Dressler’s syndrome / postmyocardial infarction / postpericardiotomy syndrome: Description, Causes, and Treatment Protocol
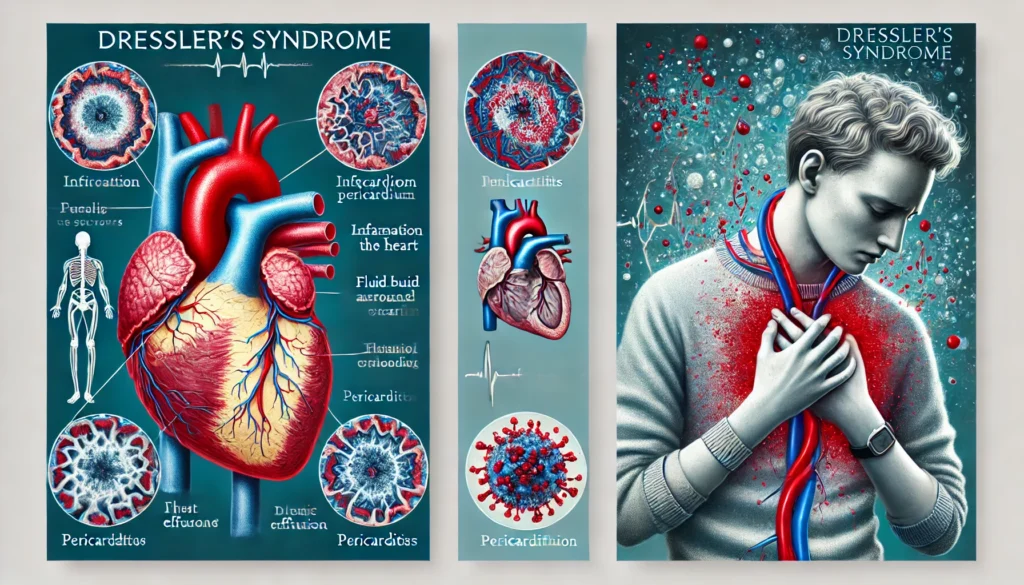
Description Dressler’s syndrome represents a rare but severe condition that often manifests weeks to months following cardiac surgery or myocardial infarction (MI) and is identified by pleuritis, pericarditis, and fever. It is named after William Dressler, who initially reported it in 1956. Due to the syndrome’s inconsistent clinical presentation and symptoms that frequently coexist with […]