Vitamin B12, commonly known as methylcobalamin, is a crucial vitamin needed for a number of metabolic processes in the body. This water-soluble vitamin is essential for the production of red blood cells, RNA, and DNA. Also, it is crucial for the health of the brain and the proper operation of the neurological system. Methylcobalamin has been more well-known recently as a nootropic vitamin because of its propensity to improve mental clarity, focus and cognition. The nature of methylcobalamin, its advantages for health, the best dosage, any potential negative effects, any drug interactions, and safe use will all be covered in this article.
You May Also Like:
THE 5 BEST ALPHA LIPOIC ACID SUPPLEMENTS REVIEWED
VITAMIN E: BENEFITS, DOSAGE, SIDE EFFECTS, DRUG INTERACTIONS, AND OTHER IMPORTANT INFORMATION
Nature of Methylcobalamin
Vitamin B12 can exist in two biologically active forms which are methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin. In contrast to other B vitamins, vitamin B12 cannot be found in plant-based meals and must instead be taken mostly from sources originating from animals, such as meat, fish, and dairy.
In the presence of the enzyme methionine synthase, vitamin B12 is activated and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate is converted to methylcobalamin by transferring a methyl group to cobalamin. Then, it is transformed into adenosylcobalamin and stored in the liver.

Health Benefits of Methylcobalamin
1. Methylcobalamin has been demonstrated to enhance memory and cognitive performance in the community including older cohorts. According to a study that appeared in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, older persons who took supplements containing methylcobalamin had better recollection and reaction times than those who did not. This is because the healthy operation of the neurological system and the state of the brain depend on methylcobalamin.
Methylcobalamin is crucial for the production of myelin, a fatty coating that protects and surrounds the nerve fibers. Myelin aids in accelerating nerve impulses, enhancing communication between various brain regions which in turn enhances cognitive ability. Additionally, methylcobalamin also lowers blood homocysteine levels. A higher risk of dementia and cognitive impairment is linked to high homocysteine levels.
2. More Energy: Methylcobalamin also contributes to the creation of red blood cells, which transport oxygen throughout the body. Moreover, it also aids in the transformation of carbohydrates into glucose. Glucose can then be directly assimilated by the body to synthesize energy. Methylcobalamin supplements may aid in boosting energy and reducing weariness.
3. A better mood: Methylcobalamin is involved in the manufacture of neurotransmitters that are crucial for controlling moods, like serotonin and dopamine. Methylcobalamin supplements have been proven in studies to potentially boost mood and lessen depressive symptoms.
4. Cardiovascular Health: As mentioned previously, methylcobalamin aids in lowering blood homocysteine levels. Lower blood homocysteine levels not only reduce the risk of dementia but also lowers the chance of developing cardiovascular disease. Heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral vascular disease are all linked to high homocysteine levels.

Chemistry of Methylcobalamin
Methylcobalamin, one of the two active forms of vitamin B12, is also a coenzyme that contains cobalt. Methylcobalamin is made up of the following chemical components: a corrin ring, a cobalt ion, a nucleotide base, and a methyl group.
A massive, intricate macrocycle made up of four pyrrole rings connected by methylene bridges is known as the corrin ring. Four nitrogen atoms from the corrin ring and a fifth nitrogen atom from the nucleotide base coordinate the cobalt ion, which is found in the core of the ring. The methyl group, which is joined to the cobalt atom contributes to the methyl transfer processes that take place inside the body.
Physiological Mechanism of Action of Methylcobalamin
Methylcobalamin is essential for several bodily metabolic processes. It takes part in the process of turning homocysteine into methionine, which also involves the enzyme methionine synthase.
The body needs methionine which is an important amino acid to create proteins, neurotransmitters, and other compounds. For instance, methylcobalamin involves in the production of the molecule S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe), which is involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters.
Moreover, methylcobalamin is important for the synthesis of DNA and RNA, which are necessary for cell division and growth. It is also necessary for the process that turns methyl malonyl-CoA into succinyl-CoA, which is crucial in the body’s synthesis of energy.
Methylcobalamin is also particularly crucial for the nervous system’s healthy operation because methylcobalamin is necessary for the creation of myelin that protects the nerve fibers and accelerate the transmission of nerve impulses. Additionally, methylcobalamin aids in the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are crucial for controlling mood, appetite, and sleep.

Optimal Dosage of Methylcobalamin
For adults, 2.4 mcg of vitamin B12 daily intake is advised. The best dose of methylcobalamin, however, may differ based on age, health, and other variables. A total of 1–5 mg used daily is a typical dosage for improving cognition. It is crucial to remember that because excess vitamin B12 is eliminated in the urine, hence, mega doses are typically safe and well tolerated.
Side effects of Methylcobalamin
When used at authorized quantities, methylcobalamin is usually regarded as safe and well-tolerated with minimal known adverse effects. Nonetheless, a few people could encounter minor side effects like nausea, diarrhea, and headaches. The majority of the time, these adverse effects are minor and momentary, and they normally go away on their own without the need for treatment.
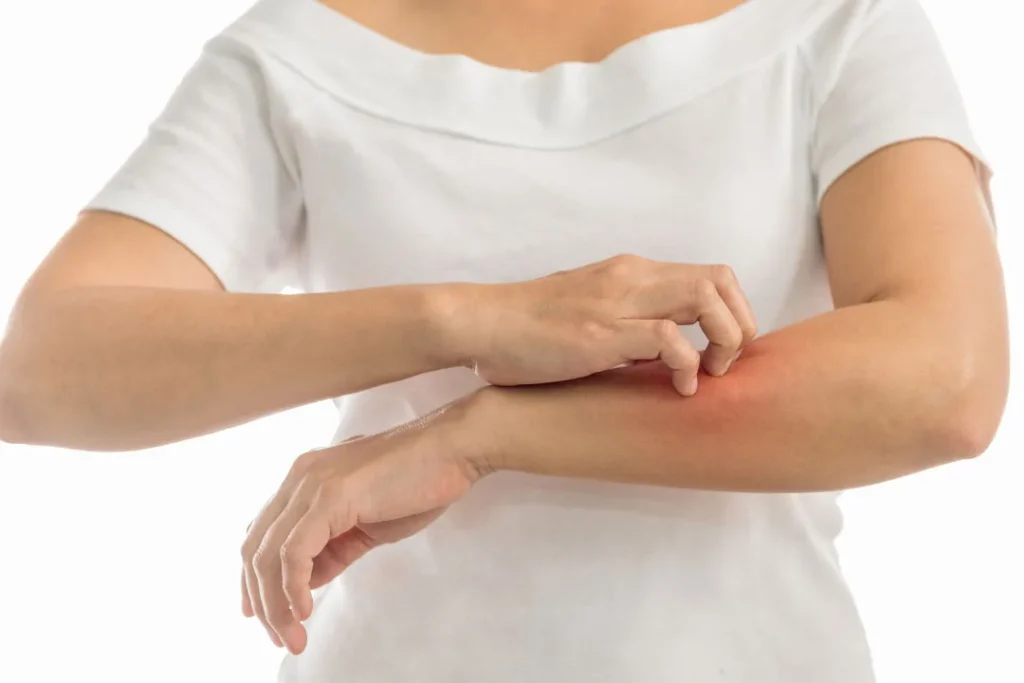
Rarely, those who are sensitive to or allergic to vitamin B12 or other substances in the supplement may experience allergic reactions. Itching, swelling, rash, breathing difficulties, and anaphylaxis are some of the signs of an allergic reaction. See a doctor right away if you suffer any of these side effects after taking methylcobalamin.
There are also instances where excessive dosages of methylcobalamin taken by someone with impaired kidney function might cause hypokalemia (low potassium levels). Weakness in the muscles, cramping, or an erratic heartbeat may result from this.
Hence, before using methylcobalamin supplements, those with renal impairment should speak with a healthcare provider. Not only that, if you are on any type of medication, you should speak with a healthcare provider before using methylcobalamin supplements.
Potential Substance Interactions with Methylcobalamin
There may be interactions between methylcobalamin and the following drugs and substances:
1. Metformin: Vitamin B12 absorption may be decreased by the type 2 diabetes medication metformin.
2. Proton pump inhibitors: These drugs, which are used to treat stomach ulcers and acid reflux, may reduce the absorption of vitamin B12.
3. Alcohol: Drinking too much alcohol can hinder the absorption of vitamin B12. Taking methylcobalamin supplements may assist those who drink too much alcohol to avoid falling short of vitamin B12.

Best Responsible Use of Methylcobalamin
If you’re thinking about using methylcobalamin as a nootropic supplement to improve your cognitive ability, it’s crucial to pick a high-quality, synergistic, and highly bioavailable supplement. Methylcobalamin and other crucial nutrients found in Brilliance by myPEAK Supplements improve cognitive health and energy production. This makes it a wise choice.
Furthermore, Brilliance features a proprietary delivery mechanism that increases methylcobalamin’s absorption and bioavailability, ensuring that you get the greatest benefit possible from your supplement.
When beginning any new supplement regimen, it’s crucial to follow suggested dosages and speak with a healthcare provider, especially if you’re expecting, nursing, or have any other medical concerns. For those seeking a synergistic and highly bioavailable form of methylcobalamin to enhance mental health and energy generation, Brilliance by myPEAK Supplements is a great option.
Methylcobalamin:
Conclusion
Methylcobalamin is made up of a corrin ring, a nucleotide base, and a cobalt atom joined to a methyl group that is used in methyl transfer processes. It impacts the neurological system and the state of the brain as it is crucial for myelin production. Next, it is involved in the manufacture of neurotransmitters that are crucial for controlling mood and lessening depressive symptoms.
Furthermore, methylcobalamin supplements might aid in boosting energy and reducing weariness as methylcobalamin aids in the creation of red blood cells for oxygen transport and the transformation of carbohydrates into glucose for energy. Before you incorporate this supplement into your daily diet, you should seek consultations from your healthcare providers if you are on any medications. It is recommended that you take a methylcobalamin supplement from a reputable source that provides a high-quality formulation such as Brilliance from myPEAK supplements.
Important Note: The information contained in this article is for general informational purposes only, and should not be construed as health or medical advice, nor is it intended to diagnose, prevent, treat, or cure any disease or health condition. Before embarking on any diet, fitness regimen, or program of nutritional supplementation, it is advisable to consult your healthcare professional in order to determine its safety and probable efficacy in terms of your individual state of health.
Regarding Nutritional Supplements Or Other Non-Prescription Health Products: If any nutritional supplements or other non-prescription health products are mentioned in the foregoing article, any claims or statements made about them have not been evaluated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, and such nutritional supplements or other health products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.