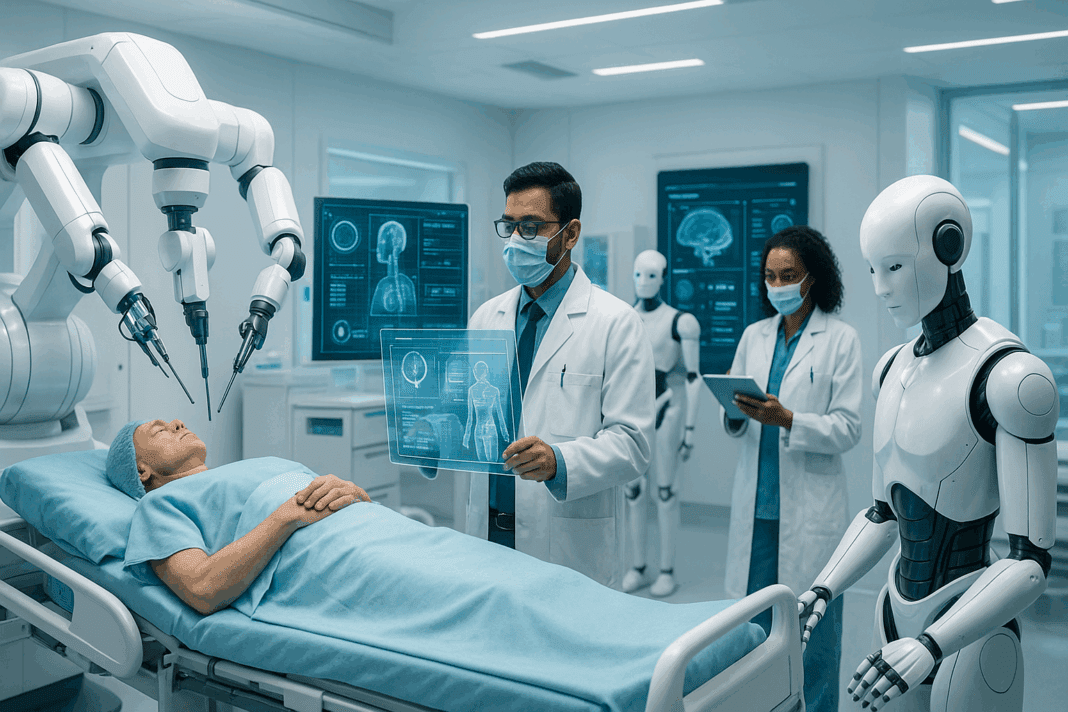
The Rise of Robotics in Modern Healthcare
Robotics in healthcare has undergone a profound evolution in the past two decades, driven by technological advancements, increased medical demand, and the pursuit of precision in clinical care. These systems are no longer confined to science fiction or isolated surgical environments. Today, robots in the healthcare industry perform tasks ranging from assisting in complex surgeries to automating mundane administrative work, enhancing both the efficiency and quality of patient care. This emergence reflects not only technological prowess but also a pivotal shift in how the healthcare sector addresses its most persistent challenges—such as medical staff shortages, procedural inconsistencies, and the need for personalized treatment approaches.
You may also like: Advancements in Healthcare Technology: How Emerging Innovations Are Transforming Patient Care

Medical robots are now viewed as indispensable allies in hospitals and research institutions worldwide. These systems integrate seamlessly with existing healthcare infrastructures and enable human professionals to focus on higher-order responsibilities. For example, robotic surgical assistants enable greater precision and minimal invasiveness, while AI-driven diagnostic tools support physicians in recognizing conditions more accurately. Such integration showcases the benefits of robotics in healthcare not just as an operational upgrade but as a transformative movement toward more intelligent, adaptive, and patient-centered care models.
This transformation has also catalyzed a broader societal and academic conversation about the ethical and practical implications of robot health care. As robotic technologies advance, they raise vital questions about the limits of automation, the preservation of empathy in medicine, and how regulatory bodies should guide these developments. Understanding these dynamics is crucial to appreciating the full scope of robotics in medicine, which extends well beyond machinery into the realm of human values, policy, and systemic reform.
Understanding the Role of Medical Robots in Clinical Settings
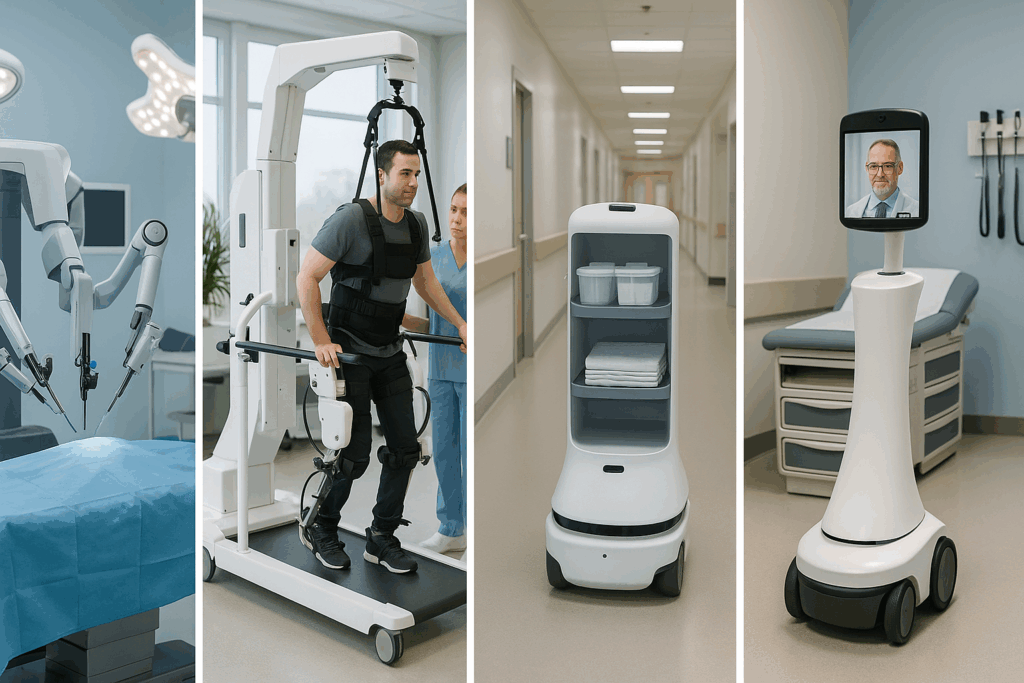
To appreciate the significance of robots in the medical field, it is essential to explore the various types of medical robots and their roles in clinical environments. These robots are typically classified into categories such as surgical robots, rehabilitation robots, hospital logistics robots, and telepresence systems. Surgical robots, exemplified by the Da Vinci Surgical System, offer unparalleled dexterity and visualization, empowering surgeons to perform procedures with enhanced precision and reduced invasiveness. These innovations have led to faster recovery times, fewer complications, and higher patient satisfaction.
Rehabilitation robots, on the other hand, assist patients recovering from strokes, spinal cord injuries, or orthopedic surgeries. These devices guide movements, track progress, and adapt to patient needs in real-time, enhancing therapy outcomes. Meanwhile, hospital logistics robots help manage internal supply chains by transporting medication, specimens, and equipment, thereby freeing up valuable human resources for direct patient care. Telepresence robots facilitate remote consultations and monitoring, making healthcare more accessible, especially in underserved or rural regions.
Each of these examples demonstrates how robotics in medicine is reshaping the landscape of patient care. The applications of robots in the healthcare setting include functions that were previously considered the exclusive domain of human clinicians. This shift does not eliminate the role of healthcare professionals but rather redefines it—moving them from the center of manual tasks to roles of oversight, decision-making, and patient engagement. The result is a more collaborative ecosystem where humans and machines work synergistically to optimize outcomes.
Artificial Intelligence and the Emergence of Smart Healthcare Systems
A particularly revolutionary aspect of robotics in healthcare is the integration of artificial intelligence. AI robots in healthcare represent the next frontier of digital medicine, combining machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision to interpret data, make recommendations, and even learn from new scenarios. These capabilities enable robots to participate in diagnostic processes, analyze imaging data, and suggest treatment options—supporting clinicians with evidence-based insights that enhance both speed and accuracy.
One of the most impactful applications of AI in healthcare is predictive analytics. AI-powered robots can sift through vast amounts of patient data to identify patterns that may indicate disease onset or treatment response. This foresight allows physicians to intervene earlier, tailor therapies to individual patients, and improve long-term prognoses. In oncology, for instance, AI robots can analyze tumor profiles and genomic data to suggest targeted treatment regimens, improving outcomes in conditions that are notoriously difficult to treat.
Equally transformative is the role of AI in patient monitoring. Smart robots equipped with sensors and machine learning algorithms can continuously assess vital signs, detect anomalies, and alert medical staff to potential emergencies. This continuous surveillance significantly reduces the risk of adverse events, particularly in intensive care units where patient conditions can deteriorate rapidly. As a result, AI robots in healthcare not only augment medical decision-making but also provide an added layer of safety, reinforcing the quality of patient care.
How Robots Are Redefining Patient Interactions and Experience
While much attention is given to the technical capabilities of medical robots, their impact on patient experience is equally profound. Robots as doctors, or more accurately, as medical assistants, play a significant role in enhancing the quality and consistency of patient interactions. These machines can deliver information clearly, answer frequently asked questions, and provide emotional support—particularly for children, the elderly, or those with cognitive impairments. By doing so, they help reduce patient anxiety and improve communication across linguistic or cultural barriers.
One compelling application is in pediatric care, where social robots are used to comfort children during hospital stays or painful procedures. These robots use facial expressions, voice modulation, and interactive storytelling to create a calming environment, promoting cooperation and emotional resilience. Similarly, elder care robots offer companionship and assist with daily routines, helping seniors maintain independence while ensuring safety and connection. This dimension of robot health care highlights how robotics can be designed not only for function but also for empathy.
Moreover, patient-facing robots streamline administrative processes, reducing wait times and minimizing errors in data entry. Automated check-in systems, robotic receptionists, and digital triage tools ensure that patients receive timely attention while alleviating the administrative burden on staff. These improvements are not mere conveniences; they address systemic inefficiencies that often hinder patient satisfaction. By enhancing both the human and logistical dimensions of care, robots in the medical field contribute to a more holistic and responsive healthcare environment.
The Benefits of Robotics in Healthcare Delivery and Outcomes
The benefits of robotics in healthcare extend across multiple dimensions, including clinical efficacy, operational efficiency, and economic sustainability. From a clinical standpoint, robots enable minimally invasive surgeries, reduce human error, and provide consistent performance across repetitive tasks. These advantages translate into fewer complications, shorter hospital stays, and improved recovery rates, all of which directly benefit patient health and satisfaction. Additionally, by supporting precision medicine and real-time data analysis, medical robots contribute to more personalized and effective treatment plans.
Operationally, the integration of robots reduces the workload on healthcare professionals, allowing them to focus on tasks that require human judgment and empathy. This reallocation of responsibilities is especially critical in the face of global healthcare staffing shortages. Robots can fill gaps without compromising quality, maintaining service levels during crises such as pandemics or natural disasters. Furthermore, their capacity to work continuously without fatigue enhances reliability and throughput, which are crucial in high-demand environments like emergency departments or surgical suites.
Economic benefits also play a vital role in the adoption of robotics in medicine. While the initial investment in robotic systems may be substantial, the long-term savings are equally significant. Reduced complications and readmissions, optimized resource allocation, and lower labor costs contribute to a positive return on investment. In this context, medical robots are not merely technological novelties but strategic assets that support the financial health of institutions while improving care delivery. Their success lies in their ability to balance cost-efficiency with clinical excellence.
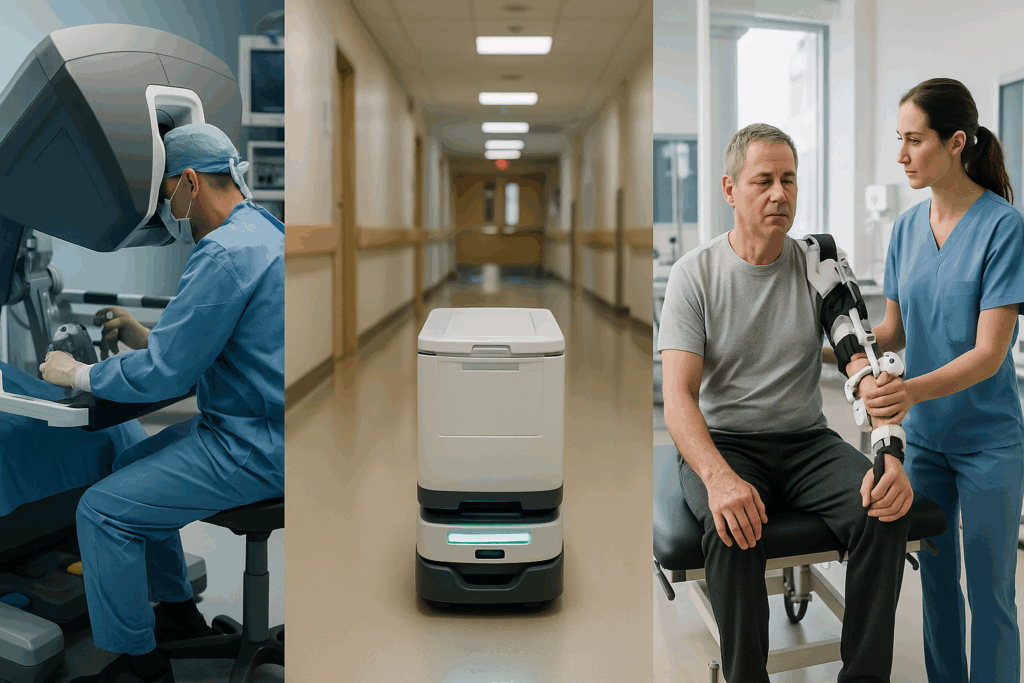

Practical Examples of Robots in the Healthcare Industry
Several real-world implementations illustrate the diverse and transformative applications of robotics in the healthcare industry. For instance, the Da Vinci Surgical System has become a benchmark for robotic-assisted surgery, with thousands of procedures performed annually across disciplines such as urology, gynecology, and cardiothoracic surgery. Surgeons operating the system benefit from enhanced visualization, tremor filtration, and articulating instruments that outperform the human hand in terms of dexterity.
In the realm of diagnostics, robots like IBM Watson Health utilize AI to assist physicians in interpreting imaging data and electronic medical records. This has proven particularly useful in oncology, where nuanced distinctions in tumor characteristics can influence treatment strategies. Another example is TUG, an autonomous mobile robot used in hospitals to transport supplies, medications, and even food trays. By automating these tasks, TUG enhances logistical efficiency and minimizes the risk of cross-contamination, especially in sterile environments.
Rehabilitation is yet another area where robots are making a significant impact. Devices like the Lokomat and HAL (Hybrid Assistive Limb) support patients in regaining mobility through guided gait training. These systems adjust resistance and support levels based on patient progress, offering a customized and data-driven rehabilitation experience. These medical robots examples underscore the breadth of robotic applications in healthcare, from operating rooms to physical therapy clinics, illustrating their versatility and value across the continuum of care.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations in Robot Health Care
The growing presence of robots in healthcare also brings forth a host of ethical and regulatory concerns. As machines assume roles traditionally held by humans, questions arise about accountability, privacy, and the preservation of human dignity. For instance, if an AI robot misdiagnoses a condition or a surgical robot malfunctions during an operation, determining liability becomes complex. Clear frameworks must be established to define the responsibilities of manufacturers, programmers, and medical institutions in such scenarios.
Privacy is another critical issue, particularly with AI robots in healthcare that process sensitive patient data. Ensuring that these systems comply with data protection regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States or GDPR in Europe, is essential to maintaining patient trust. Developers must implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect against data breaches, while also providing transparency about how information is collected, stored, and used. Ethical AI design also mandates the inclusion of bias mitigation strategies to ensure that automated decisions do not disproportionately affect vulnerable populations.
Beyond these technical considerations lies the more philosophical question of how automation affects the human experience of healthcare. While robots can perform tasks with unmatched precision, they lack the emotional intelligence and cultural sensitivity that define compassionate care. It is crucial, therefore, to use robots to enhance—not replace—the human elements of medicine. Regulatory bodies, academic institutions, and healthcare providers must collaborate to develop guidelines that balance innovation with ethical integrity, ensuring that robotics in medicine evolves in a socially responsible manner.
Future Directions: The Next Frontier in Robotics in Medicine
Looking ahead, the future of robotics in medicine promises even greater integration of technologies such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and 5G connectivity. These advancements will enable real-time collaboration between surgeons in different parts of the world, immersive training simulations, and ultra-responsive robotic systems. As 5G networks expand, latency will decrease, making remote surgeries and diagnostics more feasible and safe. This paves the way for global healthcare networks that transcend geographic barriers.
Robotic nanotechnology represents another exciting frontier. Researchers are developing microscopic robots capable of navigating the bloodstream to deliver targeted therapies, perform cellular repairs, or monitor physiological conditions in real-time. While still in experimental stages, these innovations hold the potential to revolutionize how diseases are treated at the molecular level, particularly in oncology and neurology. These robots in healthcare examples demonstrate how miniaturization and precision engineering can open new vistas in preventive and personalized medicine.
Moreover, the continuous learning capabilities of AI will lead to robots that not only perform tasks but also adapt and improve based on feedback. This iterative learning model will enhance performance over time, making robotic systems more autonomous and intelligent. As such, the applications of robots in the health care setting include not only current practices but also emergent possibilities that will reshape the medical landscape. By investing in research, education, and cross-disciplinary collaboration, society can harness these developments to build a more inclusive, effective, and forward-thinking healthcare system.
Frequently Asked Questions: Robotics in the Healthcare Industry
1. What are the most underutilized areas for robotics in healthcare today?
Despite the widespread adoption of robotics in healthcare, several areas remain underexplored. One promising frontier is behavioral health, where robots could provide consistent monitoring and support for patients with anxiety, depression, or autism spectrum disorders. Although current applications of robots in the health care setting include physical rehabilitation and surgical assistance, few systems focus on emotional or cognitive therapies. The integration of AI robots in healthcare to conduct non-intrusive mood tracking and behavioral analysis could transform mental health support, particularly in underserved populations. Expanding medical robots beyond physical tasks into neuropsychological domains may unlock transformative benefits that are currently underrecognized.
2. Can robots in healthcare support rural and underserved communities effectively?
Absolutely, one of the most impactful applications of robot health care is in bridging the accessibility gap for rural and underserved populations. With telepresence robots and mobile diagnostic units powered by AI, clinicians can offer remote consultations, follow-ups, and even real-time intervention for patients located far from urban medical centers. Unlike traditional healthcare models, robots in the medical field are not bound by geographic limitations, enabling round-the-clock support in remote regions. As 5G and satellite technologies improve connectivity, robotics in medicine will play an increasingly central role in decentralizing care and reducing health disparities. These medical robots examples highlight the social equity potential embedded within the broader robotics movement.
3. What are the long-term psychological effects of using robots as doctors or care assistants?
Using robots as doctors or long-term care assistants introduces both opportunities and concerns from a psychological standpoint. Patients often respond positively to consistent routines and nonjudgmental interactions offered by medical robots, especially in eldercare and pediatrics. However, reliance on robots in healthcare industry settings may lead to reduced human interaction, which is vital for emotional well-being. Striking the right balance is crucial—robots in healthcare examples show that companionship bots can reduce loneliness, but overdependence could hinder interpersonal development. Future designs should integrate social-emotional AI to ensure that robotics in healthcare supports—not supplants—human connection.
4. How are robots used in the medical field to reduce clinician burnout?
Clinician burnout is a growing concern, and robotics in medicine has shown great promise in alleviating some of the underlying stressors. By automating time-consuming tasks such as charting, inventory management, and medication dispensing, robots in the healthcare industry enable medical professionals to concentrate on critical, patient-facing duties. AI robots in healthcare can also manage administrative workloads, schedule appointments, and screen symptoms, creating more efficient workflow systems. The benefits of robotics in healthcare thus extend to occupational health, as reducing cognitive and emotional load directly contributes to staff retention and morale. Over time, these improvements may lower turnover rates and stabilize healthcare systems under pressure.
5. What role do robotics and AI play in surgical training and medical education?
Robotics in healthcare is not limited to patient care; it plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of medical education. Simulation platforms powered by medical robots now allow aspiring surgeons to practice procedures in highly realistic virtual environments. These training systems integrate AI algorithms that provide personalized feedback, monitor learning curves, and adapt to user skill levels. The applications of robots in the health care setting include not only live surgeries but also risk-free educational experiences that can replicate complex scenarios. As robotics in medicine evolves, its impact on academic training will become indispensable, helping bridge the gap between theory and hands-on expertise.
6. What are the most advanced types of medical robots under development today?
Several cutting-edge developments are redefining what types of medical robots can achieve. Robotic nanodevices, for instance, are being engineered to deliver drugs directly to tumor cells or clear arterial blockages at the microscopic level. Soft-bodied robots that mimic natural muscle movements are also under development for more organic interactions with human tissue. These medical robots examples go far beyond traditional exoskeletons or surgical arms, incorporating biointegration and adaptive intelligence. AI robots in healthcare are also being trained to analyze and respond to voice tone and facial expressions, offering emotional support in ways that mimic human empathy. These innovations underscore the future-facing trajectory of robotics in healthcare, blurring the lines between biology and technology.
7. How does the public generally perceive the use of robots in the medical field?
Public perception of robots in the medical field is nuanced and varies across demographics and cultural backgrounds. While many patients appreciate the precision and efficiency that robotics in healthcare brings, others express concerns about depersonalization and lack of empathy. Trust in robot health care often hinges on the transparency of AI systems and the role of human oversight. Surveys have shown that people are more comfortable with robots in supportive roles rather than as primary decision-makers. Therefore, educating the public about the benefits of robotics in healthcare, while emphasizing continued human involvement, is essential for wider acceptance and ethical integration.
8. What are the environmental implications of robotics in healthcare?
The sustainability dimension of robotics in healthcare is often overlooked but increasingly relevant. Robots in the healthcare industry can streamline resource use, minimize waste, and enhance energy efficiency, especially in large hospital systems. For example, precision dosing by medical robots can reduce pharmaceutical waste, while automated HVAC control by building-integrated robotics can cut energy consumption. However, the production and disposal of robotic systems also carry environmental costs, particularly regarding rare earth metals and electronic waste. Future applications of robots in the health care setting include designing more sustainable, recyclable systems to align medical innovation with environmental responsibility.
9. Can robots help personalize medicine beyond diagnostics and surgery?
Yes, personalization in healthcare is advancing rapidly thanks to robotics in medicine. Beyond diagnostics and surgery, robots now contribute to tailored patient engagement through behavior tracking, real-time data collection, and adaptive interfaces. AI robots in healthcare can adjust care protocols based on patient preferences, cultural considerations, and even biometric feedback. Robots as doctors or care facilitators can recommend diet, exercise, and therapy plans aligned with individual lifestyles. These capabilities mark a significant evolution in robot health care, demonstrating that personalization goes beyond clinical outcomes and touches every aspect of the patient journey.
10. What are some surprising robots in healthcare examples that most people don’t know about?
Many people are surprised to learn that robots in the healthcare industry now include sanitation bots that use UV light to sterilize hospital rooms, reducing hospital-acquired infections. Another lesser-known application involves robotic pharmacy systems that dispense medications with near-zero error rates. In maternity wards, robotic bassinets equipped with biometric monitors can adjust rocking patterns and soundscapes to soothe newborns. These unique medical robots examples expand the public’s understanding of what types of medical robots exist today. As the boundaries of robotics in healthcare continue to expand, the list of innovative and unexpected use cases will only grow richer and more diverse.
Conclusion: Embracing Robotics in Healthcare for a Smarter, Safer Future
As we reflect on the rapid advances in robotics in healthcare, it becomes clear that these technologies are not simply tools but transformative agents of change. From the operating room to the patient bedside, from administrative halls to remote monitoring centers, medical robots are enhancing accuracy, accessibility, and efficiency across the board. The integration of robotics in medicine has moved beyond novelty to necessity, driven by compelling evidence of its clinical, operational, and economic benefits.
Importantly, the adoption of these technologies does not imply the replacement of human professionals but rather a reimagining of roles and responsibilities. Robots in the healthcare industry function as partners—amplifying human capability, supporting clinical decisions, and ensuring consistency in care delivery. The success of these systems hinges on their thoughtful design, ethical deployment, and continued evaluation through rigorous research and public dialogue. By fostering trust, prioritizing safety, and investing in interdisciplinary education, the medical community can unlock the full potential of robot health care.
Ultimately, embracing robotics is not just about innovation; it’s about building a healthcare system that is smarter, safer, and more attuned to the diverse needs of patients and providers alike. As the field continues to evolve, the challenge lies in navigating its complexities with wisdom, empathy, and a steadfast commitment to excellence. With the right balance of technology and humanity, the future of healthcare will be defined not just by what robots can do, but by what we, together with them, choose to achieve.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out.
Further Reading:
5 ways that robotics are transforming healthcare
Robotics and the future of healthcare: Transforming patient care
Artificial intelligence in healthcare: transforming the practice of medicine
Disclaimer
The information contained in this article is provided for general informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as medical, legal, or professional advice. While MedNewsPedia strives to present accurate, up-to-date, and reliable content, no warranty or guarantee, expressed or implied, is made regarding the completeness, accuracy, or adequacy of the information provided. Readers are strongly advised to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider or other relevant professionals before acting on any information contained in this article. MedNewsPedia, its authors, editors, and contributors expressly disclaim any liability for any damages, losses, or consequences arising directly or indirectly from the use, interpretation, or reliance on any information presented herein. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official policies or positions of MedNewsPedia.


