for those aiming to maintain consistent ketosis.
3. Are there any cultural or artisanal yogurts that work better with keto diets? Yes, some traditional or artisanal yogurts align even better with keto goals than commercial products. For example, Bulgarian and Lebanese yogurts are often made with whole milk and contain live, active cultures, while being naturally unsweetened. These types of yogurt in keto diet plans may offer richer flavor and a more potent probiotic profile. Because many artisanal varieties are minimally processed and strained for thickness, they tend to have a lower carb count than mass-produced versions. Exploring cultural yogurts can enhance both the diversity and digestive benefits of yogurt in keto.
4. Is yogurt keto friendly for those with insulin resistance or prediabetes? For individuals managing insulin resistance, yogurt on ketogenic diet protocols can be keto friendly when selected properly. Plain Greek yogurt or skyr with no added sugars can have a stabilizing effect on blood sugar, particularly when eaten with fiber-rich or fatty foods. The fermentation process partially digests lactose, reducing blood sugar impact compared to milk. Furthermore, studies suggest that probiotic-rich yogurt may enhance insulin sensitivity, adding therapeutic potential. Still, portion control remains critical; even keto-friendly yogurt in keto diets should be consumed mindfully in blood sugar-sensitive populations.
5. What are some lesser-known ways to use yogurt in keto-friendly recipes? Beyond being a simple snack, yogurt in keto can serve as a versatile ingredient in savory and sweet recipes. It can act as a base for keto tzatziki, a high-fat dip made with cucumber, olive oil, and garlic. In baking, it adds moisture to almond flour muffins or keto-friendly bread without spiking carbs. Blended with herbs and lemon, it makes a creamy marinade for proteins. Yogurt in keto diet recipes can even replace sour cream in soups or be whipped with stevia and cacao powder for a low-carb dessert. Its culinary flexibility helps keep the diet both diverse and enjoyable.
6. Are plant-based yogurts a suitable alternative on a ketogenic diet? Some plant-based yogurts are compatible with keto, but caution is needed. Almond or coconut milk yogurts can work well, provided they are unsweetened and made without high-carb fillers like tapioca starch or maltodextrin. These alternatives can be a good choice for those with dairy intolerance who still want to include yogurt in keto routines. However, many plant-based yogurts are lower in fat and protein compared to dairy-based options, which may reduce satiety. Reading labels closely is essential to ensure that the product supports the macronutrient ratios needed for ketosis.
7. Can yogurt help address digestive discomfort common during early ketosis? Yes, including yogurt in keto diet transitions may ease some early digestive discomfort. During the shift to ketosis, some individuals experience bloating or irregularity due to reduced fiber or changes in gut flora. Probiotic-rich yogurt can help rebalance the microbiome, potentially reducing symptoms like constipation or indigestion. Its soft texture also makes it gentle on the digestive system when appetite is low. For those new to keto, adding a small daily portion of plain yogurt may help smooth the transition by supporting gut adaptation.
8. What innovations are emerging in the keto yogurt market? The rise of keto-specific yogurt products reflects growing consumer demand for low-carb dairy alternatives. Innovations include yogurts fortified with MCT oil for enhanced fat metabolism and products cultured with advanced probiotic strains tailored for immune or metabolic health. Some brands are now using goat or sheep milk to cater to those seeking alternatives to cow dairy while still enjoying yogurt on ketogenic diet plans. Additionally, advancements in fermentation are enabling further reductions in sugar while maintaining taste and texture. These trends are expanding the options for incorporating yogurt in keto diets without compromising on quality.
9. How can yogurt impact cravings or emotional eating while on keto? Yogurt may help manage cravings and emotional eating on keto by providing a comforting, nutrient-rich food that satisfies both texture and flavor preferences. The creamy mouthfeel and natural tanginess can replicate the experience of higher-carb indulgences without triggering a glycemic spike. Full-fat yogurt in keto diet strategies can also promote feelings of satiety, thanks to its protein and fat content. Additionally, some research suggests that probiotics may influence mood through the gut-brain axis, potentially aiding emotional resilience. When used intentionally, yogurt can be a psychological anchor that supports dietary adherence.
10. Is it safe to ferment homemade yogurt for ketogenic use, and what are the benefits? Homemade yogurt can be a safe and keto-friendly option when prepared correctly. By fermenting yogurt at home using full-fat milk or cream and a starter culture, individuals can control fermentation time, which affects both texture and carbohydrate content. Extended fermentation reduces lactose further, lowering the sugar content even beyond what’s typical in store-bought varieties. Homemade yogurt also avoids unnecessary additives or preservatives often found in commercial products. For those committed to clean eating and advanced keto strategies, crafting your own yogurt allows complete control over ingredients and macros, offering a deeply personalized approach to yogurt in keto diet planning.
Conclusion: Why Yogurt on a Ketogenic Diet Can Be a Smart Choice for Wellness and Gut Health
So, is yogurt keto friendly? The evidence suggests that when chosen thoughtfully and eaten in moderation, it absolutely can be. Including yogurt in keto diet plans offers more than just culinary variety—it provides essential nutrients, supports digestive health, and can help stabilize blood sugar and energy levels. Far from being a forbidden food, yogurt on ketogenic diet programs can be a strategic ally.
The most important takeaway is to avoid sweetened or low-fat varieties and to choose full-fat, unsweetened options rich in live probiotic cultures. When incorporated mindfully, yogurt can help balance the gut microbiome, enhance nutritional intake, and support sustainable long-term adherence to the ketogenic lifestyle.
For individuals seeking to personalize their nutrition while still honoring the core principles of keto, yogurt presents an opportunity—not a risk. By selecting the right product and understanding how it fits into your unique metabolic landscape, you can enjoy the creamy richness of yogurt without compromising ketosis or wellness goals.
Ultimately, yogurt in keto isn’t just a possibility—it’s a promising, research-backed inclusion that offers both practical and therapeutic benefits. With the right knowledge and a bit of label literacy, it can be one of the most rewarding and beneficial additions to a well-rounded ketogenic journey.
Further Reading:
Top 5 Best Keto Yogurt Options for a Low-Carb Diet
Is Greek Yogurt Keto? How Many Carbs Are In Greek Yogurt?


